The nurse is performing a physical assessment on the respiratory system. Although the client is currently confined to bed, they have the strength and ability to move and reposition themselves. The nurse instructs the client to assume which position for the assessment?
Sitting upright
Semi-Fowler’s
Supine
Side-lying
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason:
Sitting upright is the best position for a respiratory assessment. This position allows for optimal lung expansion and makes it easier to auscultate breath sounds accurately. It also helps in observing the client’s breathing pattern and effort.
Choice B reason:
Semi-Fowler’s position, where the head of the bed is elevated to 30-45 degrees, is often used for clients with respiratory issues to promote lung expansion and reduce the risk of aspiration. However, it is not as effective as the sitting upright position for a thorough respiratory assessment.
Choice C reason:
The supine position, where the client lies flat on their back, is not ideal for a respiratory assessment. This position can limit lung expansion and make it more difficult to hear breath sounds clearly.
Choice D reason:
The side-lying position is also not suitable for a respiratory assessment. This position can cause uneven lung expansion and make it challenging to assess both lungs accurately.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["0.5"]
Explanation
Step 1: Convert the prescribed dose from mcg to mg.
- 235 mcg ÷ 1000 = 0.235 mg
Step 2: Determine the strength of the available tablet.
- Available strength = 0.5 mg per tablet
Step 3: Calculate the number of tablets needed.
- Number of tablets = 0.235 mg ÷ 0.5 mg/tablet
Step 4: Perform the division.
- 0.235 ÷ 0.5 = 0.47
Step 5: Round the answer to the nearest tenth.
- 0.47 rounded to the nearest tenth = 0.5
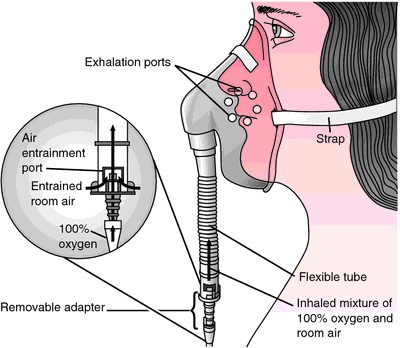
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Reducing rebreathing of exhaled air is not a primary characteristic of a Venturi mask. This feature is more associated with non-rebreather masks, which have a one-way valve to prevent exhaled air from being inhaled again.
Choice B reason:
Delivering high percentages of oxygen at flow rates of 10 to 15 L/min is not specific to Venturi masks. Non-rebreather masks are typically used for high oxygen flow rates. Venturi masks are designed to deliver precise oxygen concentrations at lower flow rates.
Choice C reason:
Providing a precise amount of oxygen is the key characteristic of a Venturi mask. Venturi masks are equipped with color-coded adapters that allow for the delivery of specific oxygen concentrations, regardless of the patient’s breathing pattern.
Choice D reason:
Working independently of client breathing factors and flow of oxygen is not entirely accurate. While Venturi masks do provide a consistent oxygen concentration, they still depend on the flow of oxygen set by the healthcare provider.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
