Exam 4 Gastrointestinal disorders
Exam 4 Gastrointestinal disorders
Total Questions : 40
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreThere is an order to administer a large volume, cleansing enema to an adult patient. The enema bag is filled with how many milliliters of fluid for this procedure?
Explanation
ChoiceA: This volume might be insufficient for a large volume, cleansing enema, as it may not effectively cleanse the colon.
Choice: This range is the appropriate volume for a large volume, cleansing enema, as it provides enough fluid to cleanse the colon effectively without causing excessive distension.
Choice C: This volume is too low for a large volume, cleansing enema, and it may not be enough to achieve the desired effect.
Choice D: This volume is too low for a large volume, cleansing enema, and it may not effectively cleanse the colon.
A nurse is monitoring bowel elimination of a patient who has a history of constipation. The nurse implements measures to assist with bowel elimination if the patient has not had a bowel movement what would be the BEST option to try first?
Explanation
Choice A: A stool softener is the best option to try first for a patient with constipation as it helps to soften the stool, making it easier to pass.
Choice B: Soap suds enemas are used to promote bowel movements, but they are more invasive and can cause discomfort. Stool softeners should be tried before resorting to enemas.
Choice C : Suppositories can also help with constipation, but they are generally not the first option to try. Stool softeners are milder and more suitable initially.
Choice D: While mineral oil enemas can provide lubrication to facilitate bowel movements, stool softeners are generally preferred for their milder action.
A nurse performs an abdominal assessment on 4 patients. Which of the following would be considered a normal abdominal assessment?
Explanation
Choice A This is considered a normal abdominal assessment. The abdomen is soft and not distended, and bowel sounds are present and normal in all four quadrants.
Choice B Abdominal distension and firmness may indicate possible bowel obstruction or other gastrointestinal issues. Hypoactive bowel sounds suggest reduced motility, which is not normal.
Choice C Abdominal distension with hyperactive bowel sounds may indicate gastrointestinal irritation or increased motility, which is not normal.
Choice D A firm abdomen with hypoactive bowel sounds is not typical of a normal abdominal assessment.
A nurse is preparing her patient to receive a Fleet enema. What position is best for the procedure?
Explanation
Choice A The supine position (lying flat on the back) is not suitable for administering an enema as it does not facilitate proper flow and retention of the solution.
Choice B High Fowler's position (sitting upright at a 90degree angle) is not appropriate for enema administration, as it might cause discomfort and hinder proper administration.
Choice C Semi Fowler's position (sitting at a semiupright angle) is also not the best option for enema administration, as it may not allow the solution to flow effectively.
Choice D The Sims position, with the patient lying on the left side with the right knee flexed, allows the enema solution to flow downward by gravity and improves retention. It is the best position for enema administration.
A patient who is constipated has just received a mineral oilretention enema. The nurse encourages this patient to hold this enema for a minimum of how long?
Explanation
Choice A: Holding the enema for only 5 minutes may not provide enough time for the mineral oil to soften the stool and facilitate a bowel movement.
Choice B Holding the enema for 60 minutes is unnecessary and can lead to discomfort and difficulty for the patient.
Choice C Holding the enema for only 1 minute is too short for the mineral oil to be effective in softening the stool.
Choice D Encouraging the patient to hold the mineral oil enema for a minimum of 15 minutes allows sufficient time for the oil to work on the stool and improve the chances of a successful bowel movement.
A nurse is digitally removing stool that is impacted from a patient. The nurse should stop the procedure immediately and take corrective action if the patient's:
Explanation
Choice A This change in blood pressure is not alarming and does not require immediate cessation of the procedure.
Choice B A slight increase in temperature is within a normal range and does not indicate an urgent issue related to the stool removal procedure.
Choice C A significant decrease in pulse rate suggests bradycardia, which can be a serious sign and might be caused by the stimulation of the vagus nerve during the procedure. The nurse should stop immediately and take corrective action.
Choice D An increase in respiratory rate may indicate increased anxiety or discomfort, but it is not an immediate cause for stopping the procedure.
A nurse is preparing her patient to receive a Fleet enema. What position is best for the procedure?
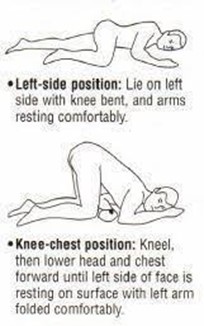
Explanation
Choice A The supine position is not suitable for administering an enema as it does not facilitate proper flow and retention of the solution.
Choice B High Fowler's position is not the best option for enema administration, as it might cause discomfort and hinder proper administration.
Choice C Semi Fowler's position is also not the best option for enema administration, as it may not allow the solution to flow effectively.
Choice D The Sims position, with the patient lying on the left side with the right knee flexed, allows the enema solution to flow downward by gravity and improves retention. It is the best position for enema administration.
A patient with a colostomy asks how often the faceplate (wafer) of the ostomy appliance should be changed. The most appropriate response by the nurse is that it is usually changed every
Explanation
Choice A Changing the faceplate every 3 to 5 days might be necessary for some individuals with specific needs, but it is not the typical frequency for most colostomy patients.
Choice B Changing the faceplate every 1 to 3 days is too frequent for most colostomy patients and might lead to unnecessary waste and discomfort.
Choice C Changing the faceplate every 2 to 3 days is still relatively frequent and might not be necessary for most colostomy patients.
Choice D Changing the faceplate every 4 to 7 days is the usual recommendation for colostomy patients, as it allows for sufficient wear time while minimizing the frequency of changes.
A nurse is preparing a cleansing enema for an adult patient who is constipated and has not responded to laxative use. Before giving the enema, the nurse should
Explanation
Choice A Using a cool solution might cause discomfort and could lead to cramping, which is not ideal for an enema administration.
Choice B Boiling the solution is unnecessary and might be unsafe, as it could cause burns or damage the components of the enema.
Choice C Warming the solution to body temperature (around 98.6°F or 37°C) is the appropriate approach, as it ensures patient comfort and reduces the risk of cramping or discomfort.
Choice D Microwaving the solution might lead to uneven heating and could potentially create hot spots, which could cause burns or discomfort for the patient.
The nurse would expect the least formed stool to be present in which portion of the digestive tract?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice b. Ascending colon.
Choice A rationale:
The sigmoid colon is the last part of the large intestine before the rectum. By this stage, the stool is usually well-formed as most water has been absorbed.
Choice B rationale:
The ascending colon is the first part of the large intestine where the stool is least formed. This is because it is the initial stage of the large intestine where water absorption begins, so the stool is still relatively liquid.
Choice C rationale:
The descending colon is further along the digestive tract, where more water has been absorbed, making the stool more formed compared to the ascending colon.
Choice D rationale:
The transverse colon is between the ascending and descending colons. While the stool here is more formed than in the ascending colon, it is less formed than in the descending and sigmoid colons.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 40 questions on the Exam 4 Gastrointestinal disorders Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



