A nurse in an obstetrics clinic is caring for a client.
Click to highlight the findings that require follow-up. To deselect a finding, click on the finding again.
Exhibit 1
Nurses' Notes
Initial visit, 1340:
29-year-old gravida 2, para 0 client presents with report of a positive home pregnancy test from 2 weeks ago. Last menstrual period was 7 weeks ago. Urine human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) positive. Client reports vomiting several times a day over the last 2 weeks and states, "I'm a vegetarian and I don't usually eat a lot of protein, but it's still hard to keep anything down." Decreased skin turgor noted, oral mucous membranes moist. Weight 79.4 kg (175 lb).
Exhibit 2
Vital Signs
Initial visit, 1330:
- Heart rate 110/min
- Respiratory rate 18/min
- Blood pressure 104/66 mm Hg
- Temperature 36.6° C (97.9° F)
- Oxygen saturation 99% on room air
- Continuation of above exhibit
Exhibit 3
The nurse is reviewing the client's assessment findings and laboratory results.
Laboratory Results
Initial visit, 1600:
- WBC count 7,500/mm3 (5,000 to 10,000/mm3)
- Hgb 10.2 g/dL (11 to 16 g/dL)
- Hct 45% (33% to 47%)
- Platelets 360,000/mm3 (150,000 to 400,000/mm3)
- Sodium 136 mEq/L (136 to 145 mEq/L)
- Potassium 3.3 mEq/L (3.5 to 5 mEq/L)
- BUN 28 mg/dL (10 to 20 mg/dL)
Urinalysis:
- Appearance clear (clear)
- Color dark amber (pale yellow amber)
- pH 7.9 (4.6 to 8)
- Protein 4 mg/dL (0 to 8 mg/dL)
- Specific gravity 1.045 (1.005 to 1.03)
- Leukocyte esterase negative (negative)
- Nitrites none (none)
Heart rate 110/min
Blood pressure 104/66 mm Hg
Hemoglobin 10.2 g/dL
Potassium 3.3 mEq/L
BUN 28 mg/dL
Urine specific gravity 1.045
Decreased skin turgor
WBC count 7,500/mm3
Client reports vomiting several times a day over the last 2 weeks
Color dark amber
The Correct Answer is ["A","C","D","E","F","G","I","J"]
-
Heart rate 110/min
Correct (requires follow-up) – A heart rate of 110/min is elevated, which could indicate dehydration or other physiological stress, such as hyperemesis gravidarum. -
Blood pressure 104/66 mm Hg
Wrong (does not require follow-up) – This blood pressure is within normal limits, particularly in pregnancy, where slight decreases in blood pressure are common. -
Hemoglobin 10.2 g/dL
Correct (requires follow-up) – This is lower than the normal range (11 to 16 g/dL) and indicates mild anemia, which should be monitored during pregnancy. -
Potassium 3.3 mEq/L
Correct (requires follow-up) – This potassium level is below the normal range (3.5 to 5 mEq/L), indicating hypokalemia, likely due to vomiting. Hypokalemia needs correction as it can cause complications. -
BUN 28 mg/dL
Correct (requires follow-up) – Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is elevated (normal range 10 to 20 mg/dL), which could indicate dehydration, a concern especially with vomiting and reduced intake. -
Urine specific gravity 1.045
Correct (requires follow-up) – This is higher than the normal range (1.005 to 1.03), suggesting concentrated urine and potential dehydration. -
Decreased skin turgor
Correct (requires follow-up) – Decreased skin turgor is a physical sign of dehydration and should be addressed, especially considering the client's vomiting. -
WBC count 7,500/mm3
Wrong (does not require follow-up) – The WBC count is within the normal range (5,000 to 10,000/mm3), so it does not indicate an infection or other abnormalities. -
Client reports vomiting several times a day over the last 2 weeks
Correct (requires follow-up) – Persistent vomiting over this time period is concerning for hyperemesis gravidarum and could lead to complications such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. -
Urine color dark amber
Correct (requires follow-up) – Dark amber urine could be a sign of dehydration, especially in combination with an elevated urine specific gravity.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Bilirubin 1 mg/dL (0.1 to 1 mg/dL):
Bilirubin levels can be elevated in conditions involving liver dysfunction or hemolysis, such as HELLP syndrome. However, a bilirubin level of 1 mg/dL falls within the normal range (0.1 to 1 mg/dL). While bilirubin levels may be elevated in some cases of HELLP syndrome, this particular value is not indicative of HELLP syndrome.
