A nurse is evaluating a client's laboratory results. The nurse should recognize which of the following results places the client at risk for coronary heart disease.
HbA1c 5%.
LDL 64 mg/dL.
Total cholesterol 173 mg/dL.
Fasting glucose 140 mg/dL.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A rationale:
An HbA1c level of 5% is within the target range for good diabetes control. HbA1c represents the average blood glucose level over the past two to three months, and an HbA1c of 5% indicates well-managed blood glucose levels.
Choice B rationale:
An LDL level of 64 mg/dL is within the recommended range for individuals at risk for heart disease. Lower LDL levels are associated with reduced risk, but 64 mg/dL is not a concerning value and is not typically associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease.
Choice C rationale:
A total cholesterol level of 173 mg/dL is within the desirable range for adults. While it's important to consider both LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, the total cholesterol value alone is not sufficient to indicate a significant risk of coronary heart disease.
Choice D rationale:
A fasting glucose level of 140 mg/dL indicates hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose) and is a significant risk factor for coronary heart disease. Hyperglycemia is associated with increased oxidative stress, inflammation, and vascular damage, all of which contribute to the development of cardiovascular complications in individuals with diabetes. It's crucial to manage blood glucose levels to reduce the risk of heart disease and other diabetes-related complications.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Distended neck veins - Distended neck veins are typically associated with increased fluid volume or right-sided heart failure. In the case of dehydration, the fluid volume is reduced, and the veins are more likely to appear collapsed rather than distended.
Choice B rationale:
Tachycardia - Dehydration leads to a reduction in blood volume and a subsequent decrease in blood pressure. To compensate for this drop in blood pressure, the heart rate tends to increase. Tachycardia (an elevated heart rate) is a compensatory mechanism aimed at maintaining an adequate cardiac output despite reduced circulating blood volume.
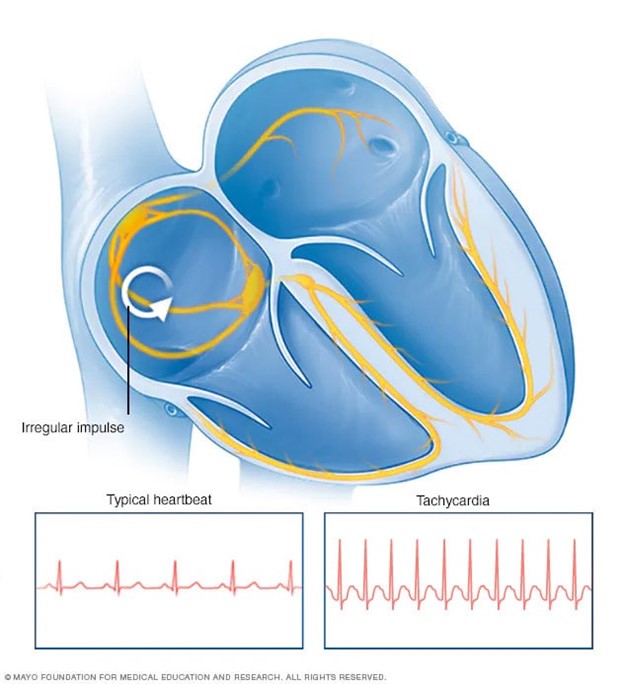
Choice C rationale:
Hypertension - Dehydration typically leads to decreased blood volume, which in turn results in decreased blood pressure. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is not a common finding in dehydration. Instead, low blood pressure (hypotension) is more likely.
Choice D rationale:
Decreased respiratory rate - Dehydration primarily affects the cardiovascular system, leading to reduced blood volume and subsequent compensatory mechanisms such as increased heart rate. The respiratory rate is not directly influenced by dehydration, so a decreased respiratory rate would not be a typical finding.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Caramel popcorn is not an appropriate choice for toddlers due to its high sugar content and potential choking hazard from hard or sticky pieces.
Choice B rationale:
Cooked spaghetti with sauce is an appropriate choice for toddlers. It provides carbohydrates for energy, and the sauce can contain vegetables and proteins, making it a balanced option.
Choice C rationale:
Steak cut into small pieces might not be suitable for toddlers, as it could be difficult for them to chew and may not provide the appropriate texture for their developing teeth.
Choice D rationale:
Hot dogs cut into fourths may pose a choking hazard for toddlers due to their cylindrical shape and potential difficulty in chewing. They are also processed meats, which are not the healthiest option for young children.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
