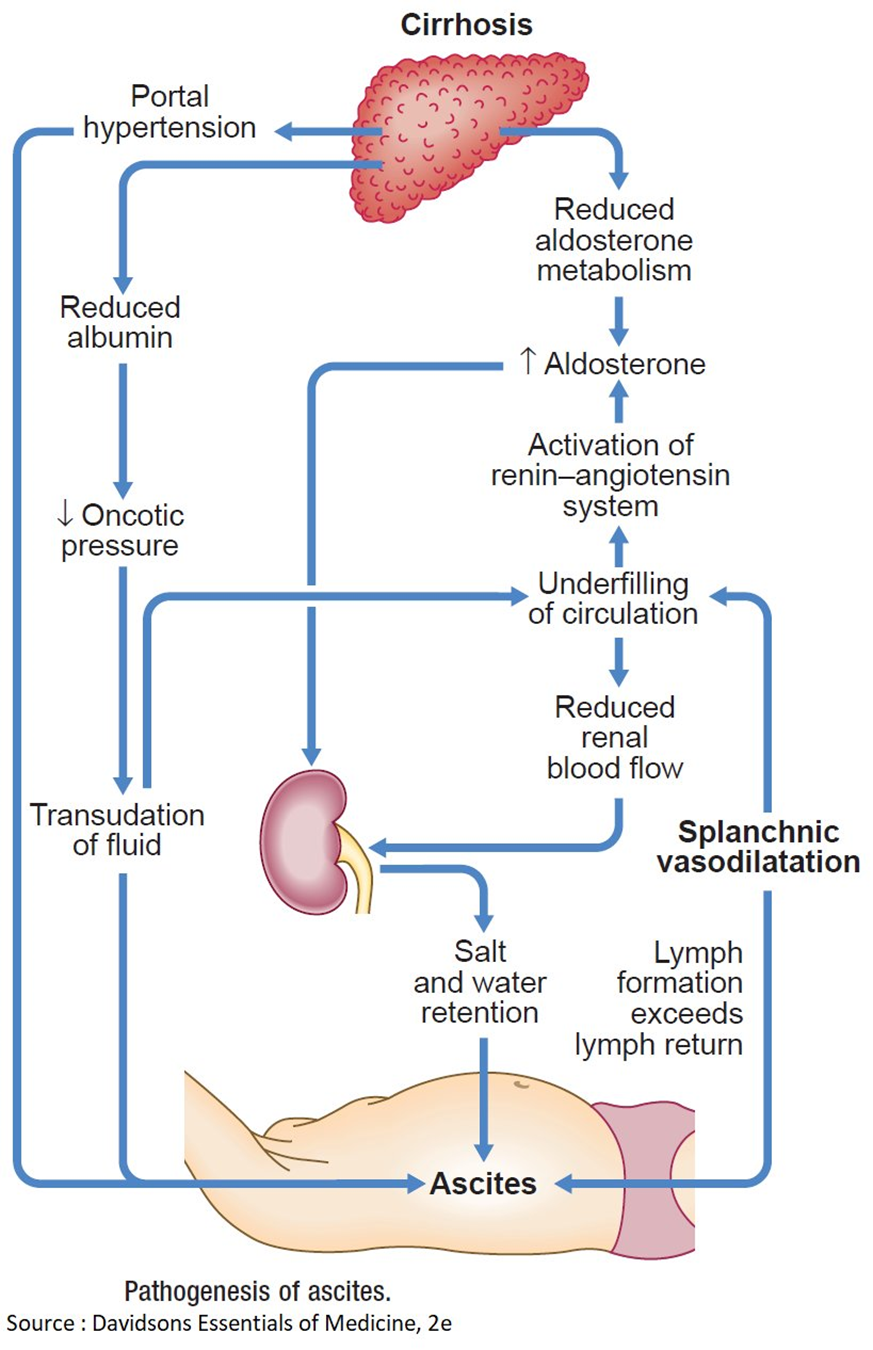
The nurse assesses a client with cirrhosis and finds 4+ pitting edema of the feet and legs, and massive ascites. Which mechanism contributes to edema and ascites in clients with cirrhosis?
Hyperaldosteronism causing an increased sodium reabsorption in renal tubules.
Decreased renin-angiotensin response related to an increase in renal blood flow.
Decreased portacaval pressure with greater collateral circulation.
Hypoalbuminemia that results in a decreased colloidal oncotic pressure
The Correct Answer is D
A. Hyperaldosteronism causing an increased sodium reabsorption in renal tubules.
Hyperaldosteronism is characterized by an excess of aldosterone, a hormone that regulates sodium and water balance. In cirrhosis, however, sodium retention is often related to other mechanisms such as portal hypertension and hypoalbuminemia, rather than hyperaldosteronism.
B. Decreased renin-angiotensin response related to an increase in renal blood flow.
Cirrhosis is more commonly associated with an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, leading to increased sodium and water retention. The increased renin-angiotensin response is a compensatory mechanism to maintain perfusion in the setting of cirrhosis and does not contribute to decreased renal blood flow.
C. Decreased portacaval pressure with greater collateral circulation.
This statement is not accurate. In cirrhosis, there is typically increased portacaval pressure due to portal hypertension, which can lead to the development of collateral circulation. However, this does not explain the edema and ascites seen in cirrhosis.
