A nurse is admitting a client who is in active labor and has had two prior cesarean births. The nurse should identify that the client is at an increased risk for which of the following complications?
Failure to progress
Abruptio placentae
Precipitous labor
Uterine rupture
The Correct Answer is D
Uterine rupture. When a client has had two prior cesarean births, she is at an increased risk for uterine rupture. Uterine rupture is a serious complication that can occur during labor, where there is a tear in the wall of the uterus. It can lead to significant blood loss for the mother and oxygen deprivation for the fetus. Other risk factors for uterine rupture include a previous uterine surgery, the use of labor-inducing drugs, and multiple gestations.
Failure to progress (choice A) refers to a labor that is not progressing as it should, and can be caused by a variety of factors, including fetal malposition or inadequate contractions. Abruptio placentae (choice B) refers to the separation of the placenta from the uterine wall before delivery, which can cause fetal distress and maternal hemorrhage. Precipitous labor (choice C) refers to a labor that progresses extremely quickly, with contractions lasting less than 3 hours from the onset of active labor. While precipitous labor can be associated with increased risk for perineal lacerations and postpartum hemorrhage, it is not typically associated with prior cesarean births.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
This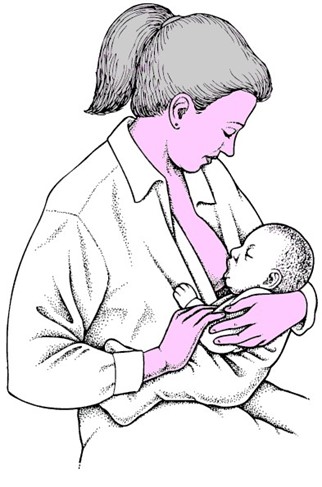 suggests that the nurse should assess the newborn's latch while breastfeeding. Sore nipples are a common concern among breastfeeding mothers, and the most common cause is an improper latch. The nurse should ensure that the baby is latching on correctly and not causing trauma to the mother's nipples. A proper latch involves the baby taking in a good portion of the areola and not just the nipple. Assessing the newborn's latch can help identify any issues with the baby's mouth or tongue that may be causing difficulty latching on. If the baby is not latching correctly, the nurse can provide education and support to help the mother correct the issue. Offering supplemental formula between feedings (choice A) is not recommended as it can decrease the frequency of breastfeeding and reduce the stimulation for milk production, leading to decreased milk supply. Instructing the client to wait 4 hours between daytime feedings (choice C) is not recommended as it can decrease milk production and lead to inadequate nutrition for the newborn.
suggests that the nurse should assess the newborn's latch while breastfeeding. Sore nipples are a common concern among breastfeeding mothers, and the most common cause is an improper latch. The nurse should ensure that the baby is latching on correctly and not causing trauma to the mother's nipples. A proper latch involves the baby taking in a good portion of the areola and not just the nipple. Assessing the newborn's latch can help identify any issues with the baby's mouth or tongue that may be causing difficulty latching on. If the baby is not latching correctly, the nurse can provide education and support to help the mother correct the issue. Offering supplemental formula between feedings (choice A) is not recommended as it can decrease the frequency of breastfeeding and reduce the stimulation for milk production, leading to decreased milk supply. Instructing the client to wait 4 hours between daytime feedings (choice C) is not recommended as it can decrease milk production and lead to inadequate nutrition for the newborn.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C, Ensure the newborn's eyes are closed beneath the shield. Phototherapy is a treatment used to reduce high bilirubin levels in newborns. It involves exposing the newborn's skin to special lights, which helps to break down the excess bilirubin in the blood. It is important to ensure that the newborn's eyes are closed beneath the shield to prevent damage to the eyes from the bright lights. Giving the newborn 1 oz of glucose water every 4 hr, applying lotion to the newborn's skin every 8 hr, and dressing the newborn in a thin layer of clothing during therapy are not indicated interventions during phototherapy.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
