At the beginning of your shift, you start your rounds on your patients. Upon entering this patient’s room, you observe that the cardiac monitor shows sinus tachycardia, is apneic and no pulses are palpable by the nurse.
What is the first action that the nurse should take?
Administer the prescribed Beta-Blocker
Prepare for Cardioversion per hospital protocol.
Give 100% oxygen per non-rebreather mask.
Start CPR
The Correct Answer is D
The absence of palpable pulses suggests a lack of effective cardiac output, and the patient is in cardiac arrest. In this situation, immediate initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is crucial to maintain circulation and provide oxygenation to vital organs.
CPR consists of chest compressions and rescue breaths to circulate oxygenated blood to the brain and other vital organs. It is the primary intervention in cardiac arrest to provide temporary life support until advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) measures, such as defibrillation or medication administration, can be initiated.
A. Administering the prescribed Beta-Blocker in (option A) is incorrect because Administering a beta-blocker is not the initial action in a patient who is in cardiac arrest and requires immediate resuscitation.
B. Prepare for Cardioversion per hospital protocol (option B) is incorrect because Cardioversion, which is the delivery of an electric shock to the heart, may be considered in certain situations like unstable ventricular tachycardia or certain supraventricular tachycardias. However, in the given scenario, the patient is unresponsive and has no pulses, indicating cardiac arrest where CPR takes precedence over cardioversion.
C. Give 100% oxygen per non-rebreather mask in (option C) is incorrect because: While oxygenation is important, it should not delay or replace the initiation of CPR, which is the immediate priority in a patient without palpable pulses.
Therefore, the first action that the nurse should take in this scenario is to start CPR.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D","E"]
Explanation
These manifestations occur as compensatory mechanisms in response to decreased blood volume and compromised tissue perfusion. The body attempts to compensate for the inadequate circulating volume by increasing heart rate (A) and respiratory rate (B) to enhance oxygen delivery.
D. The decreased systolic blood pressure (D) is a result of decreased cardiac output and vasoconstriction in an attempt to maintain perfusion to vital organs.
E. The decreased urine output (E) is a result of decreased renal perfusion due to decreased blood volume.
C. Decreased pulse rate in (option C) is incorrect because it is not typically seen in the compensatory stage of hypovolemic shock. The body tries to increase heart rate to maintain cardiac output and compensate for the decreased blood volume.
F. Bilateral crackles in (option F) is incorrect because the lung bases are more commonly associated with conditions such as pulmonary edema or fluid overload, rather than the compensatory stage of hypovolemic shock.
It's important to note that the manifestations of shock can vary depending on individual patient factors and the underlying cause of shock. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment and clinical judgment are necessary to fully evaluate the patient's condition.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
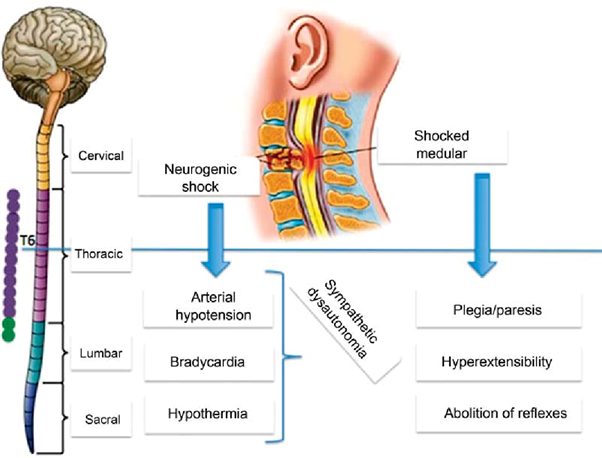
Neurogenic shock is a type of distributive shock that occurs due to the loss of sympathetic nervous system tone after a spinal cord injury or other traumatic brain injuries. This loss of sympathetic tone leads to vasodilation and decreased systemic vascular resistance, resulting in inadequate perfusion to vital organs.
One of the hallmark signs of neurogenic shock is bradycardia (a heart rate less than 60 beats/min) due to the unopposed parasympathetic activity. The parasympathetic system becomes dominant when sympathetic activity is impaired. Therefore, a heart rate of 48 beats/min in this patient suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock.
A. Cool, clammy skin in (option A) is incorrect because Cool, clammy skin is a characteristic of hypovolemic shock, where reduced blood volume leads to vasoconstriction to redirect blood flow to vital organs.
B. BP of 82/40 mm Hg in (option B) is incorrect because: Hypotension is a common finding in both neurogenic shock and hypovolemic shock. A low blood pressure reading alone does not specifically indicate neurogenic shock.
D. Shortness of breath in (option D) is incorrect because Shortness of breath is not specific to neurogenic shock but can occur in various types of shock, including hypovolemic shock. It may result from inadequate oxygenation or impaired respiratory function due to the underlying condition or associated injuries.
Therefore, the heart rate of 48 beats/min suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock in addition to hypovolemic shock in this patient.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
