A client with chronic peripheral arterial disease (PAD) asks the nurse why this disease developed. Which explanation by the nurse is most accurate?
"Excess sodium from hypertension causes direct injury to the arteries, reducing blood flow and causing obstruction."
"Excess fats in your diet are stored in the lining of the arteries, causing them to constrict."
"A combination of platelets and fats accumulate, narrowing the artery and reducing blood flow to the extremities."
"Injury to the arteries causes them to spasm, reducing blood flow to the extremities."
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A Reason
While hypertension can contribute to the development of PAD, it does not directly cause fats to deposit in the arteries. Hypertension can damage the arterial walls, making them more susceptible to atherosclerosis, but it is not the primary mechanism of PAD development.
Choice B Reason
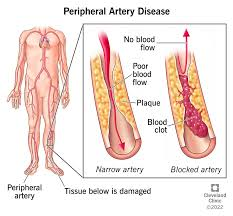
Excess fats in the diet can contribute to atherosclerosis, which is the accumulation of plaques in the arterial walls. However, the fats do not simply get stored; they combine with other substances, including calcium and inflammatory cells, to form plaques that can restrict blood flow.
Choice C Reason
This statement is the most accurate. PAD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaques formed by fats, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. These plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities. The process can be exacerbated by factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Arterial spasms can occur, but they are not the typical cause of chronic PAD. Spasms are more often associated with conditions like Raynaud's phenomenon or can be a response to stress or cold temperatures. PAD is usually a result of progressive atherosclerosis rather than intermittent spasms.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D","E"]
Explanation
Choice a reason:
Assessing capillary refill and the color of the extremity is essential for determining the vascular status of the limb. A normal capillary refill time is less than 2 seconds and indicates good blood flow. The color should be consistent with the rest of the body, without pallor or cyanosis, which could indicate compromised circulation.
Choice b reason:
Checking pedal pulses is another critical aspect of assessing vascular integrity. The presence of strong and equal pulses in both feet suggests that the blood supply to the lower extremities is not compromised.
Choice c reason:
While the ACE wrap and Velcro boot are part of the postoperative management to provide support and protection to the affected limb, and hanging weights might be used for traction, these are not part of the physiological assessment of the extremity.
Choice d reason:
Monitoring pin sites for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, is crucial in a client with ORIF. Infection can lead to complications that may affect the healing process and the integrity of the fixation.
Choice e reason:
Evaluating the temperature, sensation, and movement of toes helps in assessing for potential nerve damage or compartment syndrome. Any changes in these parameters should be reported immediately as they may signify serious complications.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Sodium levels in the blood should normally be between 135 and 145 mEq/L. A level of 152 mEq/L is considered high and can be indicative of hypernatremia, which requires prompt medical attention to address potential dehydration, kidney issues, or other underlying conditions.
Choice B Reason:
Potassium levels should be within the range of 3.5 to 5.2 mEq/L for adults. A result of 3.8 mEq/L falls within the normal range, indicating no immediate concern regarding potassium levels.
Choice C Reason:
Calcium levels in the blood are typically between 8.6 and 10.2 mg/dL for adults. Therefore, a calcium level of 10.0 mg/dL is within the normal range and does not require urgent reporting to a physician.
Choice D Reason:
Creatinine levels in the blood should be between 0.6 to 1.3 mg/dL in adults, depending on factors such as age, gender, and muscle mass. A level of 1.2 mg/dL is at the higher end of the normal range but is not typically considered critical unless there are other signs of kidney dysfunction.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
