A nurse is assessing a newborn who has a coarctation of the aorta. Which of the following should the nurse recognize as a clinical manifestation of coarctation of the aorta?
Increased blood pressure in the arms with decreased blood pressure in the legs
Increased blood pressure in both the arms and the legs
Decreased blood pressure in both the arms and the legs
Decreased blood pressure in the arms with increased blood pressure in the legs
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A Reason:
In coarctation of the aorta, the narrowing of the aorta typically occurs after the arteries that supply the upper body branch off. This results in higher blood pressure in the arms and lower blood pressure in the legs. The difference in blood pressure between the upper and lower extremities is a key diagnostic indicator of this condition.
Choice B Reason:
Increased blood pressure in both the arms and the legs is not characteristic of coarctation of the aorta. This condition specifically causes a disparity in blood pressure between the upper and lower parts of the body due to the narrowing of the aorta.
Choice C Reason:
Decreased blood pressure in both the arms and the legs is not a typical manifestation of coarctation of the aorta. The condition usually leads to increased blood pressure in the upper body and decreased blood pressure in the lower body.
Choice D Reason:
Decreased blood pressure in the arms with increased blood pressure in the legs is the opposite of what is seen in coarctation of the aorta. The narrowing of the aorta causes higher pressure in the upper body and lower pressure in the lower body.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
A backward sloping appearance of the forehead is not a typical manifestation of hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus usually causes an enlarged head or a bulging fontanelle due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Choice B Reason:
Dilated scalp veins are a common sign of hydrocephalus in newborns. The increased intracranial pressure from the excess cerebrospinal fluid can cause the veins on the scalp to become more prominent.
Choice C Reason:
Hypertension is not a typical manifestation of hydrocephalus in newborns. While increased intracranial pressure can affect various bodily functions, it does not usually cause high blood pressure in infants.
Choice D Reason:
Sunken fontanelles are generally a sign of dehydration, not hydrocephalus. In hydrocephalus, the fontanelles are more likely to be bulging due to increased intracranial pressure.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
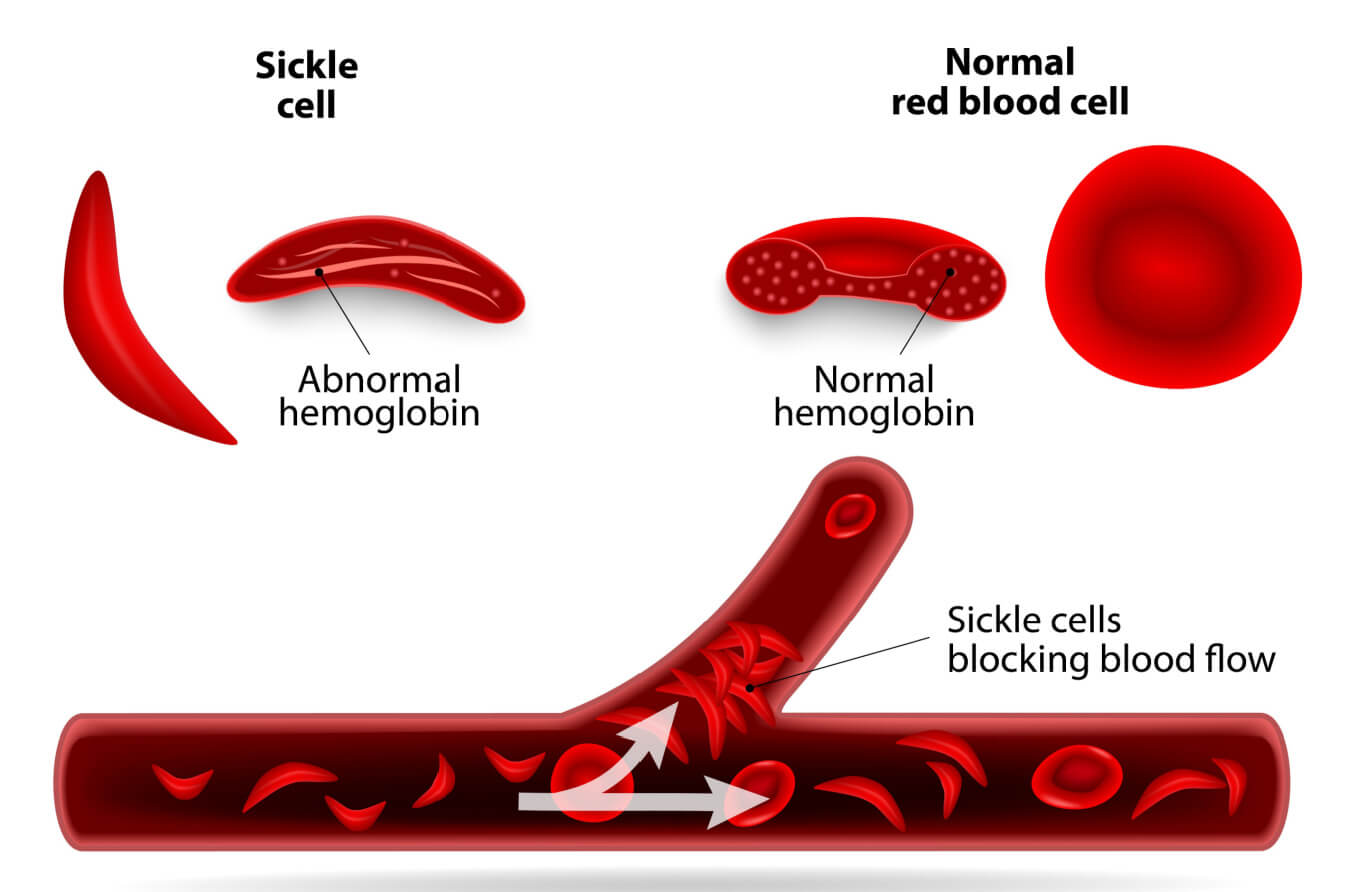
Administer meperidine every 4 hours for pain. This is not recommended for children with sickle cell anemia. Meperidine is an opioid analgesic, but it is not the preferred choice for managing pain in sickle cell patients due to its potential for causing seizures and other side effects. Instead, other pain management strategies, such as acetaminophen, NSAIDs, or other opioids like morphine, are preferred.
Choice B Reason:
Apply cold compresses to painful, swollen joints. This is not recommended for children with sickle cell anemia. Cold compresses can cause vasoconstriction, which can worsen the pain and potentially trigger a sickle cell crisis. Instead, warm compresses are recommended to help alleviate pain and promote blood flow.
Choice C Reason:
Position extremities extended. This is the correct intervention. Positioning the extremities extended helps to promote blood flow and prevent vaso-occlusive episodes, which are common in sickle cell anemia. Proper positioning can help reduce pain and improve circulation.
Choice D Reason:
Discourage a high level of fluid intake. This is not recommended for children with sickle cell anemia. Adequate hydration is crucial for preventing sickle cell crises. Encouraging a high level of fluid intake helps to keep the blood less viscous and reduces the risk of vaso-occlusive episodes. Dehydration can exacerbate the condition and lead to complications.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
