A nurse working in the perioperative area is reviewing the Quality and Safety Education in Nursing (QSEN) competencies. Which of the foIIowing competencies should the nurse identify as the priority when caring for a client during the perioperative period?
Evidence based practice
Informatics
quality improvement
Safety
The Correct Answer is D
A. Evidence-based practice:
Evidence-based practice (EBP) involves integrating the best available evidence from research, clinical expertise, and patient preferences and values to inform nursing practice. In perioperative nursing, EBP is important for making informed decisions about preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care protocols. For example, using evidence-based guidelines for surgical site infection prevention, pain management strategies, and postoperative care protocols can improve patient outcomes and safety.
B. Informatics:
Informatics refers to the use of information technology and data management systems to support nursing practice, education, research, and patient care. In perioperative nursing, informatics plays a crucial role in managing electronic health records (EHRs), accessing patient data, documenting care, and communicating with interdisciplinary team members. It also includes utilizing perioperative information systems for surgical scheduling, anesthesia records, and tracking patient progress during surgery.
C. Quality improvement:
Quality improvement (QI) involves systematic processes to monitor, assess, and improve the quality of healthcare services. In perioperative nursing, QI initiatives focus on enhancing patient safety, optimizing surgical outcomes, reducing complications, and improving efficiency in perioperative processes. Nurses participate in QI projects by analyzing data, identifying areas for improvement, implementing evidence-based practices, and evaluating the impact of interventions on patient care and outcomes.
D. Safety:
Safety is a fundamental QSEN competency, particularly critical in perioperative nursing care. Perioperative nurses are responsible for ensuring the safety of patients during all phases of surgery, including preoperative assessment, intraoperative care, and postoperative recovery. This includes measures such as verifying patient identity and surgical site, preventing surgical errors (e.g., wrong-site surgery), maintaining aseptic techniques to prevent infections, preventing falls and injuries, managing anesthesia safely, and adhering to protocols for safe medication administration and equipment use.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
-
A. How many people live in your home?
This question pertains to social and environmental factors but is not directly related to assessing skin inflammation on the chest. While social factors can impact overall health, such as stress levels or exposure to infectious agents, the number of people living in the client's home is unlikely to be directly related to a new skin inflammation unless there are specific circumstances, such as sharing personal care products or close contact with others who have similar skin issues.
B. Did you have a recent exposure to irritants?
This question is highly relevant to assessing a new skin inflammation on the chest. Exposure to irritants or allergens can trigger or worsen skin conditions, such as contact dermatitis or allergic reactions. By asking about recent exposure to potential irritants like new detergents, soaps, fabrics, chemicals, or environmental factors, the nurse can gather important information to identify possible triggers for the skin inflammation.
C. Is nausea associated with your rash?
Nausea is typically not directly associated with a skin rash or inflammation unless there is a systemic condition or allergic reaction causing both symptoms. While it's important to assess for any systemic signs or symptoms that may be related to the skin condition, such as fever or malaise, specifically asking about nausea may not provide relevant information about the skin inflammation on the chest.
D. What is your body mass index?
Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body weight relative to height and is not directly related to assessing a new skin inflammation on the chest. While obesity or changes in body weight can sometimes contribute to skin issues, such as friction-related dermatitis or hormonal changes affecting skin health, BMI alone is not a primary assessment parameter for localized skin conditions unless there are specific concerns related to weight-related skin problems.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
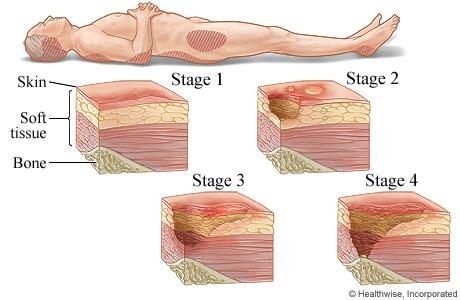
A. Stage III pressure injury
Stage III pressure injuries involve full-thickness skin loss, extending into the subcutaneous tissue but not through the fascia. These wounds typically present as deep craters and may involve undermining or tunneling. Non-blanchable erythema alone without visible skin loss is not characteristic of a Stage III pressure injury.
B. Stage IV pressure injury
Stage IV pressure injuries are the most severe and involve full-thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle. These wounds often have extensive tissue damage and can be difficult to manage. Again, non-blanchable erythema without visible skin loss is not indicative of a Stage IV pressure injury.
C. Stage II pressure injury
Stage II pressure injuries involve partial-thickness skin loss with damage to the epidermis and possibly the dermis. These wounds often present as shallow open ulcers or blisters and may have characteristics such as intact or ruptured blisters. While Stage II injuries can present with erythema, non-blanchable erythema specifically indicates a Stage I injury.
D. Stage I pressure injury
Stage I pressure injuries are the earliest stage and involve non-blanchable erythema of intact skin. The skin may be warmer or cooler than surrounding tissue and may have changes in sensation. There is no visible skin loss at this stage, but the area is at risk for further injury if pressure is not relieved. Therefore, non-blanchable erythema on the heels most likely indicates a Stage I pressure injury.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
