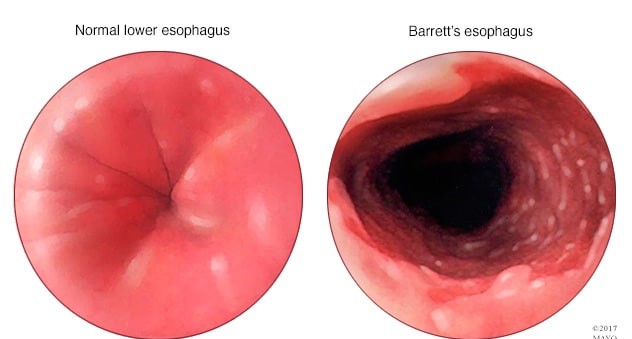
A client diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus asks how he developed this. Which of the following responses by the nurse is most accurate?
"Your allergies have most likely contributed to this."
"Your history of gastroesophageal reflux disorder is the most likely cause."
"Being a vegetarian has caused an imbalance in stomach acid."
"This is a genetic condition that you were born with."
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: This is incorrect because allergies are not a risk factor for developing Barrett's esophagus. Allergies are hypersensitive reactions of the immune system to certain substances, such as pollen, dust, or food. They can cause symptoms such as sneezing, itching, or hives, but they do not affect the esophagus or stomach acid.
Choice B reason: This is the correct answer because gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD) is the most common risk factor for developing Barrett's esophagus. GERD is a condition where the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) does not close properly and allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. This can cause inflammation, irritation, and damage to the esophageal lining. Over time, this can lead to changes in the cells of the esophagus, which is called Barrett's esophagus.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because being a vegetarian is not a risk factor for developing Barrett's esophagus. Being a vegetarian means avoiding meat and animal products in the diet. This can have health benefits such as lower cholesterol and blood pressure levels, but it does not affect the esophagus or stomach acid.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because Barrett's esophagus is not a genetic condition that one is born with. Barrett's esophagus is an acquired condition that results from chronic exposure to stomach acid in the esophagus. It is not inherited from one's parents or passed on to one's children.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Seasonal allergies are not a cause of delirium, but a common condition that affects the respiratory system and causes symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, or coughing.
Choice B Reason: History of GERD is not a cause of delirium, but a chronic condition that affects the digestive system and causes symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, or difficulty swallowing.
Choice C Reason: Benzodiazepines are a cause of delirium, especially in older adults or those with cognitive impairment. Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that act on the central nervous system and cause sedation, relaxation, and reduced anxiety. However, they can also impair memory, attention, orientation, and judgment, and lead to confusion, agitation, hallucinations, or delusions.
Choice D Reason: Completed antibiotics 10 days ago are not a cause of delirium, but a treatment for bacterial infections. Antibiotics can have side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, rash, or allergic reactions, but they do not cause delirium unless they are toxic or interact with other medications.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is the correct answer because this question will help the nurse assess the pain level and discomfort of the client with red scaling papules. Red scaling papules are raised skin lesions that are red and covered with scales. They can indicate psoriasis, which is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation and rapid turnover of skin cells. Psoriasis can cause pain, itching, burning, or stinging sensations in the affected areas. The nurse should ask the client to rate their pain on a numeric or descriptive scale and provide analgesics or topical agents as prescribed.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because this question will not help the nurse assess the condition of the client with red scaling papules. Red scaling papules are not affected by food intake but by other factors such as stress, infection, injury, or medication. Psoriasis is not an allergic or dietary disorder, but an immune-mediated disorder that causes abnormal skin cell growth. The nurse should ask the client about their medical history, current medications, and triggers or aggravating factors for their psoriasis.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because this question will not help the nurse assess the condition of the client with red scaling papules. Red scaling papules are not treated with antibiotics but with other medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologics. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, which are not the cause of psoriasis. The nurse should ask the client about their treatment regimen, compliance, and effectiveness for their psoriasis.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because this question will not help the nurse assess the condition of
the client with red scaling papules. Red scaling papules are not related to weekend activities but to chronic skin inflammation and abnormal cell turnover. Psoriasis is not a lifestyle disorder, but a genetic disorder that can be influenced by environmental factors. The nurse should ask the client about their family history, exposure to sun or cold, and stress level for their psoriasis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
