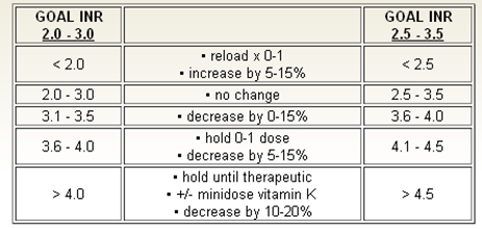
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who has atrial fibrillation and a prescription for warfarin. After informing the provider that the INR is 2.5, the nurse should expect which of the following prescriptions?
Decrease the dose of the medication.
Increase the dose of the medication.
Withhold the medication.
Administer the current dose of the medication.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason:
Decrease the dose of the medication is incorrect. Lowering the dose could potentially drop the INR below the therapeutic range, increasing the risk of clot formation.
Choice B Reason:
Increase the dose of the medication is incorrect. Raising the dose might push the INR above the therapeutic range, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Choice C Reason:
Withhold the medication is incorrect. Withholding the medication might lead to inadequate anticoagulation and an increased risk of clot formation.
Choice D Reason:
Administer the current dose of the medication. An INR of 2.5 is within the therapeutic range for many indications, including atrial fibrillation. This means the blood is appropriately anticoagulated to prevent clot formation without an excessive risk of bleeding. In this scenario, maintaining the current dose of warfarin is often appropriate to sustain the desired therapeutic effect.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
BUN 15 mg/dL (blood urea nitrogen) is incorrect. An elevated BUN level can indicate kidney dysfunction or dehydration, but it's not typically associated with azathioprine's adverse effects. Azathioprine is known to affect bone marrow, leading to decreased blood cell counts, rather than directly impacting kidney function.
Choice B Reason:
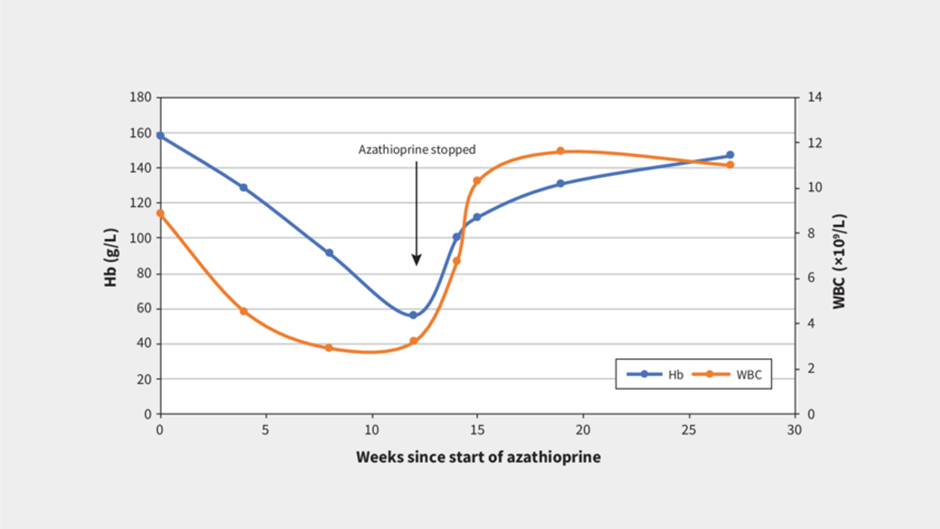
WBC 3,000/mm³ (low white blood cell count) is correct. Azathioprine is an immunosuppressive medication used to treat various conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis. One of its known adverse effects is bone marrow suppression, which can lead to decreased production of blood cells, including white blood cells (WBCs). A low WBC count (leukopenia) can increase the risk of infections due to compromised immune function, making it an important adverse effect to monitor in individuals taking azathioprine.
Choice C Reason:
Hct 45% (hematocrit) is incorrect. A hematocrit of 45% is within the normal range for both men and women. Azathioprine adverse effects usually manifest as blood cell-related issues (such as leukopenia) rather than directly impacting hematocrit levels.
Choice D Reason:
Platelets 250,000/mm³: Platelets within the range of 150,000 to 400,000/mm³ are considered normal. Azathioprine typically affects white blood cells more prominently than platelet counts.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Hypomagnesemia is incorrect. Lithium therapy itself is not a direct cause of hypomagnesemia. While exercise can affect magnesium levels to some extent, it's not a primary electrolyte imbalance that is typically associated with lithium use or considered a significant concern specifically due to lithium.
Choice B Reason:
Hypocalcemia is incorrect. Similarly, lithium therapy is not a direct cause of hypocalcemia. Exercise can affect calcium metabolism, but it's not a primary electrolyte imbalance typically associated with lithium use or considered a significant concern specifically due to lithium.
When a client taking lithium begins a new exercise program, the nurse should primarily assess for the risk of:
Choice C Reason:
Hyponatremia is correct. Lithium can affect the body's regulation of sodium, and excessive sweating due to increased exercise can lead to sodium loss. This combination can potentially contribute to the development of hyponatremia (low sodium levels). Therefore, when a client on lithium starts a new exercise regimen that may induce sweating, monitoring for signs of hyponatremia becomes crucial. Symptoms of hyponatremia can include confusion, headaches, nausea, and in severe cases, seizures or coma.
Choice D Reason:
Hypokalemia is incorrect. Lithium itself does not commonly cause hypokalemia. Exercise can lead to potassium loss through sweating, but hypokalemia is not the primary electrolyte imbalance typically associated with lithium use or considered a significant concern specifically due to lithium.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
