A nurse is assessing a child and notes several bruises. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Ask a psychiatrist to talk with the parents.
Separate the child from the parents.
Report the suspected abuse to the authorities.
Obtain a detailed history.
The Correct Answer is D
a. While involving mental health professionals can be part of a broader intervention plan, it is not the immediate priority in cases of suspected abuse. The nurse must first address the immediate safety concerns and follow the required reporting procedures.
b. Separating the child from the parents without proper authority or immediate threat can escalate the situation and may not be legally permissible. This action should be taken by authorities with the legal power to do so if deemed necessary.
c. Nurses are mandated reporters, which means they are legally required to report any suspected child abuse to the appropriate authorities immediately. This action ensures that the child’s safety is prioritized and that a proper investigation can be initiated however, obtaining a detailed history is the priority.
d. When a nurse observes several bruises on a child, the initial action should be to obtain a detailed history. This step allows the nurse to gather information about the circumstances surrounding the bruises, assess for any potential signs of abuse, and determine the most appropriate course of action.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Acute lead poisoning in toddlers can cause anorexia, as well as vomiting, abdominal pain, and constipation.
These symptoms can progress to seizures, coma, and even death if not treated promptly.
Choice A, increased urinary output, is not the correct answer because lead poisoning can cause a decrease in urinary output due to the effect of lead on the kidneys.
Choice C, diarrhea, is not the correct answer because lead poisoning is more likely to cause constipation than diarrhea.
Choice D, jaundice, is not the correct answer because jaundice is not a common finding in lead poisoning.
Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes caused by an excess of bilirubin in the blood, which is not directly related to lead poisoning.
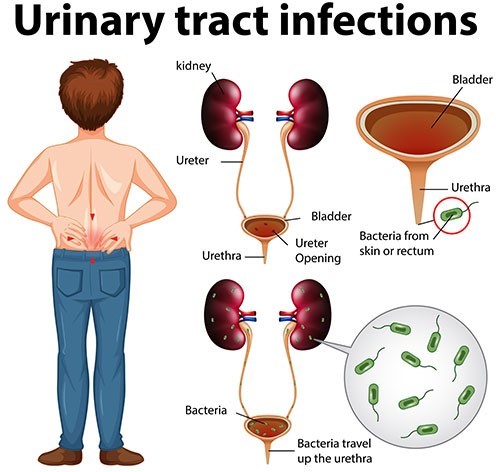
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
The nurse should include all of these points in the teaching.
A. Avoiding bubble baths can help prevent irritation and infection.
B. Watching for manifestations of infection can help detect any worsening or recurrence of the infection.
C. Emptying the bladder completely with each void can help prevent urine from remaining in the bladder and causing infection.
D. Wiping the perineal area front to back can help prevent bacteria from
spreading to the urethra.
E. Wearing cotton underpants can help keep the area dry and reduce the risk of infection.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
