A nurse is caring for a 6-month-old infant who is postoperative following a myringotomy. Which of the following pain scales should the nurse use to determine the infant's pain level?
Oucher
FLACC
FACES
Visual Analog Scale
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A: The Oucher pain scale is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 to 13 years who can point to pictures of faces that match their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or point to pictures.
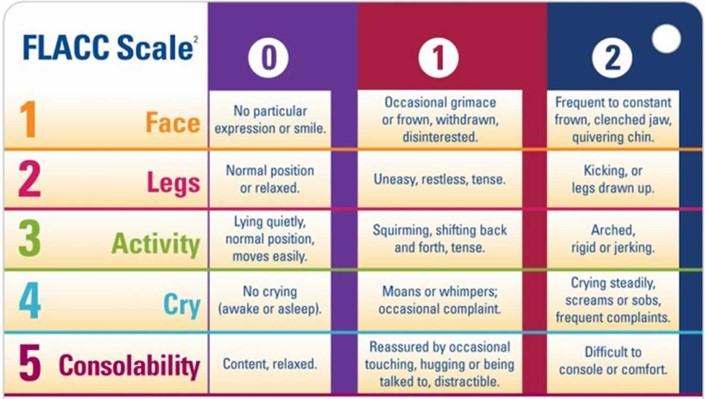
Choice B: The FLACC pain scale is suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for infants and children aged 2 months to 7 years who cannot verbalize their pain. The FLACC pain scale assesses five behavioral indicators of pain: face, legs, activity, cry, and consolability. Each indicator is scored from 0 to 2 based on the observation of the nurse. The total score ranges from 0 to 10, with higher scores indicating more pain.
Choice C: The FACES pain scale is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 years and older who can select a face that matches their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or select a face.
Choice D: The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for adults and older children who can mark a point on a line that represents their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or mark a point on a line.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A: A 3-year-old child is not developmentally ready to descend stairs by placing both feet on each step and holding on to the railing. A 3-year-old child can walk up stairs alternating feet with one hand held by an adult or on the railing. A 3-year-old child can also walk down stairs placing both feet on each step with one hand held by an adult.
Choice B: A 4-year-old child is developmentally able to descend stairs by placing both feet on each step and holding on to the railing. A 4-year-old child can also walk up stairs alternating feet without assistance.
Choice C: A 5-year-old child is developmentally more advanced than descending stairs by placing both feet on each step and holding on to the railing. A 5-year-old child can walk up and down stairs alternating feet without assistance.
Choice D: A 6-year-old child is developmentally more advanced than descending stairs by placing both feet on each step and holding on to the railing. A 6-year-old child can walk up and down stairs alternating feet without assistance and can also hop and skip on one foot.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: The OUCHER scale is not suitable for a 2-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 to 13 years who can point to pictures of faces that match their pain level. A 2-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or point to pictures.
Choice B: The FACES scale is not suitable for a 2-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 years and older who can select a face that matches their pain level. A 2-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or select a face.
Choice C: The PAINAD scale is not suitable for a 2-month-old infant, as it is designed for adults who have advanced dementia and cannot verbalize their pain. A 2-month-old infant does not have dementia and may have different behavioral indicators of pain.
Choice D: The FLACC scale is suitable for a 2-month-old infant, as it is designed for infants and children aged 2 months to 7 years who cannot verbalize their pain. The FLACC scale assesses five behavioral indicators of pain: face, legs, activity, cry, and consolability. Each indicator is scored from 0 to 2 based on the observation of the nurse. The total score ranges from 0 to 10, with higher scores indicating more pain.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
