An older adult client returned to the nursing home after a lower limb amputation. The client is scheduled for a prosthesis fitting and states, “I am too old to learn how to manage this.” Which of the following responses from the nurse is appropriate?
I will call your provider so we can discuss it.
What are you thinking that you would like to do?
You have the right to refuse if you don’t think you can do this.
Many clients your age are able to adjust surprisingly well to a prosthesis.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason: I will call your provider so we can discuss it
While this response shows the nurse’s willingness to involve the healthcare provider, it does not directly address the client’s concern about their ability to manage the prosthesis. It is important to provide immediate reassurance and encouragement to the client, which this response lacks.
Choice B Reason: What are you thinking that you would like to do?
This response is open-ended and encourages the client to express their feelings and thoughts. While it is a good approach to understand the client’s perspective, it does not provide the immediate reassurance and encouragement that the client needs to feel confident about managing the prosthesis.
Choice C Reason: You have the right to refuse if you don’t think you can do this
This response acknowledges the client’s autonomy but may inadvertently reinforce their doubts and fears about managing the prosthesis. It is important to encourage and support the client rather than focusing on their right to refuse.
Choice D Reason: Many clients your age are able to adjust surprisingly well to a prosthesis
This response is the most appropriate as it provides reassurance and encouragement to the client. By sharing that many clients of a similar age have successfully adjusted to a prosthesis, the nurse helps to build the client’s confidence and reduce their anxiety about managing the new situation. This positive reinforcement can be very motivating for the client.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D"]
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Rubeola, also known as measles, is highly contagious and spreads through airborne transmission. The virus can remain infectious in the air for up to two hours after an infected person coughs or sneezes. This makes it one of the most easily spread diseases through airborne particles.
Choice B Reason:
Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is primarily transmitted through the fecal-oral route, not through airborne transmission. It spreads via spores that can survive on surfaces and be ingested, leading to infection.
Choice C Reason:
Varicella, or chickenpox, is transmitted through airborne particles. The virus can spread through direct contact with the fluid from the blisters or through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. This makes it an airborne disease.
Choice D Reason:
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, speaks, or sings. The bacteria can remain suspended in the air for several hours, making TB an airborne disease.
Choice E Reason:
Staphylococcus aureus is not typically transmitted through airborne means. It spreads through direct contact with infected wounds, contaminated surfaces, or through respiratory droplets in some cases. However, it is not considered an airborne disease.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
There is a causal link between lying down after eating and the increased onset of GERD. Lying down can cause stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, exacerbating GERD symptoms.
Choice B Reason:
Taking aspirin with GERD is not recommended. Aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can irritate the stomach lining and worsen GERD symptoms.
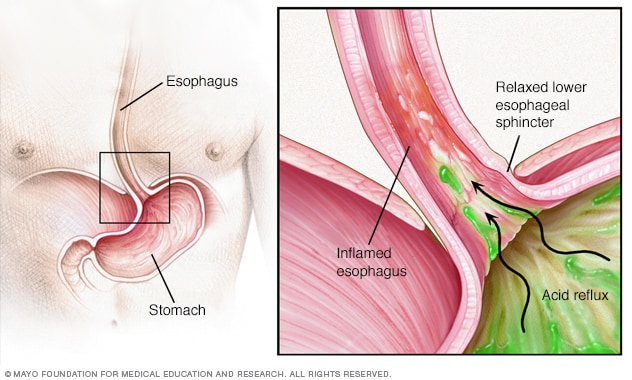
Choice C Reason:
This is the correct answer. Alcohol and caffeine can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus and aggravate GERD symptoms.
Choice D Reason:
There is no evidence to suggest that mercury-containing foods, such as some seafood, are linked to GERD. The primary dietary concerns for GERD involve foods and beverages that can relax the lower esophageal sphincter or increase stomach acid production.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
