While changing the dressing of a client who is immobile, the nurse notices the boundary of the wound has increased. Given there is a positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which is the most important action for the nurse to take?
Reapply a sterile non-adhesive dressing.
Limit visitors to immediate family only.
Administer prescribed antibiotics.
Request a nutrition consult.
The Correct Answer is C
A) Incorrect- reapplying a sterile non-adhesive dressing is not enough to address the infection.
The nurse should also clean the wound, apply topical antimicrobial agents, and change the dressing regularly.
B) Incorrect- limiting visitors to immediate family only is not a sufficient infection control measure. The nurse should also use standard precautions, such as wearing gloves, gowns, masks,
and eye protection, and educate the visitors about hand hygiene and proper disposal of contaminated items.
C) Correct- Administering prescribed antibiotics is the most important action because it can help treat the infection and prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body or to other people. MRSA is resistant to many common antibiotics, so it is essential to follow the prescription and monitor the client's response.
D) Incorrect- requesting a nutrition consult is not a priority action. While nutrition is important for wound healing, it does not directly affect the infection. The nurse should first administer antibiotics and then assess the client's nutritional status and needs.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
- Urinary output is an important indicator of fluid balance and kidney function. After delivery, a woman may experience increased urinary output due to the loss of excess fluid that was retained during pregnancy and the diuretic effect of oxytocin, which is released during breastfeeding. This is a normal and expected finding in the postpartum period.
- However, increased urinary output may also be a sign of urinary retention, which is the inability to empty the bladder completely. Urinary retention can occur due to trauma to the bladder or urethra during delivery, swelling or hematoma of the perineum, epidural anesthesia, or decreased bladder sensation. Urinary retention can lead to complications such as infection, bladder distension, or postpartum hemorrhage.
- Therefore, when a woman who delivered a normal newborn 24 hours ago reports that she seems to be urinating every hour or so, the practical nurse (PN) should measure the next voiding, and then palpate the client's bladder. This will help to assess the amount and quality of urine and the presence or absence of bladder distension. A normal urine output is about 30 ml per hour, and a normal bladder should feel soft and empty after voiding. If the urine output is low or high, or if the bladder feels firm or full after voiding, the PN should report these findings to the primary healthcare provider for further evaluation and intervention.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer, while options A, C, and D are incorrect.
Option A is incorrect because catheterizing the client for residual urine volume is an invasive procedure that should only be done if indicated by the primary healthcare provider.
Option C is incorrect because evaluating for normal involution and massaging the fundus are related to uterine function, not urinary function.
Option D is incorrect because obtaining a specimen for urine culture and sensitivity is not necessary unless there are signs of infection, such as fever, dysuria, or foul-smelling urine.
Correct Answer is ["A","E"]
Explanation
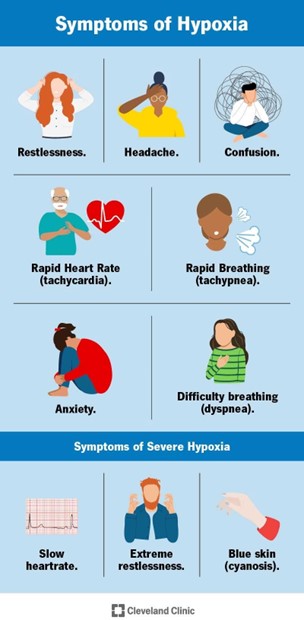
The level of hypoxemia that the child may have experienced during the submersion depends on several factors, but the most important ones are:
- The **temperature of water**: Cold water can induce a diving reflex, which lowers the heart rate and oxygen consumption, and may protect the brain from hypoxic injury¹². Cold water can also cause laryngospasm, which prevents water aspiration but also impairs gas exchange.
- The **amount of time the child was submerged**: The longer the submersion, the more severe the hypoxemia and the higher the risk of brain damage and death. The survival rate decreases significantly after 5 minutes of submersion³.
The other factors are less relevant or not directly related to the level of hypoxemia:
- The **weight of the child**: This may affect the buoyancy and the ability to float or swim, but not the oxygen consumption or gas exchange during submersion¹.
- The **oxygen concentration of the ambient air**: This may affect the pre-submersion oxygen saturation, but not the rate of oxygen depletion or gas exchange during submersion¹.
- The **witnessing of the fall into the pool**: This may affect the time to rescue and resuscitation, but not the level of hypoxemia during submersion.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
