A nurse is caring for a client who is taking lithium and reports starting a new exercise program. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following electrolyte imbalances?
Hypomagnesemia
Hyponatremia
Hypocalcemia
Hypokalemia
The Correct Answer is B
A. Hypomagnesemia:
Correct Answer: This electrolyte imbalance is the one the nurse should assess the client for.
Explanation: Lithium is primarily excreted by the kidneys, and its excretion can be influenced by factors that affect renal function, including electrolyte imbalances. Hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels) can potentially reduce the excretion of lithium, leading to increased lithium levels in the blood. This can increase the risk of lithium toxicity, which can be dangerous. Therefore, monitoring magnesium levels is important in clients taking lithium.
B. Hyponatremia:
Incorrect Explanation: While hyponatremia (low sodium levels) is a potential concern, it is not as directly linked to lithium interaction as hypomagnesemia.
Explanation: Lithium can cause diabetes insipidus, which leads to excessive urination and subsequent loss of water and electrolytes, including sodium. However, hyponatremia is not the immediate electrolyte imbalance that arises due to the interaction with lithium.
C. Hypocalcemia:
Incorrect Explanation: Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) is not a primary concern in the context of lithium use.
Explanation: Lithium does not have a direct interaction with calcium levels. Hypocalcemia is typically not a result of lithium use or its interaction with other factors.
D. Hypokalemia:
Incorrect Explanation: While electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia (low potassium levels) can have health implications, it is not the primary electrolyte imbalance to be concerned about with lithium use.
Explanation: Hypokalemia is not a direct consequence of lithium interaction. Monitoring potassium levels is important for overall health, but it's not the primary electrolyte imbalance associated with lithium use and its potential interactions.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Obtain the client's HDL level.
Explanation: This choice is not relevant to the situation. HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) level is related to cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health, which is not directly affected by the administration of metformin instead of metoprolol.
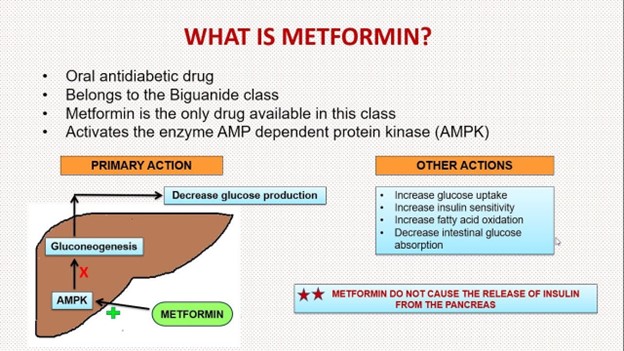
B. Check the client's glucose level.
Explanation: Correct Choice. Metformin is an oral antidiabetic medication commonly used to lower blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It works by improving insulin sensitivity and decreasing glucose production in the liver. Accidentally administering metformin instead of metoprolol could lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or other adverse effects related to glucose levels. Checking the client's glucose level is essential to assess and address any potential issues arising from this medication error.
C. Monitor the client's thyroid function levels.
Explanation: This choice is not directly relevant to the situation. Metformin and metoprolol do not significantly affect thyroid function levels. Thyroid function monitoring would not be the immediate concern in this scenario.
D. Collect the client's uric acid level.
Explanation: This choice is not directly relevant to the situation. Metformin and metoprolol do not have a primary impact on uric acid levels. Collecting the uric acid level would not be a priority in this context.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. "I should stay upright for at least 15 minutes after taking this medication.": This advice is usually given with medications like bisphosphonates to prevent esophageal irritation. It is not necessary for ferrous gluconate.
B. "I should take this medication with 8 ounces of milk.": Iron supplements should not be taken with milk or other dairy products because they can interfere with iron absorption.
C. "I should take an antacid with this medication to prevent stomach upset.": Antacids can also interfere with iron absorption and should be taken separately from iron supplements.
D. "I should notify my provider if my stools turn black."
Ferrous gluconate is an iron supplement used to treat iron deficiency anemia. One common side effect of iron supplementation is the darkening of stools, often to a black color. This is not harmful but is important for the client to be aware of. It is due to the reaction of iron with the acids and enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
