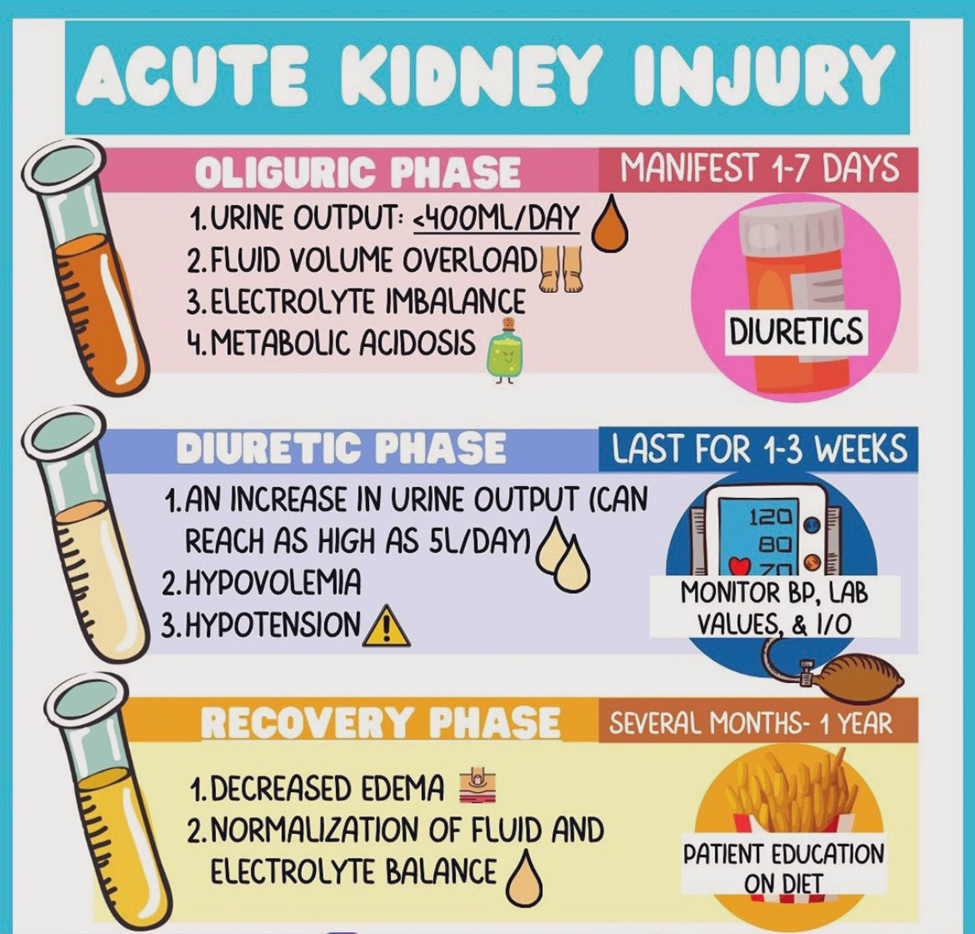
A client who has developed acute kidney injury (AKI) due to an aminoglycoside antibiotic has moved from the oliguric phase to the diuretic phase of AKI Which parameters are most important for the nurse to plan to carefully monitor?
Hypovolemia and electrocardiographic (ECG) changes.
Uremic irritation of mucous membranes and skin surfaces.
Side effects of total parental nutrition (TPN) and Intralipids.
Elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
The Correct Answer is A
A. Hypovolemia and electrocardiographic (ECG) changes:
During the diuretic phase of AKI, there is an increased urine output, and the risk of dehydration and hypovolemia is elevated. The nurse should closely monitor fluid balance to prevent dehydration, and ECG changes may occur due to electrolyte imbalances (such as hypokalemia) associated with diuresis.
B. Uremic irritation of mucous membranes and skin surfaces:
Uremic symptoms are more prominent in the oliguric phase of AKI when waste products accumulate in the blood. In the diuretic phase, the focus shifts more toward managing fluid and electrolyte balance.
C. Side effects of total parental nutrition (TPN) and Intralipids:
TPN and Intralipids are not directly related to the diuretic phase of AKI. Monitoring for side effects of TPN and Intralipids may be relevant in other clinical contexts but is not the primary concern in the diuretic phase.
D. Elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN):
Monitoring creatinine and BUN levels is important for assessing kidney function, but in the diuretic phase, the focus shifts to managing fluid and electrolyte balance. The risk of hypovolemia and electrolyte imbalances is more immediate during this phase.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Keep the room at a comfortable temperature:
While maintaining a comfortable room temperature is important for the overall well-being of the client, it is not the most essential intervention during a seizure. The priority during a seizure is to ensure the client's safety, particularly focusing on airway management.
B. Ensure oral suction is available:
This is the most essential intervention. During a seizure, the client may produce excessive saliva, and having oral suction readily available helps prevent airway obstruction and ensures a clear airway. It is crucial for the safety and well-being of the client.
C. Provide frequent mouth care:
Mouth care is important for the overall hygiene of the unconscious client, but it may not be the most immediate priority during a seizure. The focus during a seizure is on preventing complications such as aspiration or airway obstruction.
D. Maintain the client in a semi-Fowler's position:
Positioning is important for the comfort and safety of the unconscious client, but maintaining a semi-Fowler's position may not be the primary concern during an active seizure. The immediate focus is on airway management and preventing injury.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Begin continuous observation for transient episodes of neurologic dysfunction:
While continuous observation is important, the priority is to notify the stroke team for immediate assessment and management.
B. Place an indwelling urinary catheter and measure strict intake and output:
Monitoring intake and output is an important aspect of nursing care, but it is not the immediate priority when the client is presenting with signs and symptoms suggestive of a stroke.
C. Notify the stroke team to assist with acute assessment and management.
The client's symptoms, including an uneven smile with facial droop to the right side, weaker hand grasp strength on the right, and sudden, severe headache, are indicative of potential stroke symptoms. Quick notification of the stroke team is crucial to facilitate a rapid and comprehensive assessment. Time is a critical factor in the management of stroke, and prompt intervention can improve outcomes.
D. Raise the head of the bed to 30 degrees keeping head and neck in neutral alignment:
While positioning is important for maintaining physiological stability, it is not the immediate priority in the context of a potential stroke. Notifying the stroke team for rapid assessment and intervention takes precedence.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
