A nurse is providing care for an older adult client who has diabetes insipidus (DI). The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following neurological effects?
Hypotension
Poor skin turgor
Ataxia
Dilute urine
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: Hypotension
Hypotension, or low blood pressure, can be a consequence of dehydration, which is a common complication of DI due to the excessive loss of water. However, hypotension is not a direct neurological effect of DI. It is more of a circulatory system response to the changes in fluid volume within the body.
Choice B reason: Poor skin turgor
Poor skin turgor is an indicator of dehydration, which can occur in DI due to the large volume of urine excreted. Skin turgor refers to the skin's ability to change shape and return to normal (elasticity), and it becomes less elastic when the body is dehydrated. While this is an important sign to monitor, it is not a neurological effect.
Choice C reason: Ataxia
Ataxia, which is a lack of muscle coordination affecting speech, eye movements, the ability to swallow, walking, picking up objects, and other voluntary movements, can be a neurological effect of DI if severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance affect the brain. Symptoms such as confusion and muscle cramps can also be associated with ataxia, making it a relevant neurological effect to monitor in a client with DI.
Choice D reason: Dilute urine
Dilute urine is a primary symptom of DI, not a neurological effect. It is the result of the kidneys' inability to concentrate urine due to a deficiency in the anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) or the kidneys' response to ADH. Monitoring urine concentration is crucial in managing DI, but it does not represent a neurological effect.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:
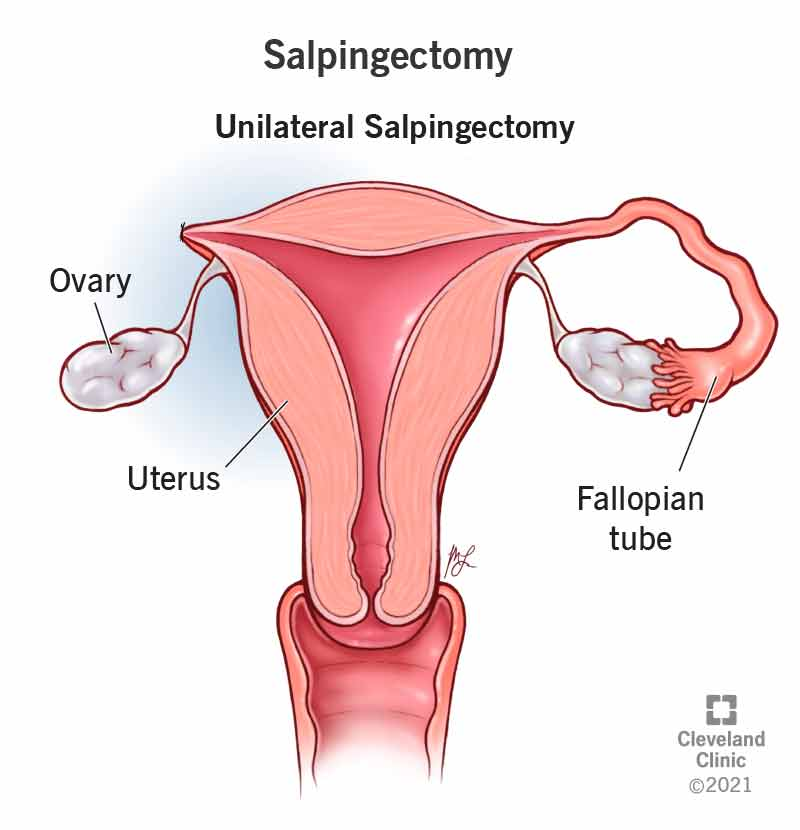
Cosmetic surgery is performed to improve the appearance of a body part. It is elective and usually not medically necessary. In the case of fallopian tube removal due to endometriosis, the surgery is not performed for aesthetic reasons but to relieve pain and treat a medical condition.
Choice B reason:
Diagnostic surgery is carried out to diagnose a condition. While endometriosis can be diagnosed through surgery, the removal of the fallopian tube in this scenario is not for diagnostic purposes but rather for treatment.
Choice C reason:
Constructive surgery is done to restore function or normal appearance by reconstructing defective organs or body parts. The removal of the fallopian tube for endometriosis does not fit this category as it does not aim to reconstruct but rather to remove a part causing pain.
Choice D reason:
Ablative surgery involves the removal of an organ or abnormal growth. It is often used to treat conditions that cause pain or to prevent further complications. The removal of the fallopian tube due to severe endometriosis falls under this category as it aims to alleviate symptoms and prevent further issues related to the condition.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: Effective hand hygiene is the most important measure to prevent the transmission of hepatitis A, as the virus can be spread through close personal contact and by eating food or drinking water handled by someone who is infected¹. Handwashing with soap and water after using the bathroom, changing diapers, and before preparing or eating food is crucial.
Choice B reason: While avoiding raw foods can help prevent the transmission of various foodborne illnesses, hepatitis A is not commonly associated with raw foods unless they are contaminated during handling after cooking. However, it is still a good practice to avoid raw or undercooked foods in areas where hepatitis A is common.
Choice C reason:
Hepatitis A virus is primarily transmitted via the fecal-oral route, not through sexual contact. However, barrier protection can reduce the risk of transmission for many other infections, including other types of viral hepatitis that are sexually transmitted.
Choice D reason:
Eating at fast food restaurants is not inherently risky for hepatitis A transmission unless the food or water is contaminated. It is more important to ensure that all food is properly handled and cooked, regardless of the dining establishment.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
