A nurse is admitting a client who experienced a vaginal birth 2 hours ago. The client is receiving an IV of lactated Ringer's with 25 units of oxytocin infusing and has large rubra lochia. Vital signs include blood pressure 146/94 mm Hg, pulse 80/min, and respiratory rate 18/min. The nurse reviews the prescriptions from the provider. Which of the following prescriptions requires clarification?
Methylergonovine 0.2 mg IM now.
Insert an indwelling urinary catheter.
Obtain laboratory study of prothrombin and partial thromboplastin time.
Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 5 L/min.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice a reason:
Methylergonovine is a medication used to prevent or control postpartum hemorrhage by contracting the uterus. However, it is contraindicated in patients with hypertension, as it can further increase blood pressure. Given that the client's blood pressure is already elevated at 146/94 mm Hg, administering methylergonovine could pose a risk. Therefore, this prescription requires clarification from the provider before administration.
Choice b reason:
Inserting an indwelling urinary catheter can be a standard procedure after vaginal birth if the client is unable to void or if accurate measurement of urine output is needed. This does not require clarification unless there are specific contraindications or the client's condition does not warrant it.
Choice c reason:
Obtaining a laboratory study of prothrombin and partial thromboplastin time is a common practice to assess the blood's clotting ability, especially if there is a concern for bleeding disorders or if the client is at risk for postpartum hemorrhage. This prescription is clear and does not require further clarification.
Choice d reason:
Administering oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 5 L/min may be indicated if the client is showing signs of respiratory distress or hypoxia. The client's current respiratory rate is within normal limits, but if there are concerns about oxygenation, this intervention would be appropriate.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Precipitous labor is characterized by a labor that progresses rapidly and ends within three hours of its onset. It is not typically associated with painless, bright red vaginal bleeding. This condition is more likely to present with intense, frequent contractions and a rapid change in cervical dilation. Therefore, precipitous labor is not the correct answer in this scenario.
Choice B reason:
Abruptio placentae, also known as placental abruption, is a condition where the placenta detaches from the uterus before delivery. It can cause significant maternal and fetal complications. The classic presentation includes painful bleeding, uterine tenderness, and contractions. Given that the scenario describes painless bleeding, abruptio placentae is less likely to be the correct diagnosis.
Choice C reason:
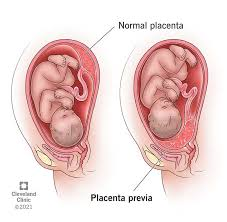
Placenta previa is a condition where the placenta covers the cervix partially or completely. The hallmark sign of placenta previa is painless, bright red vaginal bleeding, which aligns with the scenario provided. This bleeding can occur spontaneously or be triggered by intercourse or a medical exam. Placenta previa is a serious condition that can lead to maternal and fetal hemorrhage and warrants immediate medical attention. Based on the information provided, placenta previa is the most likely diagnosis for the client described.
Choice D reason:
Threatened abortion refers to vaginal bleeding that occurs in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, which may indicate a potential miscarriage. Since the client is at 36 weeks gestation, threatened abortion is not a relevant diagnosis for late-term bleeding. Additionally, threatened abortion is often accompanied by abdominal cramping, which is not mentioned in the scenario.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Elevating the client's legs can help increase venous return to the heart and may be beneficial in some cases of hypotension. However, it is not the first-line action for hypotension in a client with an epidural block during labor.
Choice B reason:
Notifying the provider is important, but it is not the immediate priority action. The provider should be informed after initial measures to stabilize the client's blood pressure have been taken.
Choice C reason:
Placing the client in a lateral position is the priority nursing action for hypotension during labor with an epidural block. This position helps improve uterine blood flow and can help increase blood pressure. It is a part of the initial management of hypotension in this situation.
Choice D reason:
Monitoring vital signs every 5 minutes is an important part of ongoing assessment but is not the immediate priority action. The nurse should first address the hypotension and then continue to monitor the client closely.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
