A client is admitted with hypovolemia due to severe bleeding. Which IV fluid does the nurse anticipate using to replace fluid losses?
5% dextrose in water (D5W).
5% dextrose in 0.25% sodium chloride (D5 1/4 NS).
0.9% normal saline (0.9% NaCl).
3% sodium chloride (3% NaCl).
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason:
5% dextrose in water (D5W) is not typically used for fluid resuscitation in cases of hypovolemia due to severe bleeding. D5W is a hypotonic solution once the dextrose is metabolized, which means it does not remain in the intravascular space and is not effective in expanding blood volume. It is more commonly used for providing free water and calories.
Choice B reason:
5% dextrose in 0.25% sodium chloride (D5 1/4 NS) is also not suitable for fluid resuscitation in hypovolemia due to severe bleeding. This solution is hypotonic and will not adequately expand the intravascular volume. It is generally used for maintenance fluids rather than for resuscitation.
Choice C reason:
0.9% normal saline (0.9% NaCl) is the preferred choice for fluid resuscitation in hypovolemia due to severe bleeding. It is an isotonic solution, meaning it has the same osmolarity as blood and remains in the intravascular space, effectively expanding blood volume. This helps to restore circulating volume and improve tissue perfusion.
Choice D reason:
3% sodium chloride (3% NaCl) is a hypertonic solution and is not typically used for fluid resuscitation in hypovolemia due to severe bleeding. Hypertonic solutions can cause rapid shifts of fluid from the intracellular to the extracellular space, which can lead to complications such as hypernatremia and osmotic demyelination syndrome. It is generally reserved for specific situations such as severe hyponatremia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
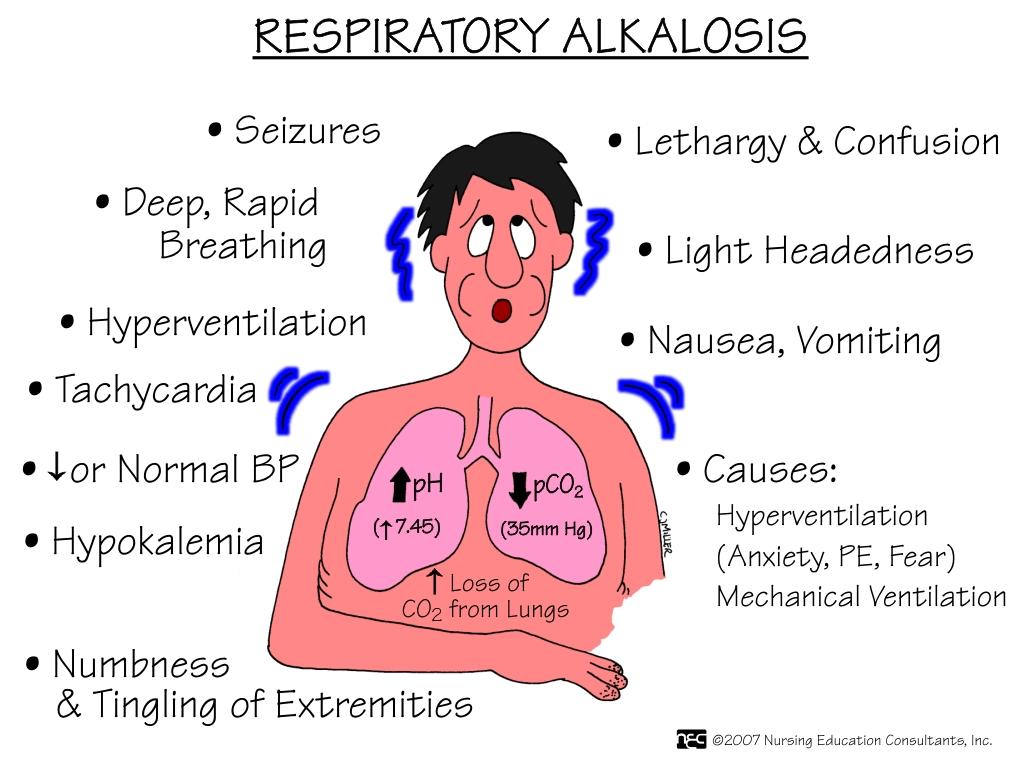
Choice A reason: Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an elevated pH and an increased bicarbonate (HCO3) level. In this case, the pH is elevated (7.51), but the bicarbonate level is within the normal range (24 mEq/L), indicating that the alkalosis is not metabolic in origin.
Choice B reason: Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decreased pH and a decreased bicarbonate (HCO3) level. In this scenario, the pH is elevated, not decreased, and the bicarbonate level is normal, ruling out metabolic acidosis.
Choice C reason: Respiratory alkalosis is characterized by an elevated pH and a decreased partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2). The given values show a pH of 7.51 (elevated) and a PaCO2 of 28 mmHg (decreased), which are indicative of respiratory alkalosis. This condition often occurs in the early stages of an asthma attack due to hyperventilation, which causes excessive exhalation of CO2.
Choice D reason: Respiratory acidosis is characterized by a decreased pH and an increased PaCO2. In this case, the pH is elevated, and the PaCO2 is decreased, which is the opposite of what is seen in respiratory acidosis.
Correct Answer is ["10"]
Explanation
- 125 units of insulin in 250 mL of normal saline
Step 2: Calculate the concentration of insulin per mL.
- Concentration = 125 units ÷ 250 mL
- Concentration = 0.5 units/mL
Step 3: Determine the required rate of insulin administration.
- Ordered dose = 5 units per hour
Step 4: Calculate the IV flow rate.
- Flow rate (mL/hr) = Ordered dose ÷ Concentration
- Flow rate (mL/hr) = 5 units ÷ 0.5 units/mL
- Flow rate (mL/hr) = 10 mL/hr
The nurse should set the IV pump to 10 mL/hr.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