B. Uric acid 6.8 mg/dL (2 to 6.6 mg/dL):
Elevated uric acid levels are commonly seen in preeclampsia, but they are not specific to HELLP syndrome. Uric acid levels can rise due to decreased renal function and increased cell breakdown. However, while a level of 6.8 mg/dL is slightly elevated compared to the normal range (2 to 6.6 mg/dL), it alone does not confirm the presence of HELLP syndrome.
C. Fibrinogen 500 mg/dL (200 to 400 mg/dL):
Fibrinogen levels are typically increased in pregnancy, but they can be decreased in conditions associated with consumption coagulopathy, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). However, elevated fibrinogen levels are not typically associated with HELLP syndrome. A level of 500 mg/dL is above the normal range (200 to 400 mg/dL), but this finding alone does not indicate HELLP syndrome.
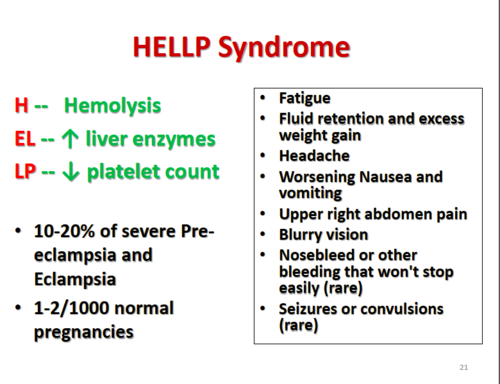
D. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 80 units/L (4 to 20 units/L):
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is a liver enzyme that can be elevated in liver injury or dysfunction, which can occur in HELLP syndrome. An AST level of 80 units/L is significantly elevated compared to the normal range (4 to 20 units/L), suggesting liver dysfunction. Elevated liver enzymes are a characteristic feature of HELLP syndrome, making this finding the most indicative of HELLP syndrome among the options provided.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine:
The HPV vaccine is not recommended during pregnancy because there is limited safety data regarding its use in pregnant women. It is typically administered to individuals before they become sexually active to prevent HPV infections, which can lead to cervical cancer and other HPV-related diseases. Since the client is currently pregnant, administering the HPV vaccine would not be appropriate due to the lack of safety data during pregnancy.
B. Rubella vaccine:
The rubella vaccine is a live attenuated vaccine, and its administration during pregnancy is contraindicated due to the risk of congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) if the vaccine were to cause rubella infection in the pregnant woman. Rubella vaccination should be provided to non-pregnant individuals, particularly women of childbearing age, to prevent CRS. Administering the rubella vaccine to a pregnant woman at 28 weeks of gestation would pose a risk to both the mother and the developing fetus.
C. Varicella vaccine:
Similar to the rubella vaccine, the varicella (chickenpox) vaccine is a live attenuated vaccine and is contraindicated during pregnancy due to the risk of varicella infection in the pregnant woman, which can lead to severe complications for both the mother and the fetus. Varicella vaccination is recommended for individuals who have not had chickenpox or received the vaccine previously but should not be administered to pregnant women.
D. Tetanus vaccine:
Tetanus vaccination during pregnancy is recommended to prevent maternal and neonatal tetanus. Tetanus toxoid is considered safe during pregnancy and is routinely administered as part of the tetanus-diphtheria-pertussis (Tdap) vaccine. The tetanus vaccine helps protect against tetanus, a potentially fatal bacterial infection. Administering the tetanus vaccine during pregnancy is important for the health and safety of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
