In an ECG pattern, the P wave is caused by:
Repolarization of atrial muscle fibers.
Depolarization of atrial muscle fibers.
Depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers.
Repolarization of ventricular muscle fibers.
The Correct Answer is B
This means that the electrical activity that causes the atria to contract starts from the sinoatrial node and spreads across the atria.
The P wave on the ECG reflects this atrial depolarization.
Choice A is wrong because repolarization of atrial muscle fibers is not visible on the ECG, as it occurs during the QRS complex when the ventricular depolarization masks it.
Choice C is wrong because the depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers is represented by the QRS complex on the ECG, not the P wave.
Choice D is wrong because the repolarization of ventricular muscle fibers is represented by the T wave on the ECG, not the P wave.
Normal ranges for the P wave are:
Duration: less than 0.12 seconds (less than 3 small squares)
Amplitude: less than 2.5 mm (0.25 mV) in the limb leads, less than 1.5 mm (0.15 mV) in the precordial leads
Axis: between 0° and +75°12
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The right atrium receives blood directly from the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus.
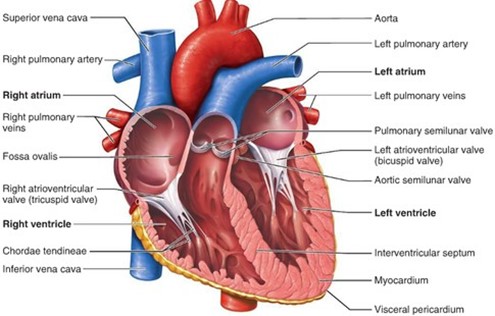
The superior vena cava and inferior vena cava bring deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower body, respectively.
The coronary sinus brings blood from the heart muscle.
Choice B is wrong because it excludes the coronary sinus, which also empties into the right atrium.
Choice C is wrong because it includes the pulmonary veins, which carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium, not the right atrium.
Choice D is wrong because it only includes the pulmonary veins, which are not connected to the right atrium at all.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The thymus gland is an essential part of the immune system that produces and matures T cells, a type of white blood cell that defends the body from infections.
Thymosins also regulate immune cell production and inhibit aging.
Choice A is wrong because thyroxines are hormones produced by the thyroid gland, not the thymus gland.
Thyroxines control metabolism and affect growth and development.
Choice B is wrong because melatonins are hormones produced by the pineal gland, not the thymus gland.
Melatonins control circadian rhythms and sleep cycles.
Choice D is wrong because prostaglandins are not hormones, but lipid compounds that have hormone-like effects.
Prostaglandins control inflammation, blood pressure, muscle contraction, and other functions.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
