During a clinic visit 3 months following a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, the patient reports following a reduced-calorie diet. The patient has not lost any weight and did not bring the glucose-monitoring record. The nurse will plan to obtain a(n)
fasting blood glucose level.
oral glucose tolerance test.
urine dipstick for glucose.
glycosylated hemoglobin level.
The Correct Answer is D
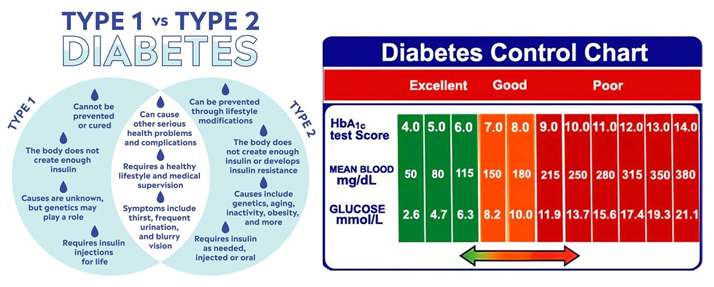
The patient has been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and reports following a reduced-calorie diet but has not lost any weight. This suggests that the patient may not be following the diet as prescribed or may have other factors affecting their blood glucose levels. Additionally, the patient did not bring their glucose monitoring record, which is an important tool for assessing blood glucose control over time.
In this situation, obtaining a fasting blood glucose level or an oral glucose tolerance test may provide a snapshot of the patient's blood glucose level at the time of the test, but these tests do not provide information about blood glucose control over the past few months. A urine dipstick for glucose is a less reliable method for assessing blood glucose control and is not recommended for routine monitoring.
Therefore, obtaining a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level is the most appropriate test in this situation. HbA1c reflects the average blood glucose level over the past 2-3 months and is recommended for routine monitoring of blood glucose control in patients with diabetes. This test can provide valuable information about the effectiveness of the patient's diet and any other interventions aimed at controlling their blood glucose levels.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
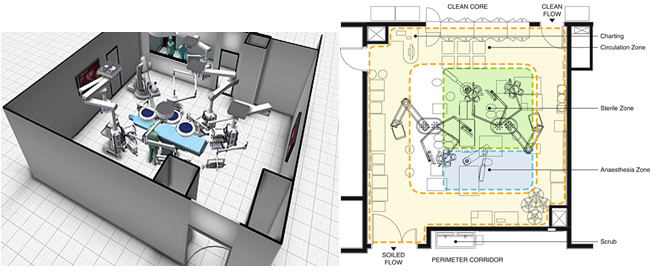
The operating room is a sterile environment, and it is critical to maintain a clean and controlled environment to reduce the risk of infection to the patient. The measures taken include maintaining positive air pressure, controlling temperature and humidity, filtering the air, using sterile surgical instruments, and limiting traffic in and out of the operating room. These measures help to prevent the spread of infectious agents that may be present in the operating room. While the other options (a, b, and d) may also be important considerations in the design of the operating room, preventing transmission of infection is the primary goal.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
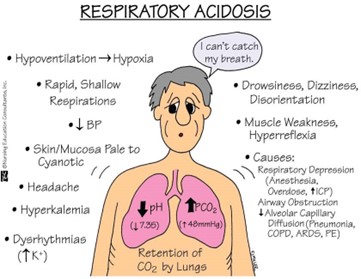
The pH value is less than the normal range of 7.35-7.45, indicating acidosis. The PaCO2 value is elevated above the normal range of 35-45 mmHg, indicating respiratory acidosis. The PaO2 value is lower than normal, but not significantly low enough to indicate hypoxemia. The HCO3- level is within the normal range, but not significantly high enough to indicate metabolic compensation for respiratory acidosis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.