A mother calls the nurse to report that at 0900 she administered an oral dose of digoxin to her 4-month-old infant, but at 0920 the baby vomited the medicine. Which instruction should the nurse provide to this mother?
Administer a half dose now.
Give another dose.
Mix the next dose with food.
Withhold this dose.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A: Administering a half dose now is not advisable, because it may result in underdosing or overdosing of digoxin. Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic range and a high risk of toxicity, especially in infants and children. The amount of digoxin absorbed by the infant before vomiting is unknown, so giving a partial dose may not achieve therapeutic levels or may exceed safe levels.
Choice B: Giving another dose is not advisable, because it may result in overdosing of digoxin. Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic range and a high risk of toxicity, especially in infants and children. The amount of digoxin absorbed by the infant before vomiting is unknown, so giving a full dose may exceed safe levels and cause adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, bradycardia, arrhythmias, or visual disturbances.
Choice C: Mixing the next dose with food is not advisable, because it may affect the absorption and bioavailability of digoxin. Digoxin should be taken on an empty stomach or at least one hour before or two hours after meals, because food can interfere with its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and reduce its effectiveness.
Choice D: Withholding the dose is the safest option. If vomiting occurs within 30 minutes of administration, it’s generally advised to skip that dose to avoid the risk of overdose. The next dose should be given as scheduled Digoxin has a long half-life and accumulates in tissues, so missing one dose will not significantly affect its therapeutic effect. Withholding this dose will avoid overdosing and toxicity of digoxin, which can be life-threatening in infants and children. The nurse should also advise the mother to resume the regular dosing schedule and monitor the infant's pulse rate and signs of digoxin toxicity.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
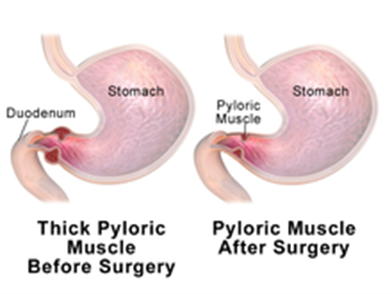
Choice A reason: Marking an outline of the "olive-shaped" mass in the right epigastric area is not a priority nursing action. The mass is caused by hypertrophy of the pyloric sphincter, which obstructs gastric emptying and causes projectile vomiting. The mass may not be palpable in all cases.
Choice C reason: Monitoring amount of intake and infant's response to feedings is important, but not the highest priority. The infant may have difficulty feeding due to nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Choice D reason: Instructing parents regarding care of the incisional area is a post-operative nursing action, not a pre-operative one. The parents will need to learn how to keep the incision clean and dry, monitor for signs of infection, and administer pain medication as prescribed.
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D","E"]
Explanation
Choice A: Applying an allergy identification wrist band is an intervention that the nurse should implement, as this can alert other health care providers of the client's allergies and prevent adverse reactions. Therefore, this is a correct choice.
Choice B: Instructing the client to avoid medication containing milk and eggs is not an intervention that the nurse should implement, as this is not a common or relevant source of allergens for this client. This is an incorrect choice.
Choice C: Entering allergy information in the client's electronic medical record is an intervention that the nurse should implement, as this can ensure accurate and updated documentation of the client's allergies and facilitate communication among health care providers. Therefore, this is another correct choice.
Choice D: Ensuring the client's selections from her dietary menu is an intervention that the nurse should implement, as this can help avoid foods that may trigger allergic reactions or intolerance for this client. Therefore, this is another correct choice.
Choice E: Notifying the dietary department of the client's egg intolerance is an intervention that the nurse should implement, as this can help modify or substitute foods that contain eggs for this client. Therefore, this is another correct choice.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
