The surgical ICU nurse is caring for postoperative clients at risk for hypovolemic shock. Which condition represents an early symptom of shock?
Tachypnoea
Heart blocks
Vomiting
Bradycardia
Hypotension
The Correct Answer is A
Tachypnoea, which refers to an increased respiratory rate, is an early symptom of hypovolemic shock. It is the body's compensatory response to inadequate tissue perfusion and decreased oxygen delivery. The increased respiratory rate is an attempt to improve oxygenation and maintain vital organ function.
B. Heart blocks in (option B) are incorrect because Heart blocks refer to disruptions in the electrical conduction system of the heart and are not specific to hypovolemic shock.
C. Vomiting in (option C) is incorrect because: Vomiting may occur in various conditions, including shock, but it is not exclusive to hypovolemic shock and can be present in other forms of shock or illnesses.
D. Bradycardia in (option D) is incorrect because Bradycardia, or a slow heart rate, is not typically an early symptom of hypovolemic shock. Instead, tachycardia (rapid heart rate) is more commonly observed as a compensatory response to maintain cardiac output.
E. Hypotension in (option E) is incorrect because Hypotension, or low blood pressure, can occur in hypovolemic shock but is generally considered a later-stage symptom. In the early stages, compensatory mechanisms may help maintain blood pressure, so hypotension may not be present initially.
F. Bradypnea in (option F) is incorrect because: Bradypnea refers to a slow respiratory rate, which is not typically an early symptom of hypovolemic shock. Tachypnoea, as mentioned earlier, is the more common early respiratory symptom.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D","E"]
Explanation
These manifestations occur as compensatory mechanisms in response to decreased blood volume and compromised tissue perfusion. The body attempts to compensate for the inadequate circulating volume by increasing heart rate (A) and respiratory rate (B) to enhance oxygen delivery.
D. The decreased systolic blood pressure (D) is a result of decreased cardiac output and vasoconstriction in an attempt to maintain perfusion to vital organs.
E. The decreased urine output (E) is a result of decreased renal perfusion due to decreased blood volume.
C. Decreased pulse rate in (option C) is incorrect because it is not typically seen in the compensatory stage of hypovolemic shock. The body tries to increase heart rate to maintain cardiac output and compensate for the decreased blood volume.
F. Bilateral crackles in (option F) is incorrect because the lung bases are more commonly associated with conditions such as pulmonary edema or fluid overload, rather than the compensatory stage of hypovolemic shock.
It's important to note that the manifestations of shock can vary depending on individual patient factors and the underlying cause of shock. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment and clinical judgment are necessary to fully evaluate the patient's condition.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
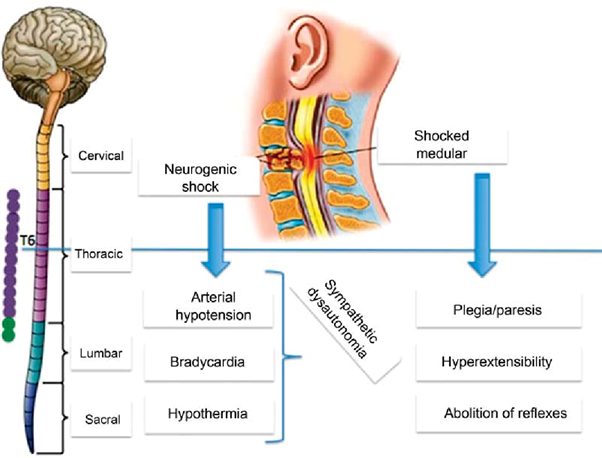
Neurogenic shock is a type of distributive shock that occurs due to the loss of sympathetic nervous system tone after a spinal cord injury or other traumatic brain injuries. This loss of sympathetic tone leads to vasodilation and decreased systemic vascular resistance, resulting in inadequate perfusion to vital organs.
One of the hallmark signs of neurogenic shock is bradycardia (a heart rate less than 60 beats/min) due to the unopposed parasympathetic activity. The parasympathetic system becomes dominant when sympathetic activity is impaired. Therefore, a heart rate of 48 beats/min in this patient suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock.
A. Cool, clammy skin in (option A) is incorrect because Cool, clammy skin is a characteristic of hypovolemic shock, where reduced blood volume leads to vasoconstriction to redirect blood flow to vital organs.
B. BP of 82/40 mm Hg in (option B) is incorrect because: Hypotension is a common finding in both neurogenic shock and hypovolemic shock. A low blood pressure reading alone does not specifically indicate neurogenic shock.
D. Shortness of breath in (option D) is incorrect because Shortness of breath is not specific to neurogenic shock but can occur in various types of shock, including hypovolemic shock. It may result from inadequate oxygenation or impaired respiratory function due to the underlying condition or associated injuries.
Therefore, the heart rate of 48 beats/min suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock in addition to hypovolemic shock in this patient.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
