A patient suspected of having a severe medication reaction goes into shock. Which of the following first aid measures should the phlebotomist take?
Keep the patient as upright as possible.
Provide a cooling blanket.
Administer oral fluids.
Maintain an open airway.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason:
Keeping the patient as upright as possible is not recommended in cases of shock. When a patient is in shock, it is important to lay them down and elevate their legs slightly, unless this position causes pain or further injury. This position helps improve blood flow to the brain.
Choice B Reason:
Providing a cooling blanket is not a standard first aid measure for shock due to a medication reaction. A cooling blanket may be used in cases of hyperthermia or heatstroke to reduce body temperature, but not typically for shock, which requires maintaining normal body temperature and preventing chilling.
Choice C Reason:
Administering oral fluids to a patient in shock is not advisable. During shock, a patient may have an impaired swallowing reflex or be unconscious, increasing the risk of aspiration. It is best to avoid giving anything by mouth until medical personnel arrive.
Choice D Reason:
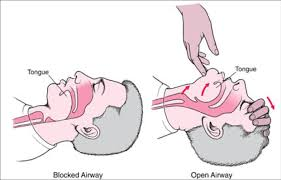
Maintaining an open airway is crucial for a patient in shock. Ensuring that the airway is clear allows the patient to breathe effectively, which is essential for delivering oxygen to the tissues and organs. If the patient is unconscious or has an altered level of consciousness, the phlebotomist should check for breathing and begin CPR if necessary.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
A patient's room number is not considered a unique identifier by the Joint Commission standards. Room numbers can change if patients are moved, and they do not reliably identify an individual.
Choice B Reason:
A patient's bed label is also not a unique identifier. Bed labels can be switched, and similar to room numbers, they are not specific to the individual patient.
Choice C Reason:
A patient's inpatient chart typically contains multiple unique identifiers, such as the patient's name, an assigned identification number, date of birth, or other person-specific identifiers. These are considered acceptable by the Joint Commission for verifying patient identity, ensuring that the service or treatment is intended for that individual.
Choice D Reason:
Patient's verbal confirmation alone is not sufficient for establishing correct inpatient identification. While it can be used as one method of identification, it should be supplemented with another identifier to meet the Joint Commission's requirement of using at least two patient identifiers.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
The red top tube is typically used for serum determinations in chemistry, serology, and blood bank. It contains no additive or may contain a clot activator. The red top tube is not the first choice for capillary puncture order of draw because it is designed for tests that require serum and not whole blood.
Choice B Reason:
The lavender top tube is used for whole blood hematology determinations, as it contains EDTA as an anticoagulant. According to the order of draw for capillary punctures, the EDTA tube should be collected first to ensure adequate volume and accurate hematology test results. This makes the lavender top tube the correct choice for the first collection in this scenario.
Choice C Reason:
The light blue top tube contains sodium citrate and is used for coagulation tests. In venipuncture, it is drawn after the blood culture bottle and before other tubes to prevent contamination with additives from other tubes. However, for capillary punctures, it is not the first choice as hematology tests take precedence.
Choice D Reason:
The royal blue top tube is used for trace element, toxicology, and nutrient determinations². While it may be used for lead and toxicology screens mentioned in the question, it is not the first tube to be drawn in a capillary puncture sequence. The EDTA tube (lavender top) is drawn first to prevent clotting and ensure accurate CBC results.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
