Which information will the nurse include when teaching the patient with a urinary tract infection (UTI) about the use of phenazopyridine?
Take phenazopyridine for at least 7 days.
Phenazopyridine may change the urine color.
Take phenazopyridine before sexual intercourse.
Phenazopyridine may cause photosensitivity.
The Correct Answer is B
The nurse should explain to the patient that phenazopyridine is a medication that can help relieve the pain, burning, and urgency associated with UTIs. However, it does not treat the underlying infection. The nurse should also instruct the patient to take the medication as prescribed by the healthcare provider and inform them that the medication may turn their urine an orange or red color, which is a harmless and expected side effect.
The nurse should also inform the patient that taking phenazopyridine before sexual intercourse is not recommended and that the medication should be taken as directed by the healthcare provider.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
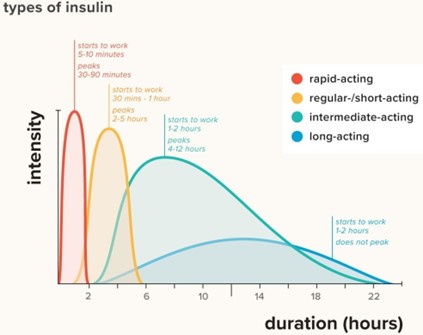
The nurse will discuss using rapid-acting insulin such as Lispro (Humalog) for mealtime coverage in a patient with diabetes who is starting insulin therapy. Rapid-acting insulin begins to work quickly after injection, usually within 15 minutes, and peaks at around 1 hour. This makes it an effective choice for covering the rise in blood sugar that occurs after meals.
Options A, B, and D are all long-acting insulins that are used to provide a basal level of insulin coverage throughout the day but are not appropriate for mealtime coverage.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The patient received 38 U of NPH insulin at 7:00 AM, and by 1:00 PM, the insulin has been active for approximately 6 hours. The patient has missed lunch, which may lead to hypoglycemia, especially with the activity of the insulin.
Sending a glass of orange juice will provide the patient with a quick source of glucose to prevent hypoglycemia. If testing is further delayed, the nurse may request that the patient be allowed to eat lunch first or save the lunch tray for later, but immediate intervention is necessary to prevent hypoglycemia. Discontinuing the evening dose of insulin is not an appropriate action and should not be considered without consulting the healthcare provider.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
