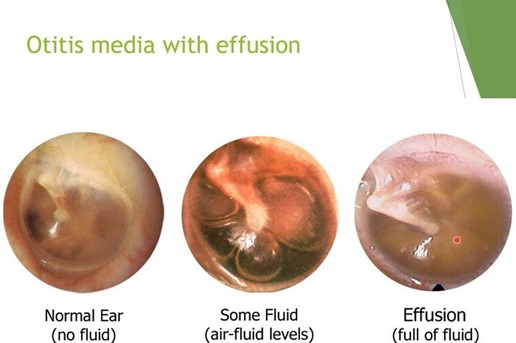
A nurse is caring for a child who has otitis media with effusion. The nurse should identify which of the following manifestations indicates a tympanic membrane rupture.
Popping sensation when swallowing
Green-blue discharge in the ear canal
Sudden pain relief
Increased temperature
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A: A popping sensation when swallowing is not a sign of a tympanic membrane rupture, as it is a normal phenomenon that occurs when the eustachian tube opens and closes to equalize the pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. A popping sensation when swallowing may be associated with otitis media with effusion, which is a condition that causes fluid accumulation behind the eardrum, but it does not indicate a rupture.
Choice B: Green-blue discharge could be indicative of infection but is not as directly related to the rupture event as the sudden pain relief is.
Choice C: The correct answer is sudden relief of pain. This is because the rupture of the tympanic membrane releases the pressure and fluid that has built up in the middle ear, leading to an immediate decrease in pain.
Choice D: An increased temperature is not a sign of a tympanic membrane rupture, as it is a nonspecific symptom that may indicate various conditions, such as inflammation, infection, or fever. An increased temperature may be associated with otitis media with effusion, which is a condition that causes fluid accumulation behind the eardrum, but it does not indicate a rupture.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Allowing for imaginative play with peers without supervision is not an appropriate intervention for a child who has autism spectrum disorder, as it can cause frustration, anxiety, or isolation for the child. A child who has autism spectrum disorder may have difficulty with social skills, communication, and imagination, which can affect their ability to interact and play with others. The nurse should provide structured and supervised play activities that promote socialization and cooperation.
Choice B: Providing a completely unpredictable schedule that adjusts to the child's interests is not an appropriate intervention for a child who has autism spectrum disorder, as it can cause confusion, stress, or tantrums for the child. A child who has autism spectrum disorder may have difficulty with transitions, changes, and flexibility, which can affect their ability to cope and adapt to different situations. The nurse should provide a consistent and predictable schedule that follows a routine and gives clear expectations.
Choice C: Allowing for adjustment of rules to correlate with the child's behavior is not an appropriate intervention for a child who has autism spectrum disorder, as it can cause inconsistency, insecurity, or manipulation for the child. A child who has autism spectrum disorder may have difficulty understanding and following rules, which can affect their ability to behave and function appropriately. The nurse should provide firm and fair rules that are enforced consistently and respectfully.
Choice D: Establishing a reward system for positive behavior with prizes is an appropriate intervention for a child who has autism spectrum disorder, as it can provide motivation, reinforcement, and feedback for the child. A child who has autism spectrum disorder may have difficulty with learning and performing new skills, which can affect their ability to achieve and succeed. The nurse should provide a reward system that recognizes and rewards positive behavior with tangible or intangible prizes.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is incorrect because the BCG vaccine is not recommended for adolescents in the United States. The BCG vaccine is a vaccine that protects against tuberculosis (TB), a bacterial infection that affects the lungs and other organs. It may be used for children who live in countries where TB is common or who have a high risk of exposure to TB, but it is not routinely given in the United States because of the low incidence of TB and the possibility of false-positive results on TB skin tests.
Choice B reason: This choice is incorrect because the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine is not recommended for adolescents unless they have certain medical conditions. The pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine is a vaccine that protects against pneumococcal disease, a bacterial infection that can cause pneumonia, meningitis, or sepsis. It may be used for adults who are 65 years or older or who have chronic diseases, immunosuppression, or cochlear implants, but it is not routinely given to adolescents who are healthy.
Choice C reason: This choice is incorrect because the influenza vaccine is recommended for adolescents every year, not just before college. The influenza vaccine is a vaccine that protects against influenza, a viral infection that affects the respiratory system. It may be given as an injection or a nasal spray, and it may prevent or reduce the severity of influenza and its complications. It is recommended for everyone who is 6 months or older, especially those who have a high risk of influenza-related complications.
Choice D reason: This choice is correct because the meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine is recommended for adolescents before college. The meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine is a vaccine that protects against meningococcal disease, a bacterial infection that can cause meningitis, septicemia, or death. It may be given as a single dose or a booster dose, and it may prevent outbreaks of meningococcal disease in crowded settings such as dormitories or military barracks. It is recommended for adolescents who are 11 to 12 years old, with a booster dose at 16 years old, or for those who are entering college and have not been previously vaccinated.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
