A nurse is preparing to administer medications to a client and discovers a medication error. The nurse should recognize that which of the following staff members is responsible for completing an incident report?
The nurse who identifies the error
The quality Improvement committee
The charge nurse
The nurse who caused the error
The Correct Answer is A
A. The nurse who identifies the error:
This choice is correct. When a medication error is identified, the nurse who discovers the error is responsible for completing an incident report. Incident reports are a formal way to document any unexpected or adverse events that occur in a healthcare setting, including medication errors. The report helps track incidents, analyze their causes, and implement preventive measures. It's important for the reporting nurse to provide accurate and detailed information about the error.
B. The Quality Improvement Committee:
This choice is incorrect. While the Quality Improvement (QI) Committee plays a role in analyzing trends, identifying areas for improvement, and developing strategies to enhance patient care quality, they are not typically responsible for completing individual incident reports. The responsibility for reporting and documenting a specific incident, such as a medication error, lies with the staff members directly involved.
C. The charge nurse:
This choice is incorrect. The charge nurse is responsible for overseeing the nursing unit's operations, including staffing and patient care coordination. While the charge nurse may be involved in addressing the situation and ensuring appropriate actions are taken following a medication error, they are not necessarily responsible for completing the incident report. The reporting responsibility usually falls on the nurse who identifies the error.
D. The nurse who caused the error:
This choice is incorrect. While it's important for the nurse who caused the error to communicate the error to appropriate parties and participate in any necessary corrective actions, the primary responsibility for completing the incident report usually lies with the nurse who identifies the error. The reporting nurse's perspective is crucial for understanding the context and details of the error.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Warmer skin:
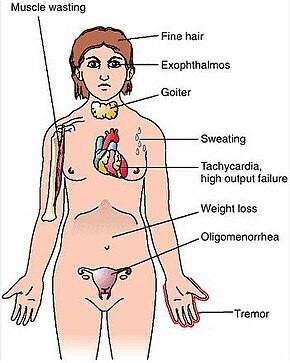
Correct Answer: This is an expected effect after taking methimazole for 2 months.
Explanation: Hyperthyroidism, including Graves' disease, can lead to an overactive metabolism, which can cause the person to feel unusually warm. Methimazole helps reduce the production of thyroid hormones, which can lead to a decrease in the metabolic rate and result in the client feeling less warm.
B. Increased sleeping:
Correct Explanation: This is an expected effect after taking methimazole for 2 months.
Explanation: Hyperthyroidism can cause insomnia or difficulty sleeping due to the increased metabolic rate and heightened levels of thyroid hormones. As methimazole helps normalize thyroid hormone levels, improved sleep patterns can be observed in clients with Graves' disease.
C. Increase in pulse rate:
Incorrect Explanation: An increase in pulse rate is not the expected effect after taking methimazole for 2 months.
Explanation: Hyperthyroidism can lead to an elevated resting heart rate due to increased thyroid hormone levels stimulating the cardiovascular system. Methimazole is used to help bring thyroid hormone levels back to normal, which should lead to a reduction in the pulse rate over time.
D. Weight loss:
Correct Explanation: This is an expected effect after taking methimazole for 2 months.
Explanation: Weight loss is a common symptom of hyperthyroidism due to the increased metabolic rate. Methimazole helps lower thyroid hormone levels, which can result in a decreased metabolic rate and gradual weight stabilization.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. For assessing pain in a 4-year-old child following an orthopedic procedure, the nurse should use the FACES pain scale.
The FACES pain scale uses a series of faces with varying expressions, from smiling to crying, to help children express their level of pain. Children are asked to point to the face that best matches how they feel. This scale is particularly useful for young children who may not have the verbal skills to describe their pain accurately using words or numbers.
B. Word-graphic
Explanation: The word-graphic pain scale typically uses a combination of words and drawings to assess pain, making it more suitable for children who are slightly older and can understand simple words and concepts.
C. Numeric
Explanation: The numeric pain scale involves asking the child to rate their pain on a scale from 0 to 10. This scale is more appropriate for older children who can understand and assign numerical values to their pain intensity.
D. CRIES
Explanation: The CRIES pain scale is often used for assessing pain in newborns and infants up to 6 months old. It focuses on crying, oxygen saturation, vital signs, and facial expressions.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
