Which of the following interventions is considered a priority when treating a patient who presents with septic shock?
obtaining wound and blood
removing or controlling potentially infected sources
initiation of an intravenous line and fluid
drawing blood for hematology and chemistry studies
The Correct Answer is C
Septic shock is a life-threatening condition characterized by severe infection, systemic inflammation, and inadequate tissue perfusion. In this critical situation, one of the initial priorities is to restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion. Initiation of an intravenous line allows for the administration of fluids and other necessary medications to support the patient's hemodynamic stability.
While the other interventions mentioned are also important components of septic shock management, the immediate priority is to address hypotension and tissue hypoperfusion through fluid resuscitation:
A. Obtaining wound and blood cultures in (option A) is incorrect because: Cultures are important to identify the source and causative organisms of the infection. However, fluid resuscitation should take priority over obtaining cultures, as it is necessary to stabilize the patient's hemodynamics.
B. Removing or controlling potentially infected sources in (option B) is incorrect because: Identifying and controlling the source of infection is crucial in septic shock management to prevent further progression. However, initiating fluid resuscitation is more time-sensitive and should be prioritized.
D. Drawing blood for hematology and chemistry studies in (option D) is incorrect because Laboratory studies are important for evaluating organ function and guiding treatment. However, the immediate focus should be on fluid resuscitation to address the underlying hypoperfusion and stabilize the patient's condition.
Therefore, the intervention considered a priority when treating a patient who presents with septic shock is the initiation of an intravenous line and fluid administration to restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The absence of palpable pulses suggests a lack of effective cardiac output, and the patient is in cardiac arrest. In this situation, immediate initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is crucial to maintain circulation and provide oxygenation to vital organs.
CPR consists of chest compressions and rescue breaths to circulate oxygenated blood to the brain and other vital organs. It is the primary intervention in cardiac arrest to provide temporary life support until advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) measures, such as defibrillation or medication administration, can be initiated.
A. Administering the prescribed Beta-Blocker in (option A) is incorrect because Administering a beta-blocker is not the initial action in a patient who is in cardiac arrest and requires immediate resuscitation.
B. Prepare for Cardioversion per hospital protocol (option B) is incorrect because Cardioversion, which is the delivery of an electric shock to the heart, may be considered in certain situations like unstable ventricular tachycardia or certain supraventricular tachycardias. However, in the given scenario, the patient is unresponsive and has no pulses, indicating cardiac arrest where CPR takes precedence over cardioversion.
C. Give 100% oxygen per non-rebreather mask in (option C) is incorrect because: While oxygenation is important, it should not delay or replace the initiation of CPR, which is the immediate priority in a patient without palpable pulses.
Therefore, the first action that the nurse should take in this scenario is to start CPR.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
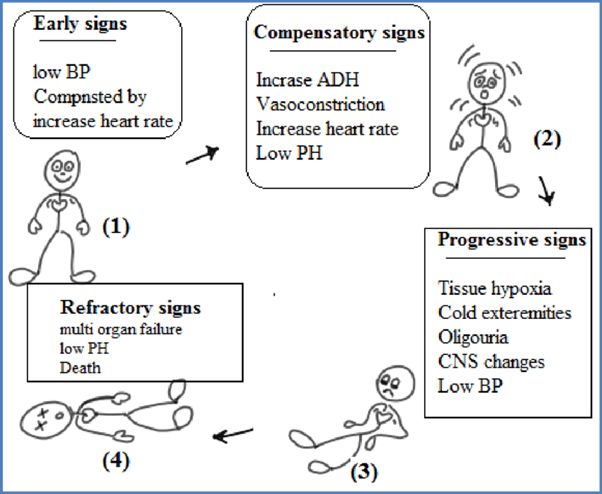
The stages of shock are commonly described as the initial, compensatory, progressive, and refractory stages. Here is an explanation of each stage and why the patient's assessment findings correspond to the progressive stage:
B. The compensatory stage in (option B) is incorrect because, In the compensatory stage, the body continues to activate compensatory mechanisms to maintain perfusion. This includes increased heart rate, peripheral vasoconstriction, and shunting of blood to vital organs. The patient's assessment findings of decreasing cardiac output, decreased peripheral perfusion, and increased capillary permeability suggest that the body's compensatory mechanisms are no longer sufficient to maintain perfusion adequately. Therefore, the patient has progressed beyond the compensatory stage.
C. The initial stage in (option C) is incorrect because, In the initial stage, there is an initial insult or injury that triggers the shock state. The body's compensatory mechanisms are activated, such as increased heart rate and vasoconstriction, to maintain blood pressure and perfusion. However, the patient's assessment findings indicate that they have progressed beyond the initial stage.
D. The refractory stage in (option D) is incorrect because The refractory stage represents a severe and irreversible state of shock where vital organs fail, and despite interventions, the patient's condition does not improve. The patient's assessment findings do not suggest the refractory stage, as there is still potential for intervention and management.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
