The ICU charge nurse will evaluate that teaching about hemodynamic monitoring for a new staff nurse has been effective when the new nurse does which of the following?
Position the limb with the catheter insertion site at the level of the transducer.
Positions the transducer level with the phlebostatic axis.
Ensures that the patient is lying with the head of the bed flat for all readings.
Balances and calibrates the hemodynamic monitoring equipment every hour.
The Correct Answer is B
Positioning the transducer level with the phlebostatic axis is a crucial step in accurate hemodynamic monitoring. The phlebostatic axis is an imaginary reference point located at the fourth intercostal space, mid-anterior/posterior chest. Placing the transducer at this level ensures that the pressure measurements obtained are reflective of the patient's true hemodynamic status.
A. Positioning the limb with the catheter insertion site at the level of the transducer in (option A) is incorrect because: While it is important to position the limb appropriately to avoid kinks or occlusions in the catheter tubing, this is not directly related to the accurate measurement of hemodynamic parameters.
C. Ensuring that the patient is lying with the head of the bed flat for all readings in (option C) is incorrect because The position of the patient's head does not directly impact the accuracy of hemodynamic monitoring unless it specifically relates to changes in preload or intracranial pressure monitoring.
D. Balancing and calibrating the hemodynamic monitoring equipment every hour in (option D) is incorrect because: While it is important to ensure that the monitoring equipment is calibrated and functioning properly, doing so every hour may not be necessary. Calibration frequency may vary based on institutional policies and patient stability.
Therefore, the correct action that demonstrates effective teaching about hemodynamic monitoring is positioning the transducer level with the phlebostatic axis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
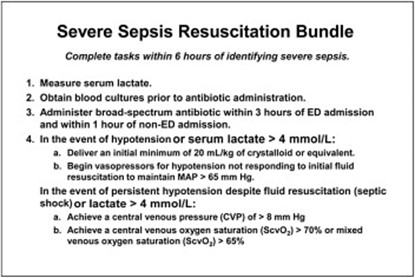
The patient's symptoms of fever and elevated white blood cell count suggest a potential infection and sepsis. Broad-spectrum antibiotics should be initiated promptly to cover a wide range of possible pathogens until further diagnostic tests and identification of the specific causative agent are obtained. Early administration of appropriate antibiotics is crucial in sepsis management to target the suspected infection and improve patient outcomes.
A. Cooling baths in (option A) is incorrect because: Cooling baths are typically used in the management of hyperthermia or specific conditions like heatstroke. While the patient has an elevated temperature, it is likely due to the systemic inflammatory response rather than solely hyperthermia.
C. Blood transfusion in (option C) is incorrect because Blood transfusion may be required in certain cases of sepsis if there is evidence of significant anemia or active bleeding. However, based on the information provided, there is no immediate indication of a blood transfusion.
D. NPO status in (option D) is incorrect because NPO status (nothing by mouth) is a general precautionary measure used in various situations, such as prior to surgery or to manage gastrointestinal complications. It is not a specific intervention in the sepsis resuscitation bundle.
Therefore, the nurse should initiate the intervention of administering broad-spectrum antibiotics in this scenario.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Positioning the transducer level with the phlebostatic axis is a crucial step in accurate hemodynamic monitoring. The phlebostatic axis is an imaginary reference point located at the fourth intercostal space, mid-anterior/posterior chest. Placing the transducer at this level ensures that the pressure measurements obtained are reflective of the patient's true hemodynamic status.
A. Positioning the limb with the catheter insertion site at the level of the transducer in (option A) is incorrect because: While it is important to position the limb appropriately to avoid kinks or occlusions in the catheter tubing, this is not directly related to the accurate measurement of hemodynamic parameters.
C. Ensuring that the patient is lying with the head of the bed flat for all readings in (option C) is incorrect because The position of the patient's head does not directly impact the accuracy of hemodynamic monitoring unless it specifically relates to changes in preload or intracranial pressure monitoring.
D. Balancing and calibrating the hemodynamic monitoring equipment every hour in (option D) is incorrect because: While it is important to ensure that the monitoring equipment is calibrated and functioning properly, doing so every hour may not be necessary. Calibration frequency may vary based on institutional policies and patient stability.
Therefore, the correct action that demonstrates effective teaching about hemodynamic monitoring is positioning the transducer level with the phlebostatic axis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
