A nurse in a clinic is assessing a 7-month-old infant. Which of the following indicates a need for further evaluation?
Uses a pincer grasp
Has a fear of strangers
Shows preferences towards foods
Babbles one-syllable sounds
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A: Using a pincer grasp indicates a need for further evaluation, as it is a developmental milestone that is usually achieved by 9 to 10 months of age. A pincer grasp is the ability to pick up small objects using the thumb and index finger. A 7-month-old infant should be able to use a raking grasp, which is the ability to scoop up objects using all fingers.
Choice B: Having a fear of strangers does not indicate a need for further evaluation, as it is a normal and expected behavior for a 7-month-old infant. A fear of strangers is a sign of attachment and recognition of familiar and unfamiliar faces. A 7-month-old infant may cry, cling, or turn away from strangers.
Choice C: Showing preferences towards foods does not indicate a need for further evaluation, as it is a normal and expected behavior for a 7-month-old infant. Showing preferences towards foods is a sign of individuality and taste development. A 7-month-old infant may accept or reject certain foods based on their flavor, texture, or appearance.
Choice D: Babbling one-syllable sounds does not indicate a need for further evaluation, as it is a normal and expected behavior for a 7-month-old infant. Babbling one-syllable sounds is a sign of language and communication development. A 7-month-old infant may make sounds such as "ba", "da", "ga", or "ma".
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A: This statement is correct, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate, which is a cartilage layer at the end of a long bone where growth occurs, can impair the normal growth and development of the bone. Depending on the type and severity of the fracture, the epiphyseal plate may close prematurely, stop growing, or grow unevenly, resulting in deformity, shortening, or angular deviation of the affected limb.
Choice B: This statement is incorrect, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate does not necessarily disrupt the blood supply to the bone unless there is also damage to the periosteum, which is a membrane that covers and nourishes
the bone. A disruption of the blood supply to the bone can cause avascular necrosis, which is a condition that causes bone death due to lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Choice C: This statement is incorrect, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate does not cause bone marrow loss through the fracture unless there is damage to the medullary cavity, which is a hollow space within the bone that contains bone marrow. Bone marrow loss through the fracture can cause bleeding, infection, or anemia.
Choice D: This statement is incorrect, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate does not take longer to heal in younger children than in older children. In fact, younger children tend to heal faster than older children due to their higher metabolic rate, greater blood supply, and more active growth factors. The healing time of a fracture depends on various factors, such as the type and location of the fracture, the treatment method, and the presence of complications.
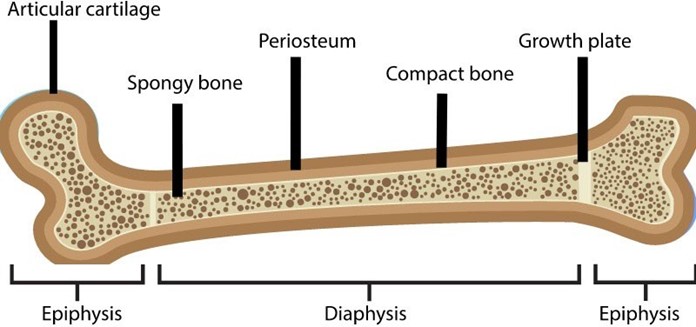
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A: The Oucher pain scale is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 to 13 years who can point to pictures of faces that match their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or point to pictures.
Choice B: The FLACC pain scale is suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for infants and children aged 2 months to 7 years who cannot verbalize their pain. The FLACC pain scale assesses five behavioral indicators of pain: face, legs, activity, cry, and consolability. Each indicator is scored from 0 to 2 based on the observation of the nurse. The total score ranges from 0 to 10, with higher scores indicating more pain.
Choice C: The FACES pain scale is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 years and older who can select a face that matches their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or select a face.
Choice D: The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for adults and older children who can mark a point on a line that represents their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or mark a point on a line.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
