A nurse is planning care for a client who has diverticulitis. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following complications of diverticulitis?
Ulcerative colitis
Dysphagia
Peritonitis
Crohn's disease
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: Ulcerative colitis is not a complication of diverticulitis. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes ulcers and inflammation in the colon and rectum. Diverticulitis is an acute condition that occurs when small pouches called diverticula in the colon become infected or inflamed.
Choice B reason: Dysphagia is not a complication of diverticulitis. Dysphagia is a term for difficulty swallowing, which can have many causes, such as stroke, nerve damage, or esophageal cancer. Diverticulitis affects the lower part of the digestive tract, not the upper part.
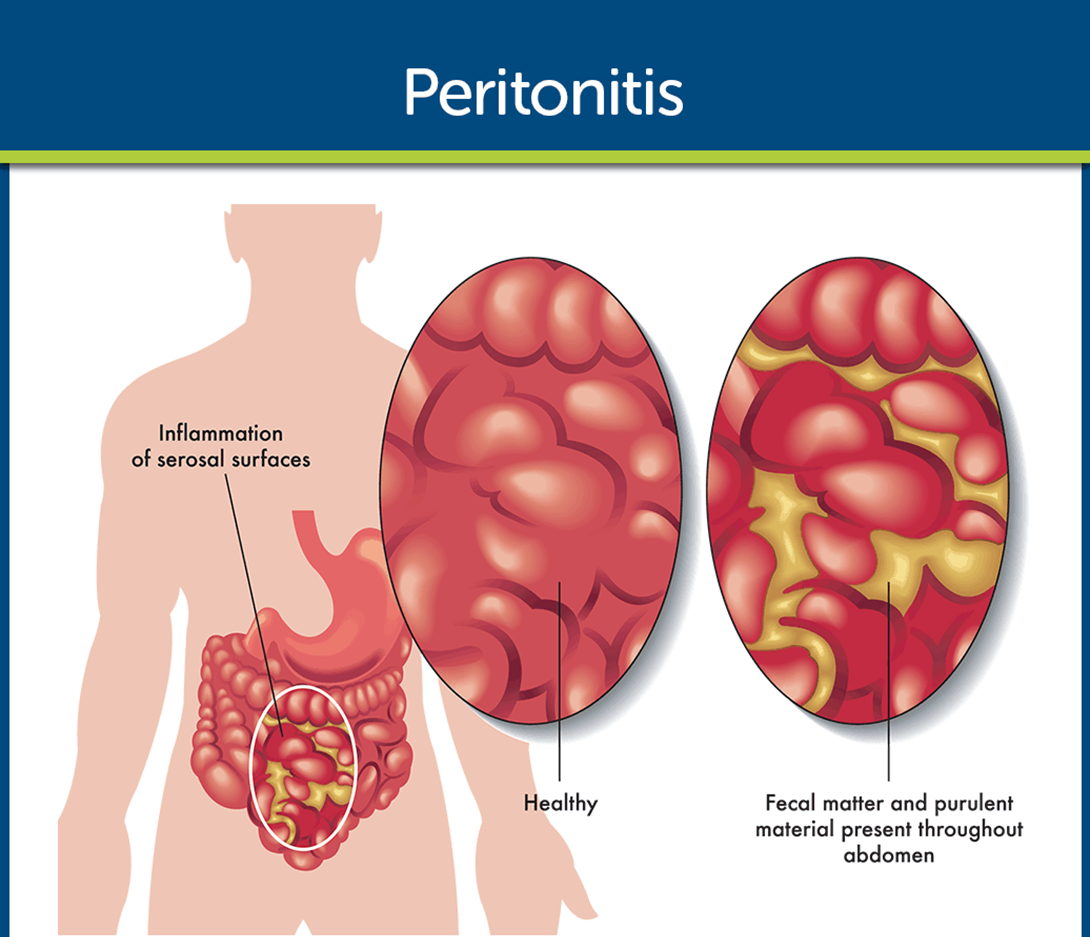
Choice C reason: Peritonitis is a complication of diverticulitis. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It can be caused by a perforation or rupture of a diverticulum, which allows bacteria and fecal matter to enter the peritoneal space. Peritonitis is a serious and life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Choice D reason: Crohn's disease is not a complication of diverticulitis. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that can affect any part of the digestive tract, causing ulcers, fistulas, and strictures. Diverticulitis is an acute condition that affects only the colon, not the entire digestive tract.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: Active transport is the process of moving molecules across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient, requiring energy.
Choice B reason: Diffusion is the process of moving molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, without using energy.
Choice C reason: Filtration is the process of moving fluid and solutes through a membrane by a pressure gradient.
Choice D reason: Osmosis is the process of moving water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: Fried cheese is a food that the nurse will question on the tray for a client with acute gallbladder inflammation. Fried cheese is high in fat, which can trigger or worsen the symptoms of gallbladder disease. Fat can stimulate the contraction of the gallbladder, which can cause pain and inflammation if there are gallstones blocking the bile ducts.
Choice B reason: Green beans are not a food that the nurse will question on the tray for a client with acute gallbladder inflammation. Green beans are low in fat and high in fiber, which can help prevent or reduce the symptoms of gallbladder disease. Fiber can help lower the cholesterol levels in the bile, which can reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
Choice C reason: Grilled chicken breast is not a food that the nurse will question on the tray for a client with acute gallbladder inflammation. Grilled chicken breast is a lean protein source, which can provide essential amino acids for the client's health. Protein can also help maintain the muscle mass and strength of the client, who may have reduced appetite and weight loss due to gallbladder disease.
Choice D reason: Whole grain dinner roll is not a food that the nurse will question on the tray for a client with acute gallbladder inflammation. Whole grain dinner roll is a complex carbohydrate source, which can provide energy and fiber for the client. Carbohydrates can also help balance the acid-base status of the client, who may have metabolic acidosis due to impaired bile secretion and digestion.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
