A client receives a tuberculin (PPD) skin test on Thursday at 1200. The nurse documents on the medication record that the results need to be read:
Sunday morning
Saturday morning
Friday morning
Monday morning
The Correct Answer is A
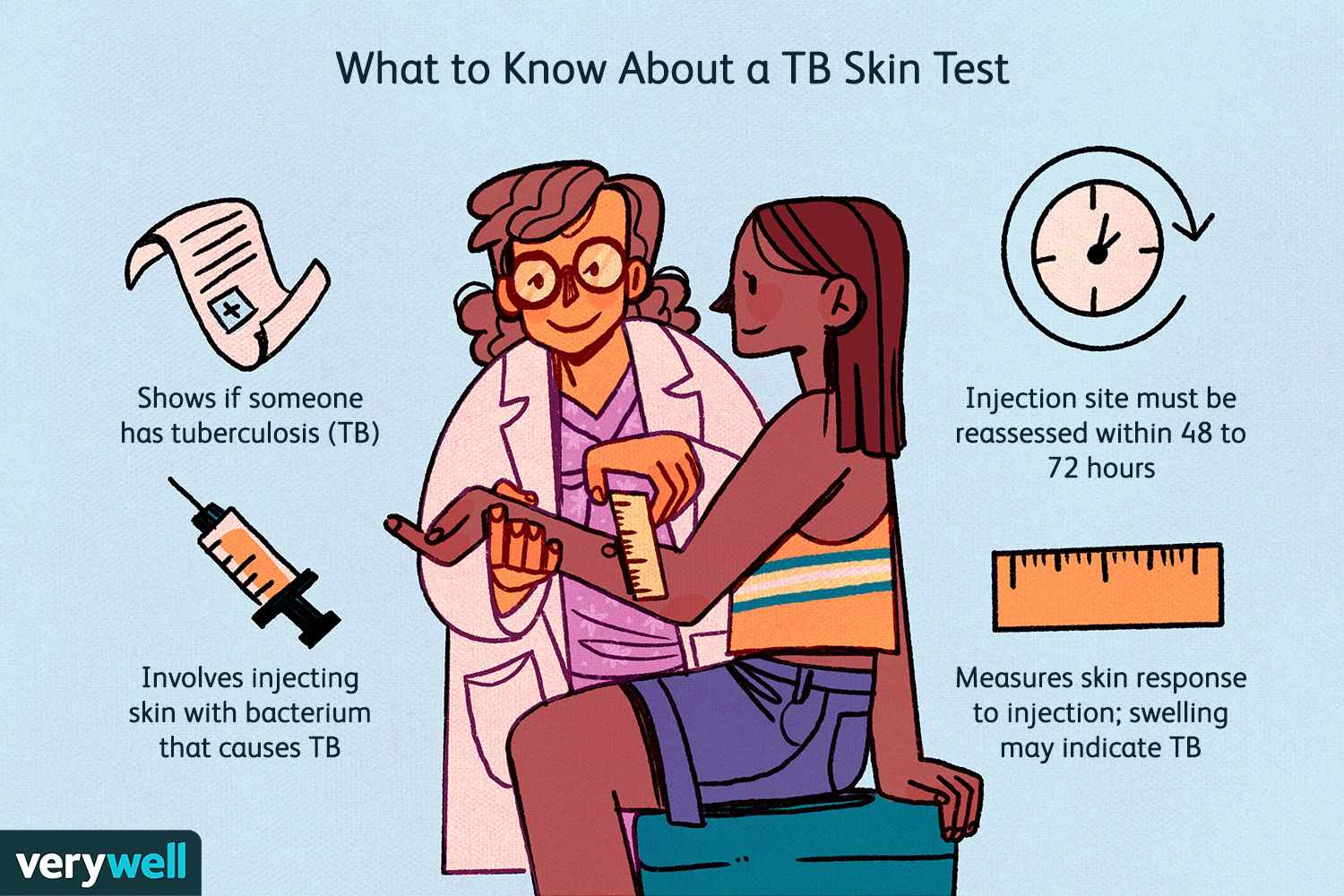
The tuberculin skin test (TST), also known as the Mantoux test, is used to determine if a person has been infected with the tuberculosis (TB) bacteria. The test involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) into the skin of the forearm. The injection site is then examined 48 to 72 hours later for a reaction, which is measured in millimeters of induration (swelling).
Choice A reason:
Sunday morning is the correct time to read the test results. Since the test was administered on Thursday at 1200, the 48 to 72-hour window for reading the results would fall between Saturday at 1200 and Monday at 1200. Reading the results on Sunday morning falls within this time frame, making it the appropriate choice.
Choice B reason:
Saturday morning is not the correct time to read the test results. Reading the test results on Saturday morning would be less than 48 hours after the test was administered, which is too early to accurately assess the reaction. The test needs to be read between 48 and 72 hours after administration to ensure accurate results.
Choice C reason:
Friday morning is also not the correct time to read the test results. Reading the test results on Friday morning would be only 24 hours after the test was administered, which is far too early. The immune response to the PPD injection takes time to develop, and reading the test too early can result in a false-negative result.
Choice D reason:
Monday morning is within the acceptable time frame to read the test results, but it is at the very end of the 72-hour window. While it is still technically correct, it is generally recommended to read the test closer to the 48-hour mark to ensure the most accurate results. Therefore, Sunday morning is a better choice.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Pulmonary function testing is not the immediate priority for a client with status asthmaticus who is showing signs of respiratory failure, such as diminished breath sounds and confusion. Pulmonary function tests are useful for diagnosing and assessing the severity of asthma but are not appropriate during an acute, life-threatening exacerbation.
Choice B reason:
Mechanical ventilation is the correct intervention for a client with status asthmaticus who is exhibiting signs of respiratory failure. Diminished breath sounds and confusion indicate severe airway obstruction and hypoxia, necessitating immediate intervention to secure the airway and ensure adequate ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps to maintain oxygenation and ventilation until the underlying cause can be treated.
Choice C reason:
A chest x-ray can be useful in diagnosing complications such as pneumothorax or pneumonia in a client with status asthmaticus, but it is not the immediate priority when the client is showing signs of respiratory failure. The primary focus should be on stabilizing the client’s respiratory status.
Choice D reason:
Administering 2 liters of oxygen via nasal cannula is not sufficient for a client with severe status asthmaticus and signs of respiratory failure. High-flow oxygen delivery methods or mechanical ventilation are required to adequately support the client’s respiratory needs.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Asking if the client would like to see a member of the clergy to receive a blessing can be supportive, but it may not directly address the client’s immediate emotional needs. While spiritual support is important, the nurse should first focus on the client’s expressed concerns about their wife.
Choice B reason: Inquiring if the client has children who can help their wife is practical, but it may not address the client’s emotional distress. The nurse should prioritize providing emotional support and facilitating communication between the client and their family.
Choice C reason: Asking if the client has a living will is important for end-of-life planning, but it does not directly address the client’s emotional concerns. This question is more appropriate for a discussion about advance directives rather than an immediate response to the client’s expressed worries
Choice D reason: Encouraging the client to discuss their feelings with their wife is the most appropriate response. It addresses the client’s emotional needs and promotes open communication between the client and their spouse. This can help alleviate some of the client’s anxiety and ensure that their wife is aware of their feelings and concerns.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
