A client who underwent cardiac stent placement four days ago arrives to the emergency department reporting a sudden onset of chest pressure and shortness of breath. Which action should the nurse take next?
Evaluate upper and lower extremities for perfusion, pulse volume, and pitting edema.
Listen for extra heart sounds, murmurs, and rhythm with the bell of the stethoscope.
Obtain a 12-lead electrocardiogram and begin continuous cardiac monitoring.
Verify troponin level assessments are scheduled every 3-6 hours for a series of three
The Correct Answer is C
A. Evaluate upper and lower extremities for perfusion, pulse volume, and pitting edema:
This option focuses on assessing perfusion and circulation in the extremities. While it's important in certain situations, in the context of a client who recently underwent cardiac stent placement and is now experiencing chest pressure and shortness of breath, the priority is to assess the cardiac status more directly.
B. Listen for extra heart sounds, murmurs, and rhythm with the bell of the stethoscope:
This option involves auscultating the heart for abnormal sounds or rhythms. While it's a valuable assessment in general, in this particular scenario, obtaining an electrocardiogram (ECG) and initiating continuous cardiac monitoring would provide a more comprehensive and immediate evaluation of the cardiac status.
C. Obtain a 12-lead electrocardiogram and begin continuous cardiac monitoring:
This is the correct choice. Obtaining a 12-lead ECG and initiating continuous cardiac monitoring is crucial in assessing the client's cardiac function. It allows for the detection of any acute changes in the heart's electrical activity or rhythm, which is essential for timely intervention and management.
D. Verify troponin level assessments are scheduled every 3-6 hours for a series of three:
Monitoring troponin levels is important in assessing cardiac damage, but in this acute situation, obtaining an immediate ECG and initiating continuous cardiac monitoring take precedence for a more real-time evaluation of the client's cardiac status. Troponin levels may be monitored subsequently based on the initial findings.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D"]
Explanation
A. Skin elasticity:
Assessing skin elasticity is a measure of hydration status. Improved skin turgor may suggest that the client is responding positively to diuretic therapy by eliminating excess fluid. However, this may not be as immediate or specific as other indicators of response.
B. Urinary output:
Monitoring urinary output is crucial when administering diuretics like furosemide. Increased urine output indicates that the diuretic is promoting the elimination of excess fluid from the body, which is a desired effect in managing heart failure and fluid overload.
