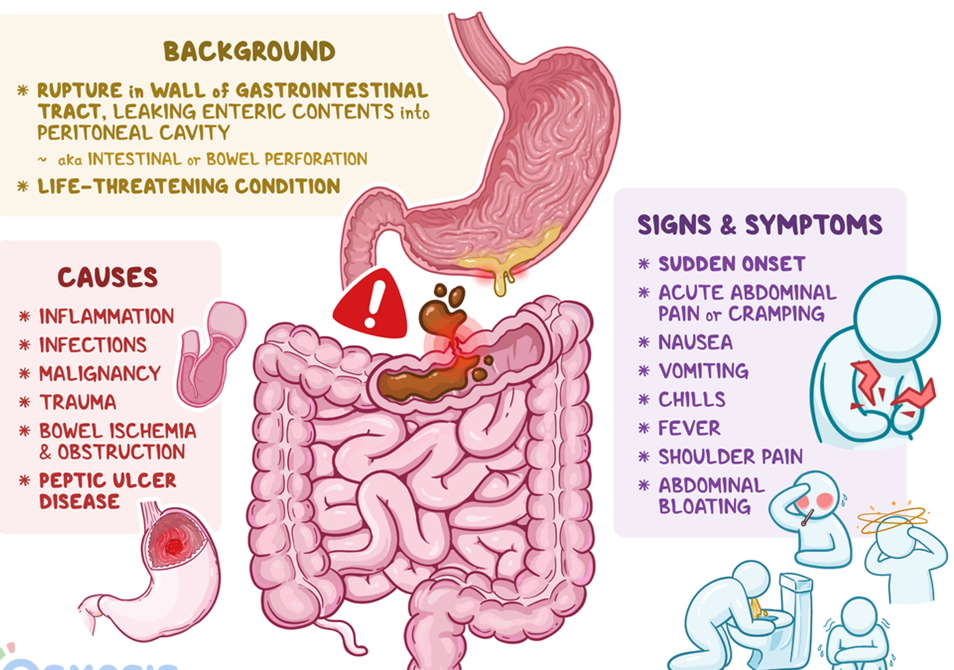
A nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following findings as an indication of gastrointestinal perforation?
Bradycardia
Hyperactive bowel sounds
Increased blood pressure
Sudden abdominal pain
The Correct Answer is D
A. Bradycardia is not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. Instead, tachycardia may be observed due to the body's response to a potential emergency or shock.
B. Hyperactive bowel sounds are not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. In fact, bowel sounds may decrease or become absent in severe cases of peritonitis or abdominal emergencies.
C. Increased blood pressure is not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. Hypotension may be observed due to hypovolemia resulting from fluid leakage into the peritoneal cavity.
D. Sudden abdominal pain is a key clinical manifestation of gastrointestinal perforation. The perforation of the stomach or intestines allows the contents to leak into the abdominal cavity, leading to peritonitis. Sudden and severe abdominal pain is a hallmark symptom, often described as sharp, stabbing, and constant.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Warfarin:
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that works by inhibiting the synthesis of certain clotting factors, including factors II, VII, IX, and X. While it is used to prevent thromboembolic events, in a client with cirrhosis and an elevated PT, the priority is addressing the coagulation factor deficiency rather than adding an anticoagulant.
B. Vitamin K:
Vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin, and it helps in the synthesis of clotting factors. In cirrhosis, there can be impaired synthesis of clotting factors due to liver dysfunction. Administering vitamin K can aid in correcting coagulation abnormalities.
C. Heparin:
Heparin is another anticoagulant, but it does not reverse the effects of warfarin. It works by a different mechanism and is typically used in acute settings, such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. It is not the primary intervention for an elevated PT in cirrhosis.
D. Ferrous sulfate:
Ferrous sulfate is an iron supplement and is not indicated for the correction of an elevated PT. Iron supplements are typically used to address iron deficiency anemia.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
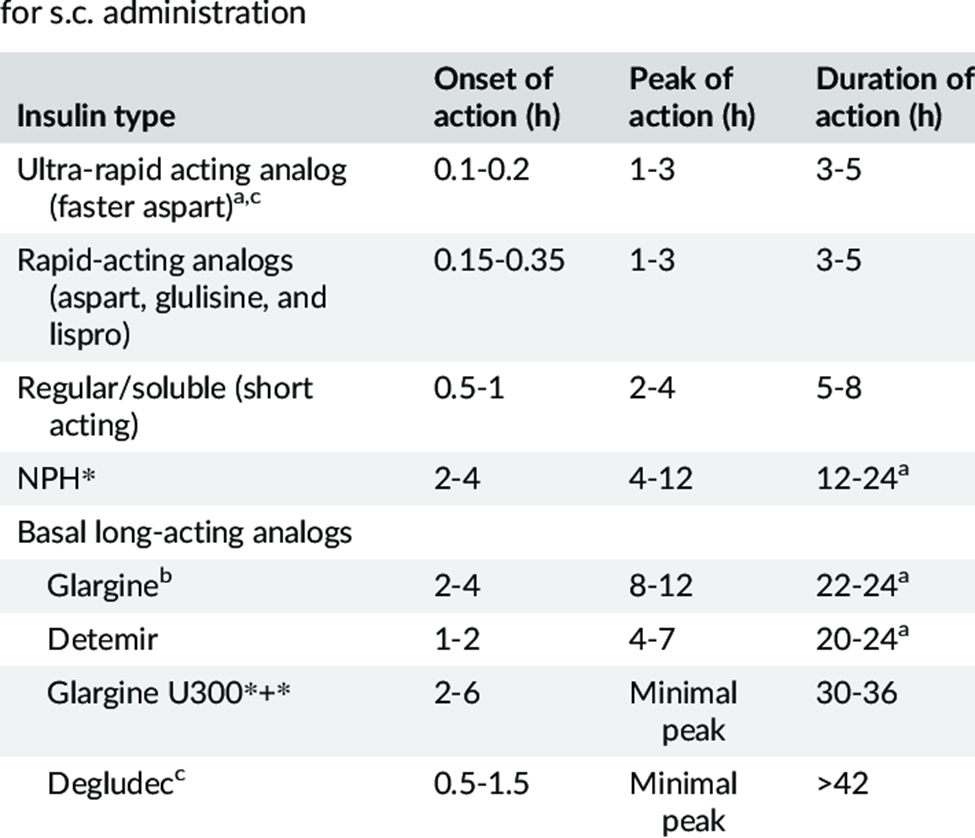
A. Insulin glargine does not have a duration of 3 to 6 hours. This duration of action is much shorter than the actual duration of insulin glargine.
B. Insulin glargine does not have a duration of 14 to 22 hours. This duration is shorter than the typical duration of action for insulin glargine.
C. Insulin glargine, a long-acting insulin, has a duration of action that lasts approximately 24 to 36 hours. It provides a slow and steady release of insulin, offering a relatively consistent blood sugar-lowering effect over an extended period.
D. Insulin glargine does not have a duration of 6 to 10 hours. This duration is shorter than the actual duration of action for insulin glargine.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
