A nurse is caring for an infant who has a tracheoesophageal fistula. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? (Select all that apply)
Anoxia
Frothy saliva
Apnea
Sunken abdomen
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A: Anoxia
Reason: Anoxia refers to an absence of oxygen supply to an organ or a tissue. While it is a serious condition, it is not a typical finding specifically associated with tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF). TEF primarily affects the esophagus and trachea, leading to issues with feeding and breathing, but not directly causing anoxia. Anoxia could be a secondary complication if the infant experiences severe respiratory distress, but it is not a primary symptom.
Choice B: Frothy Saliva
Reason: Frothy saliva is a common and significant finding in infants with tracheoesophageal fistula. This occurs because the abnormal connection between the trachea and esophagus allows saliva to accumulate and bubble up, leading to frothy secretions. This symptom is often one of the first signs that alert healthcare providers to the presence of TEF.
Choice C: Apnea
Reason: Apnea, or temporary cessation of breathing, is another expected finding in infants with tracheoesophageal fistula. The abnormal connection can cause aspiration of saliva or food into the lungs, leading to respiratory distress and apnea. This is a critical symptom that requires immediate medical attention to prevent severe complications.
Choice D: Sunken Abdomen
Reason: A sunken abdomen is not typically associated with tracheoesophageal fistula. In fact, infants with TEF might present with abdominal distension due to air entering the stomach through the fistula. A sunken abdomen could indicate other conditions such as dehydration or malnutrition, but it is not a characteristic finding of TEF.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain, leading to increased pressure inside the skull. This can cause an enlarged head, developmental delays, and other neurological impairments. While hydrocephalus can be associated with neural tube defects, it is not itself a neural tube defect. It can occur as a secondary condition to neural tube defects like spina bifida, but it is not classified as one.
Choice B: Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement, muscle tone, and posture. It is caused by damage to the developing brain, often before birth. Cerebral palsy is not a neural tube defect; it is a result of brain injury or malformation during brain development. Neural tube defects specifically refer to abnormalities in the development of the neural tube, which forms the brain and spinal cord.
Choice C: Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic diseases characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of the skeletal muscles that control movement. It is caused by mutations in genes responsible for muscle function. Muscular dystrophy is not related to neural tube defects; it is a separate category of genetic disorders affecting muscle tissue rather than the neural tube.
Choice D: Spina Bifida
Spina bifida is a type of neural tube defect that occurs when the spine and spinal cord do not form properly. It is one of the most common neural tube defects and can lead to physical and neurological impairments. Spina bifida can range in severity from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the spinal cord involvement. It is a direct result of the neural tube failing to close completely during early embryonic development.
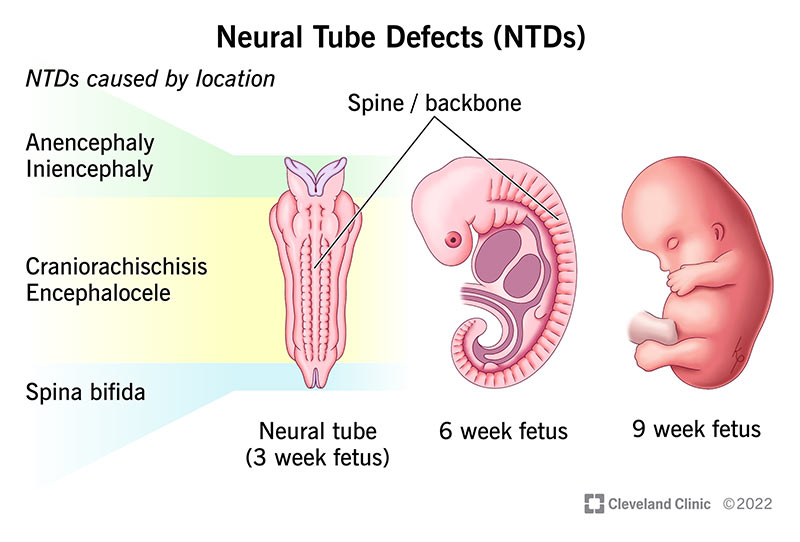
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Impetigo contagiosa is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that primarily affects children. It typically presents as reddish sores on the face, especially around the nose and mouth, which quickly rupture, ooze for a few days, and then form a honey-colored crust. While impetigo can cause itching, it does not produce silver specks that resemble dandruff or cause persistent scratching at the nape of the neck.
Choice B Reason:
Folliculitis is an infection of the hair follicles, often caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses. It presents as small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles. Folliculitis can cause itching and discomfort, but it does not typically produce silver specks that resemble dandruff. The symptoms are more likely to include clusters of small red bumps or pus-filled blisters rather than dandruff-like specks.
Choice C Reason:
Tinea capitis, also known as scalp ringworm, is a fungal infection of the scalp. It can cause patches of hair loss, dry scaly rashes, severe itchiness, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes. While tinea capitis can cause flaking that resembles dandruff, it does not typically present with silver specks that do not brush off. The primary symptoms are more likely to include red, inflamed patches and hair loss.
Choice D Reason:
Pediculosis capitis, or head lice infestation, is characterized by the presence of lice and their eggs (nits) on the scalp and hair. The nits are often mistaken for dandruff but do not brush off easily. The primary symptoms include intense itching, especially at the nape of the neck and behind the ears, and the presence of small, white or silver specks (nits) attached to the hair shafts. This matches the description provided in the question, making pediculosis capitis the most likely diagnosis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
