A client with a history of asthma reports having episodes of bronchoconstriction and increased mucous production while exercising. Which action should the nurse implement?
Assess client for signs and symptoms of upper airway infection.
Determine if the client is using an inhaler before exercising.
Teach client to use pursed lip breathing when episodes occur.
Review the client's routine asthma management prescriptions
The Correct Answer is D
A. Assess client for signs and symptoms of upper airway infection:
While upper airway infections can contribute to respiratory symptoms, the client's history of asthma and the exacerbation of symptoms during exercise suggest that asthma management should be a priority.
B. Determine if the client is using an inhaler before exercising:
This is a relevant consideration, and ensuring proper pre-exercise use of bronchodilators (such as an inhaler) is an important aspect of asthma management. However, the question is broader and involves a review of the client's overall asthma management.
C. Teach client to use pursed lip breathing when episodes occur:
Pursed lip breathing is a technique that can help manage symptoms, especially during episodes of bronchoconstriction. However, the focus here is on a more comprehensive assessment and review of the client's routine asthma management.
D. Review the client's routine asthma management prescriptions:
This is the correct answer. The client's reported symptoms during exercise suggest a potential need for adjustments to the routine asthma management plan. Reviewing the client's prescriptions, including the type and timing of medications, can help ensure optimal control of symptoms, especially during physical activity.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Initiate cardiac telemetry:
Cardiac telemetry is not the immediate priority in this case. Kidney stones are more likely to cause severe localized pain rather than cardiac-related symptoms.
B. Administer a PRN dose of a laxative:
Laxatives are not indicated for the management of kidney stones or the associated flank pain. The priority is to address the specific needs related to the possible passage of kidney stones.
C. Implement seizure precautions:
Seizure precautions are not relevant to the sudden onset of severe flank pain in the context of hyperparathyroidism. The focus should be on managing pain, assessing for kidney stone passage, and addressing the underlying cause.
D. Begin straining all urine.
Straining all urine allows for the collection and examination of any passed stones. This information is important for identifying the composition of the stones and guiding further management.
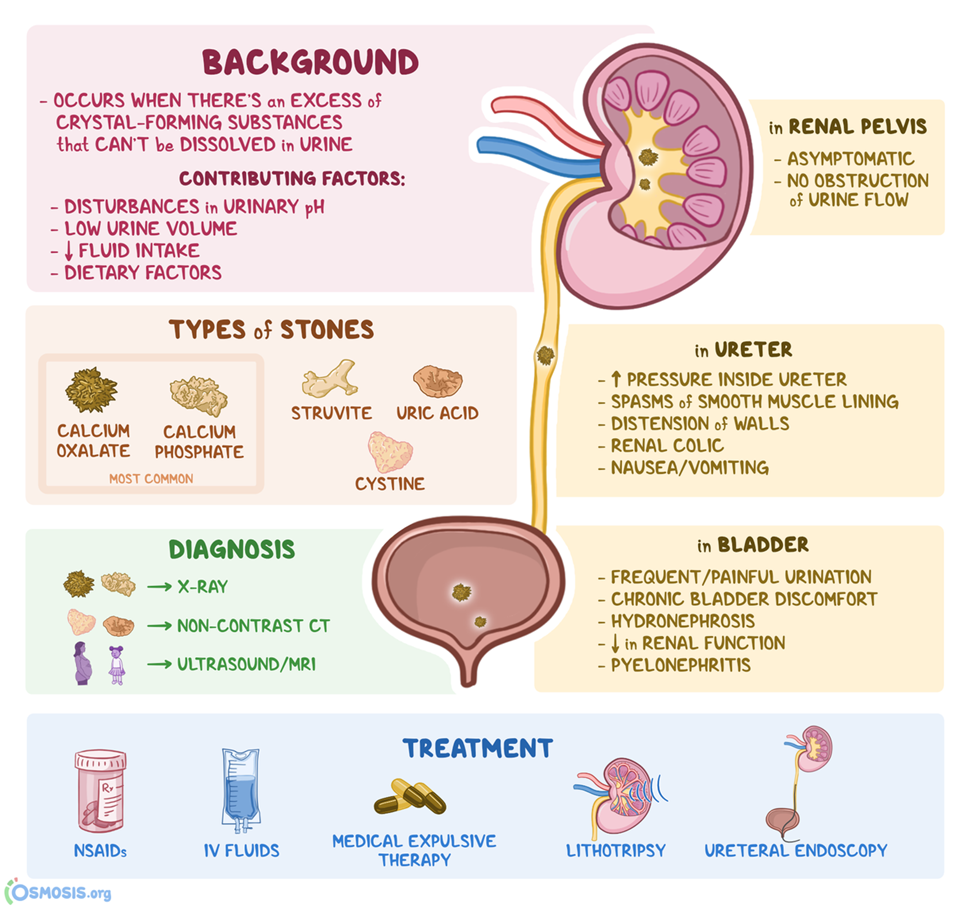
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Reduced pain in eczematous areas:
While hydration of the skin may contribute to reduced pain in some cases, the primary goal of urea cream is to moisturize and hydrate the skin rather than directly address pain.
B. Healing with a return to normal skin appearance:
Urea cream can contribute to the healing process by hydrating the skin and promoting the removal of dry, scaly skin. However, complete healing and a return to normal skin appearance may also depend on the underlying cause of eczema and other factors.
C. Decreased weeping of ulcerations in affected areas:
Urea cream can help reduce excessive dryness and weeping in eczematous areas by promoting hydration and moisture balance. However, it may not directly address ulcerations, and other interventions may be needed for open wounds.
D. Hydration of affected dry skin areas:
This is the correct answer. Urea is a natural moisturizing factor that helps retain water in the skin. Applying urea cream to affected dry skin areas is expected to hydrate the skin, reduce dryness, and improve the overall moisture balance.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
