The nurse is completing an admission assessment on a client diagnosed with asthma. What clinical manifestations are typical of the disorder?
Fever and bradypnea
Dyspnea and wheezing
Crackles and productive cough
Normal chest shape and orthopnea
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason:
Fever and bradypnea are not typical manifestations of asthma. Fever is more commonly associated with infections, and bradypnea (abnormally slow breathing) is not a characteristic symptom of asthma.
Choice B reason:
Dyspnea (shortness of breath) and wheezing are hallmark symptoms of asthma. Asthma is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which leads to difficulty breathing and a whistling sound (wheezing) when exhaling. These symptoms are often triggered by allergens, exercise, or respiratory infections.
Choice C reason:
Crackles and a productive cough are more indicative of conditions like pneumonia or chronic bronchitis rather than asthma. Asthma typically involves a dry cough rather than a productive one.
Choice D reason:
A normal chest shape and orthopnea (difficulty breathing when lying flat) are not specific to asthma. While some individuals with severe asthma may develop a barrel chest over time due to chronic overinflation of the lungs, this is not a typical early manifestation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Initiating droplet precautions is not sufficient for a client presenting with symptoms such as coughing up blood, productive cough, and night sweats. These symptoms are indicative of possible tuberculosis (TB), which is an airborne disease. Droplet precautions are used for infections spread through large respiratory droplets, such as influenza or pertussis, but not for TB.
Choice B reason:
Considering standard precautions to be sufficient is incorrect. Standard precautions are the basic level of infection control that should be used in the care of all patients to prevent the spread of infections. However, for a client with symptoms suggestive of TB, additional airborne precautions are necessary to prevent the spread of the disease.
Choice C reason:
Transferring the client to a positive pressure room is inappropriate. Positive pressure rooms are designed to keep contaminants out and are used for protecting immunocompromised patients from infections. For a client with suspected TB, a negative pressure room is required to prevent the spread of infectious particles to other areas.
Choice D reason:
Initiating airborne precautions is the correct intervention. Airborne precautions are necessary for diseases that are transmitted through smaller respiratory droplets that can remain suspended in the air and be inhaled by others. Tuberculosis is one such disease, and initiating airborne precautions helps to prevent the spread of the infection to healthcare workers and other patients.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
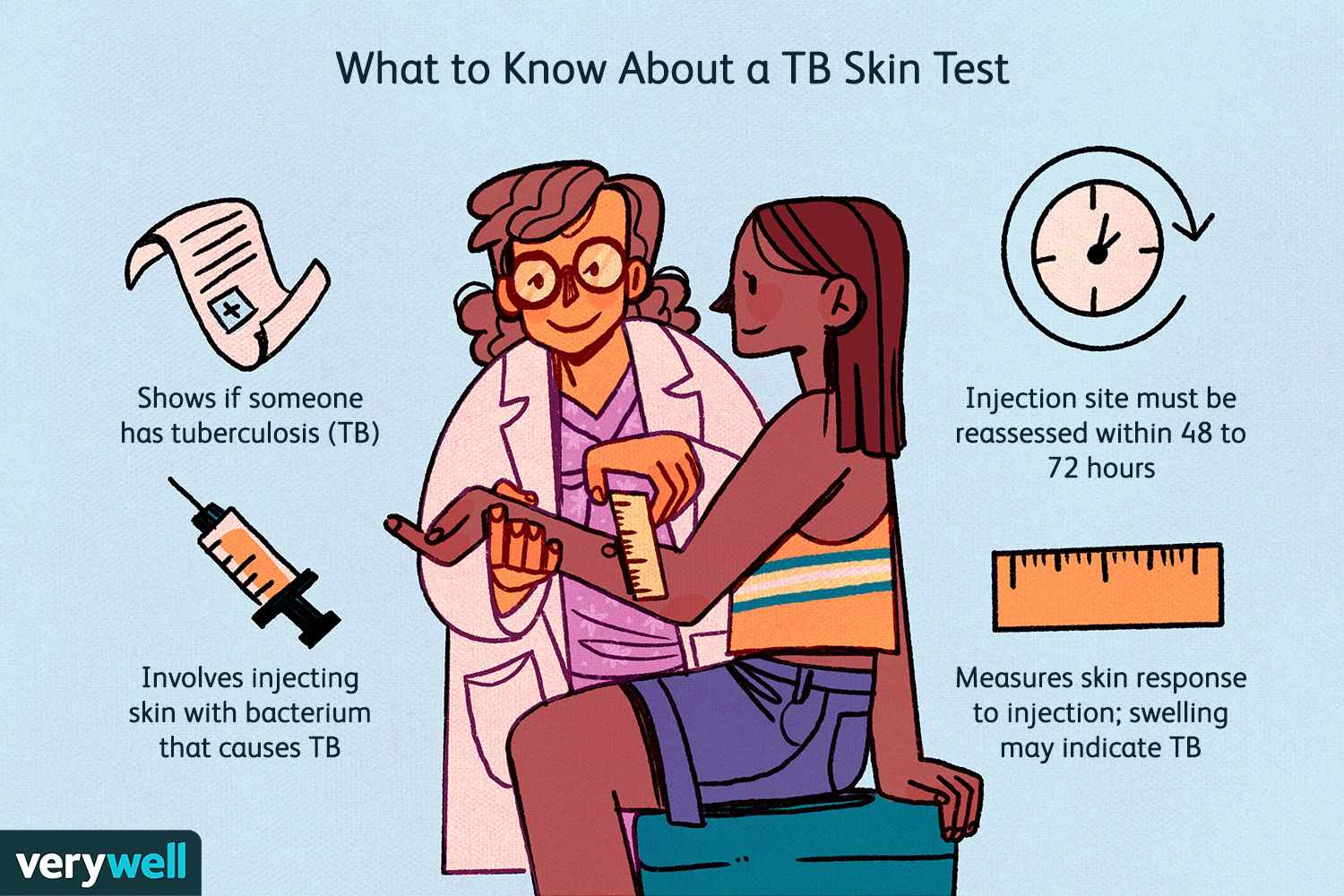
The tuberculin skin test (TST), also known as the Mantoux test, is used to determine if a person has been infected with the tuberculosis (TB) bacteria. The test involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) into the skin of the forearm. The injection site is then examined 48 to 72 hours later for a reaction, which is measured in millimeters of induration (swelling).
Choice A reason:
Sunday morning is the correct time to read the test results. Since the test was administered on Thursday at 1200, the 48 to 72-hour window for reading the results would fall between Saturday at 1200 and Monday at 1200. Reading the results on Sunday morning falls within this time frame, making it the appropriate choice.
Choice B reason:
Saturday morning is not the correct time to read the test results. Reading the test results on Saturday morning would be less than 48 hours after the test was administered, which is too early to accurately assess the reaction. The test needs to be read between 48 and 72 hours after administration to ensure accurate results.
Choice C reason:
Friday morning is also not the correct time to read the test results. Reading the test results on Friday morning would be only 24 hours after the test was administered, which is far too early. The immune response to the PPD injection takes time to develop, and reading the test too early can result in a false-negative result.
Choice D reason:
Monday morning is within the acceptable time frame to read the test results, but it is at the very end of the 72-hour window. While it is still technically correct, it is generally recommended to read the test closer to the 48-hour mark to ensure the most accurate results. Therefore, Sunday morning is a better choice.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
