A nurse is assisting in the plan of care for a client who has dehydration and hypotension. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Encourage the client to use guided imagery to relax.
Elevate the head of the client's bed.
Increase the client's fluid intake.
Instruct the client to perform the Valsalva maneuver.
Instruct the client to perform the Valsalva maneuver.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason : Guided imagery is a relaxation technique that can help reduce stress and anxiety, but it does not directly address the physiological issues of dehydration and hypotension. While it may be beneficial as a complementary therapy, it is not the primary intervention for a patient suffering from these conditions.
Choice B reason : Elevating the head of the bed is generally recommended for patients who have difficulty breathing or to prevent aspiration, but it is not the standard care for hypotension. In fact, for a hypotensive patient, elevating the legs might be more beneficial to promote venous return to the heart⁹[^20^].
Choice C reason : Increasing fluid intake is the most direct and effective way to treat dehydration. When a patient is hypotensive, it often indicates a low blood volume, which can be improved by increasing fluid intake. This can be done orally if the patient is conscious and able to drink, or intravenously if they are not. The normal range for blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg, and maintaining adequate hydration helps to ensure blood pressure stays within this range⁸.
Choice D reason : The Valsalva maneuver is a technique used to potentially correct certain types of abnormal heart rhythms, particularly supraventricular tachycardia, and not for treating hypotension or dehydration. It involves increasing intrathoracic pressure by exhaling forcefully with a closed airway, which can have various effects on the cardiovascular system. However, it is not an appropriate intervention for a dehydrated, hypotensive patient⁹[^10^].
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason : The statement that warfarin dissolves clots in the bloodstream is incorrect. Warfarin does not dissolve existing clots. Instead, it is an anticoagulant that works by decreasing the production of certain clotting factors in the blood, which helps prevent the formation of new clots.
Choice B reason : This statement is not accurate regarding the action of warfarin. Warfarin does not affect the electrical impulses of the heart. Medications that slow the response of the ventricles to fast atrial impulses are typically antiarrhythmic drugs, not anticoagulants like warfarin.
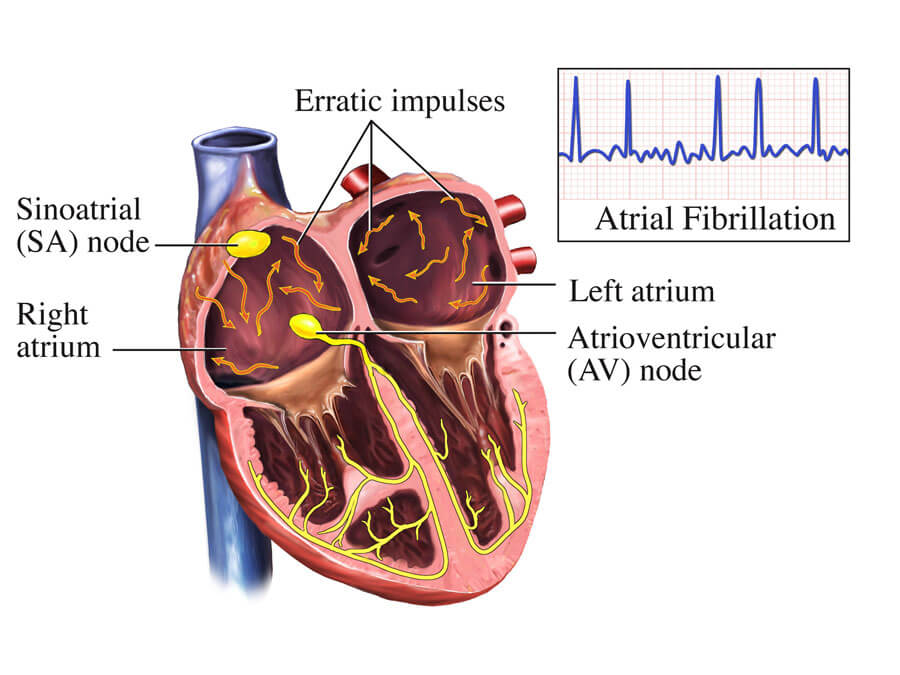
Choice C reason : This is the correct statement. Warfarin is prescribed for clients with atrial fibrillation to reduce the risk of stroke. Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of forming blood clots in the heart, which can then travel to the brain, causing a stroke. Warfarin's anticoagulant effect helps to prevent these clots from forming.
Choice D reason : Warfarin does not help maintain a normal heart rhythm. It is not an antiarrhythmic drug but an anticoagulant. The purpose of warfarin in atrial fibrillation is to prevent stroke by reducing the risk of clot formation, not to correct the heart rhythm.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason : A hemoglobin (Hgb) level of 16 g/dL is within the normal range for adults, which typically falls between 13.8 to 17.2 g/dL for men and 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL for women. Therefore, this value does not warrant reporting to the provider as it does not indicate an immediate concern.
Choice B reason : A prothrombin time (PT) of 45 seconds is significantly higher than the normal range of 11 to 13.5 seconds for individuals not on anticoagulation therapy. For patients on warfarin, the target PT is usually 1.5 to 2 times the normal value, depending on the indication for therapy. However, a PT of 45 seconds suggests a high risk of bleeding and requires immediate medical attention.
Choice C reason : The activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) of 36 seconds is within the normal range of approximately 21 to 35 seconds⁸. This result indicates that the blood's intrinsic clotting pathway is functioning within expected parameters and does not need to be reported.
Choice D reason : A platelet count of 190,000/mm is within the normal range, which is typically 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/mm. This value is not concerning and does not need to be reported to the provider.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
