A nurse accidently administers the medication metformin instead of metoprolol to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Obtain the client's HDL level.
Check the client's glucose level.
Monitor the client's thyroid function levels.
Collect the client's uric acid level.
The Correct Answer is B
A. Obtain the client's HDL level.
Explanation: This choice is not relevant to the situation. HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) level is related to cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health, which is not directly affected by the administration of metformin instead of metoprolol.
B. Check the client's glucose level.
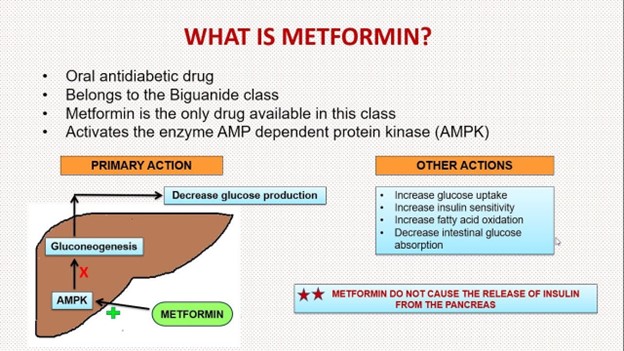
Explanation: Correct Choice. Metformin is an oral antidiabetic medication commonly used to lower blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It works by improving insulin sensitivity and decreasing glucose production in the liver. Accidentally administering metformin instead of metoprolol could lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or other adverse effects related to glucose levels. Checking the client's glucose level is essential to assess and address any potential issues arising from this medication error.
C. Monitor the client's thyroid function levels.
Explanation: This choice is not directly relevant to the situation. Metformin and metoprolol do not significantly affect thyroid function levels. Thyroid function monitoring would not be the immediate concern in this scenario.
D. Collect the client's uric acid level.
Explanation: This choice is not directly relevant to the situation. Metformin and metoprolol do not have a primary impact on uric acid levels. Collecting the uric acid level would not be a priority in this context.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Naloxone IV:
This choice is incorrect. Naloxone is an opioid receptor antagonist used to reverse the effects of opioid overdose. It works by displacing opioids from the receptors and rapidly reversing their effects. However, in this scenario, the client is experiencing pain 1 hour after receiving morphine, indicating that the morphine's analgesic effects have likely worn off. Naloxone is not used to manage pain, but rather to reverse opioid overdose.
B. Fentanyl transmucosal:
This choice is incorrect. Fentanyl transmucosal formulations are used for breakthrough pain in opioid-tolerant patients with chronic pain conditions. It is not typically the first choice for immediate pain relief after intravenous morphine administration. Additionally, it's worth noting that fentanyl transmucosal products, like fentanyl lollipops, are usually reserved for chronic pain management and may not be suitable for immediate post-administration pain relief.
C. Morphine tablet:
This is the correct choice. If the client is experiencing pain 1 hour after receiving morphine intravenously, it's reasonable to administer an oral or sublingual form of morphine for continued pain relief. Morphine tablets are commonly used for pain management and can provide sustained relief over a longer duration. This choice aligns with the patient's initial prescription for pain control.