C. Oxygen saturation:
Assessing oxygen saturation is important in monitoring respiratory status. Improvement in oxygen saturation levels indicates that the client is responding to interventions aimed at relieving respiratory distress, such as the administration of furosemide.
D. Lung sounds:
Monitoring lung sounds is a key aspect of assessing respiratory function. Reduction in wheezes and crackles suggests that the diuretic is helping to alleviate pulmonary congestion and fluid accumulation in the lungs, contributing to improved respiratory function.
E. Pain scale:
Assessing pain is relevant if the client has reported chest pain or discomfort associated with heart failure. Reduction in pain may indicate improved cardiac function and response to treatment. However, it's important to note that pain assessment may not be as specific to the effects of furosemide as other respiratory and fluid status indicators.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
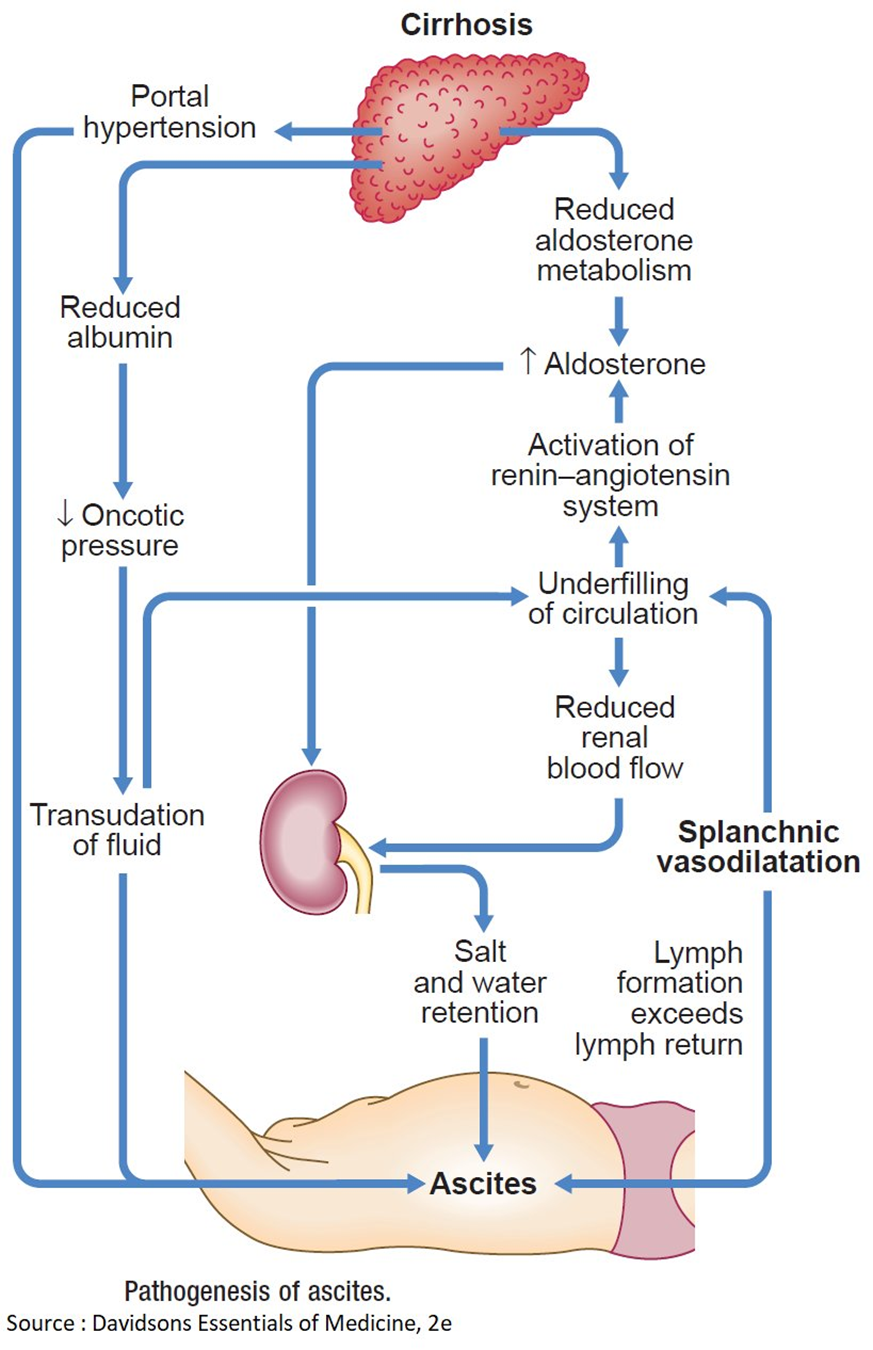
A. Hyperaldosteronism causing an increased sodium reabsorption in renal tubules.
Hyperaldosteronism is characterized by an excess of aldosterone, a hormone that regulates sodium and water balance. In cirrhosis, however, sodium retention is often related to other mechanisms such as portal hypertension and hypoalbuminemia, rather than hyperaldosteronism.
B. Decreased renin-angiotensin response related to an increase in renal blood flow.
Cirrhosis is more commonly associated with an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, leading to increased sodium and water retention. The increased renin-angiotensin response is a compensatory mechanism to maintain perfusion in the setting of cirrhosis and does not contribute to decreased renal blood flow.
C. Decreased portacaval pressure with greater collateral circulation.
This statement is not accurate. In cirrhosis, there is typically increased portacaval pressure due to portal hypertension, which can lead to the development of collateral circulation. However, this does not explain the edema and ascites seen in cirrhosis.
D. Hypoalbuminemia that results in a decreased colloidal oncotic pressure.
This is the correct choice. In cirrhosis, liver damage leads to decreased synthesis of albumin. Albumin plays a crucial role in maintaining colloidal oncotic pressure, and when it is decreased (hypoalbuminemia), fluid is more likely to leak out of blood vessels, resulting in edema. The same mechanism contributes to the development of ascites in the abdominal cavity.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