D. Hypoalbuminemia that results in a decreased colloidal oncotic pressure.
This is the correct choice. In cirrhosis, liver damage leads to decreased synthesis of albumin. Albumin plays a crucial role in maintaining colloidal oncotic pressure, and when it is decreased (hypoalbuminemia), fluid is more likely to leak out of blood vessels, resulting in edema. The same mechanism contributes to the development of ascites in the abdominal cavity.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Discuss approaches to chronic pain control with the client:
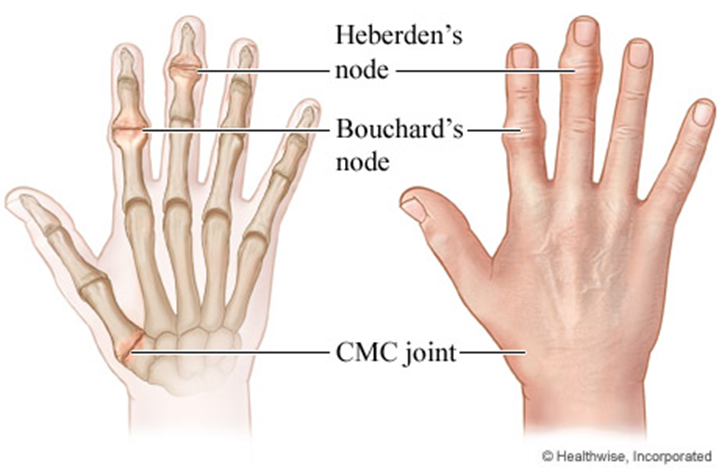
This is the correct answer. Heberden's nodes are bony enlargements that can occur in osteoarthritis, particularly in the joints of the fingers. These nodes can be associated with pain. Discussing approaches to chronic pain control with the client is an appropriate nursing intervention to address the client's pain and improve quality of life.
B. Review the client's dietary intake of high-protein foods:
Dietary intake of high-protein foods is not directly related to the management of Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease. Pain control and joint protection measures are more relevant.
C. Notify the healthcare provider of the finding immediately:
While it's important to communicate significant findings to the healthcare provider, the presence of Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease may not require immediate notification unless there are other concerning symptoms or complications.
D. Assess the client's radial pulses and capillary refill time:
Assessing radial pulses and capillary refill time is not directly related to managing Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease. These nodes are primarily a result of joint changes in osteoarthritis.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
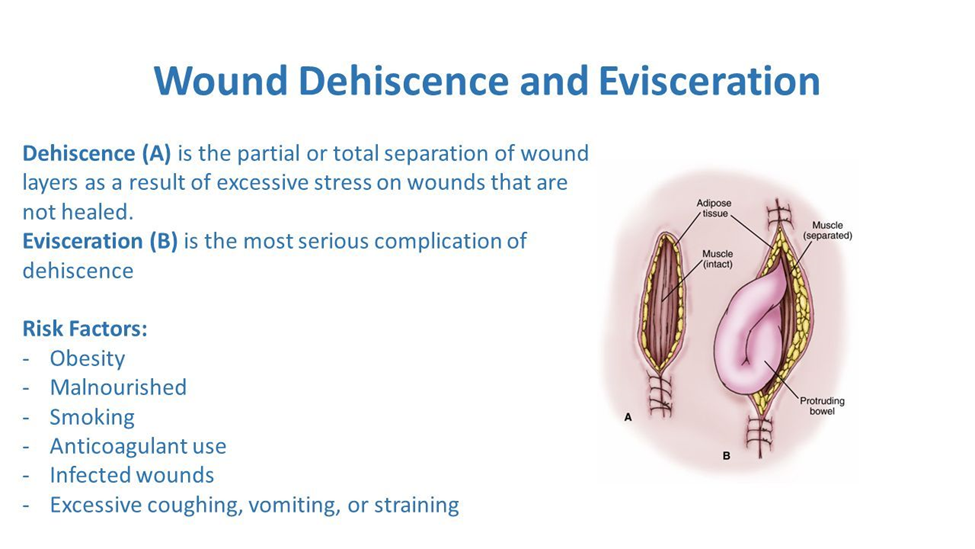
A. Prepare the client to return to the operating room:
This is the correct and immediate priority. Evisceration, where internal organs protrude through the surgical incision, is a surgical emergency. Returning the client to the operating room is necessary to assess the extent of the complication, address the wound dehiscence, and protect the exposed organs. This intervention aims to prevent further complications and provide necessary surgical interventions.
B. Obtain a sample of the drainage to send to the lab:
While obtaining samples for laboratory analysis can be important for infection control, in the context of a client with evisceration, the primary concern is the surgical emergency. The priority is to address the wound complication by returning to the operating room rather than focusing on laboratory analysis at this immediate moment.
C. Bring additional sterile dressing supplies to the room:
While bringing additional supplies may be necessary, the priority in this situation is to prepare for the client's return to the operating room. Once the client is in a controlled surgical environment, additional dressing changes and wound care can be performed as needed.
D. Auscultate the abdomen for bowel sound activity:
While monitoring bowel sounds is a routine nursing assessment, in the context of evisceration, the immediate concern is the exposure of internal organs and the risk of infection. Preparing for the operating room takes precedence over routine assessments.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