D. Lidocaine patch:
This choice is incorrect. Lidocaine patches are used to manage localized neuropathic pain, such as postherpetic neuralgia. They work by numbing the skin and underlying tissues in the area where they are applied. While lidocaine patches can be effective for certain types of pain, they are not typically used to address the acute pain associated with cancer and immediate post-administration pain relief.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Place the medications on the back of the client's tongue:
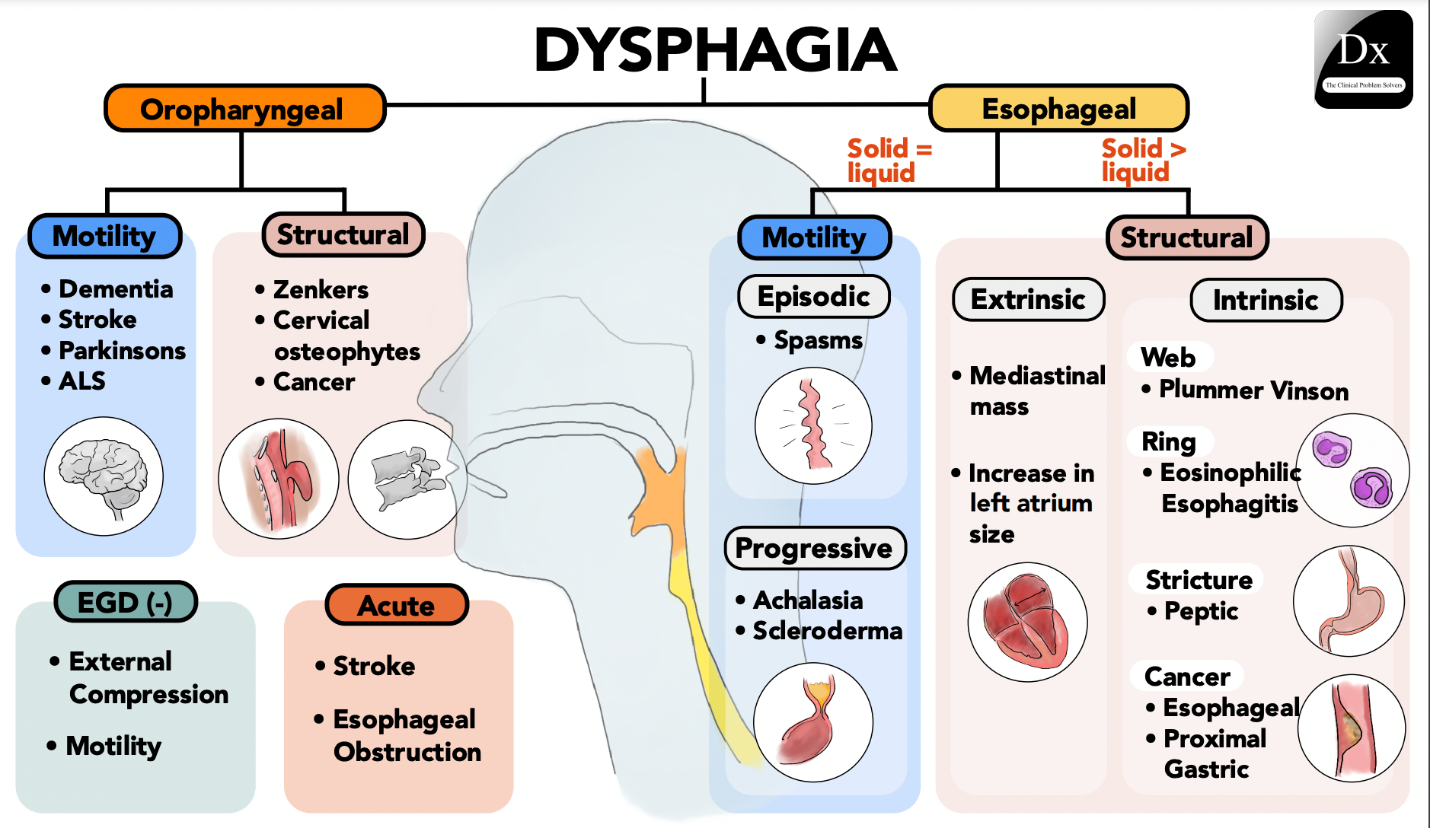
Incorrect Explanation: Placing medications on the back of the tongue can increase the risk of choking and aspiration, especially in individuals with dysphagia.
Explanation: Individuals with dysphagia have difficulty swallowing and are at an increased risk of choking or aspirating (inhaling) substances into the lungs. Placing medications on the back of the tongue can be unsafe and is not recommended.
B. Tilt the client's head back when administering the medications:
Incorrect Explanation: Tipping the head back can worsen swallowing difficulties and increase the risk of choking or aspiration.
Explanation: Tipping the head back can compromise the natural swallowing mechanism and increase the risk of aspiration. It's important to keep the client's head in an upright position to aid safe swallowing.
C. Administer more than one pill to the client at a time:
Incorrect Explanation: Administering multiple pills at once can increase the risk of choking and aspiration, especially in individuals with dysphagia.
Explanation: Administering multiple pills at once can overwhelm the client's ability to swallow safely. This action can increase the risk of choking and aspiration, which is especially dangerous for individuals with dysphagia.
D. Mix the medications with a semisolid food for the client:
Correct Answer: This action is appropriate and safer for administering medications to an older adult client with dysphagia.
Explanation: Mixing medications with semisolid food, such as applesauce or yogurt, can help the client swallow more easily and reduce the risk of choking or aspiration. It's important to check with the healthcare provider or pharmacist to ensure that the medications can be mixed with food and that there are no interactions.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
