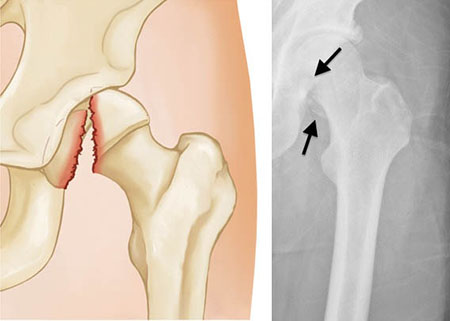
A nurse is caring for an older adult client who had a femoral head fracture 24 hours ago and is in skin traction. The client reports shortness of breath and dyspnea. The nurse should suspect that the client has developed which of the following complications?
Pneumothorax
Pneumonia
Airway obstruction
Fat embolism
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason:
Pneumothorax, a collapsed lung, can indeed cause shortness of breath and dyspnea. However, it is typically associated with a sudden onset of these symptoms following a chest injury or spontaneously in the case of a ruptured air blister. In the context of a femoral head fracture, pneumothorax is less likely unless there was additional trauma to the chest area.
Choice B reason:
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that leads to inflammation of the air sacs, causing them to fill with fluid or pus. Symptoms include cough with phlegm, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. While pneumonia could cause dyspnea, it usually develops due to an infectious process rather than directly from a femoral head fracture.
Choice C reason:
Airway obstruction involves a blockage that prevents air from passing freely to the lungs. It can be caused by foreign objects, swelling due to allergic reactions, or other medical conditions. The symptoms of airway obstruction include difficulty breathing, wheezing, and potential changes in skin color. However, airway obstruction is not commonly a direct complication of a femoral head fracture.
Choice D reason:
Fat embolism syndrome is a serious condition that occurs when fat globules enter the bloodstream and lodge within the pulmonary vasculature, leading to respiratory distress. It is a known complication following long bone fractures, such as the femur, and presents with symptoms like shortness of breath, hypoxemia, and neurological manifestations. Given the recent femoral head fracture and the symptoms reported, fat embolism syndrome is the most likely diagnosis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is not typically an expected finding in hypovolemic shock. In fact, one would expect the opposite, hypotension, due to the decreased circulating blood volume. Hypertension might be present in the initial stages due to compensatory mechanisms, but as the condition progresses, blood pressure usually drops.
Choice B reason: Bradypnea
Bradypnea, or abnormally slow breathing, is not a common finding in hypovolemic shock. Instead, tachypnea, or rapid breathing, may be observed as the body attempts to compensate for reduced oxygen delivery to tissues.
Choice C reason: Oliguria
Oliguria, or low urine output, is an expected finding in hypovolemic shock. As the blood volume decreases, the kidneys receive less blood flow, leading to reduced urine production. This is a protective mechanism to conserve body fluids, but it also indicates the severity of fluid loss and the need for urgent intervention.
Choice D reason: Flushing of the skin
Flushing of the skin is not an expected finding in hypovolemic shock. Instead, the skin may appear pale, cool, and clammy due to vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow to the periphery as the body prioritizes blood flow to vital organs.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Generalized urticaria, or hives, is not a common side effect of radiation therapy for lung cancer. While skin reactions can occur, they are usually localized to the area being treated. Urticaria might be a sign of an allergic reaction, which would require immediate attention, but it is not typically associated with radiation therapy¹.
Choice B reason:
Xerostomia, or dry mouth, is a common side effect of radiation therapy, especially when the radiation field includes salivary glands. For lung cancer patients, if the radiation field is near the neck or upper chest, it could potentially affect salivary gland function. Monitoring for xerostomia is important because it can lead to difficulties in speaking, eating, and swallowing, and it increases the risk for dental problems².
Choice C reason:
While reviewing laboratory test results for low hemoglobin is an important part of nursing care, it is not specific to radiation therapy for lung cancer. Low hemoglobin could be related to the cancer itself or a side effect of other treatments like chemotherapy. It is important to monitor, but not the primary action related to radiation therapy³.
Choice D reason:
Observing for signs of infection is a general nursing responsibility for all patients, not specific to those receiving radiation therapy for lung cancer. However, if the patient's immune system is compromised due to the cancer or other treatments, vigilance for infection is heightened.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
