A nurse is assessing a client who is brought to the emergency room with burn injuries. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a deep partial-thickness burn?
The burned area is yellow in color with severe edema.
The burned area is black in color and pain is absent.
The burned area is pink in color with blisters present.
The burned area is red in color with soft eschar present.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason: The burned area is yellow in color with severe edema is not a finding of a deep partial-thickness burn, but a superficial partial-thickness burn. A superficial partial-thickness burn involves the epidermis and the upper layer of the dermis, causing pain, redness, swelling, and blistering.
Choice B Reason: The burned area is black in color and pain is absent is not a finding of a deep partial-thickness burn, but a full-thickness burn. A full-thickness burn involves the epidermis, dermis, and underlying tissues, causing necrosis, charred skin, and loss of sensation.
Choice C Reason: This description aligns with a superficial partial-thickness (first-degree or mild second-degree) burn rather than a deep partial-thickness burn. Superficial partial-thickness burns involve the epidermis and the upper portion of the dermis. These burns appear pink or red, often accompanied by moisture and blister formation due to fluid leakage from damaged capillaries. They are painful because nerve endings remain intact. Healing occurs within 10 to 21 days without significant scarring.
Choice D Reason: Deep partial-thickness burns extend deeper into the dermis, damaging a larger portion of skin structures, including sweat glands and hair follicles. These burns typically appear red or white and may have a soft eschar (dead tissue), which differentiates them from more superficial burns that do not develop eschar. Unlike full-thickness burns, nerve endings remain partially intact, so the patient may still experience some pain. These burns take more than 21 days to heal and often require skin grafting to prevent complications such as contractures or hypertrophic scarring.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
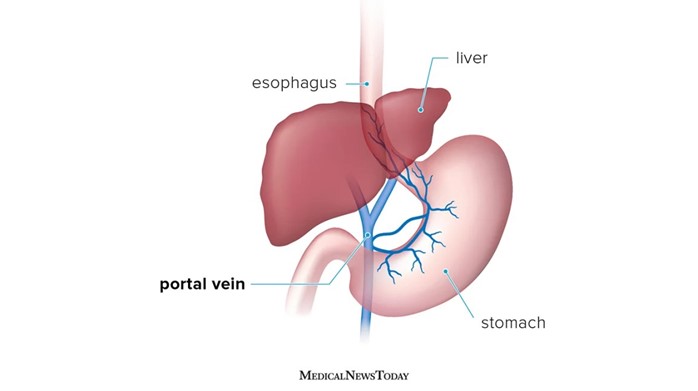
Choice A reason: This is the correct answer because portal hypertension means that there is high blood pressure in the portal vein, which carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver. When the liver is damaged by hepatitis, it becomes scarred and obstructs the blood flow, causing increased pressure in the portal vein. This leads to fluid accumulation in the abdomen, called ascites, which causes abdominal swelling.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because portal hypertension is not caused by the heart overworking but by liver damage. The heart does not pump blood into the portal vein, but into the hepatic artery, which supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because portal hypertension does not develop when cirrhosis begins to resolve, but when it progresses. Cirrhosis is a chronic condition that causes irreversible scarring of the liver tissue, which worsens over time and increases portal hypertension.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because eating high-sodium foods and a stressful lifestyle do not cause portal hypertension, but they can aggravate it. High-sodium foods can increase fluid retention and worsen ascites, while stress can increase blood pressure and worsen bleeding complications. The nurse should advise the client to limit sodium intake and manage stress levels.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because Ménière's disease is not caused by an allergic response. Ménière's disease is a disorder of the inner ear that causes vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. The exact cause of Ménière's disease is unknown, but it may be related to fluid imbalance, infection, trauma, or autoimmune reaction.
Choice B Reason: This is correct because diphenhydramine can help offset the nauseous feeling. Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine that blocks histamine receptors in the brain and inner ear, which can reduce nausea and vomiting associated with vertigo.
Choice C Reason: This is correct because anticholinergics will help you rest. Anticholinergics are a class of drugs that block acetylcholine receptors in the brain and body, which can have sedative effects and reduce motion sickness. Diphenhydramine has anticholinergic properties.
Choice D Reason: This is correct because diphenhydramine can help reduce vomiting episodes. As mentioned above, diphenhydramine can reduce nausea and vomiting by blocking histamine receptors in the brain and inner ear.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
