A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and is taking hydrochlorothiazide. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following manifestations as an adverse effect of the medication?
Hypocalcemia
Hypernatremia
Hypokalemia
Hypermagnesemia
The Correct Answer is C
A. Hypocalcemia: Hydrochlorothiazide is not typically associated with lowering calcium levels. Hypocalcemia is not a common adverse effect of this medication.
B. Hypernatremia: Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic that increases urination, leading to the loss of water and sodium. While it can cause sodium depletion, it's less likely to result in hypernatremia, which refers to high sodium levels in the blood.
C. Hypokalemia: Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic that can increase the excretion of potassium in the urine. Hypokalemia (low potassium levels) is a known adverse effect of this medication due to its action on the kidneys leading to potassium loss.
D. Hypermagnesemia: Hydrochlorothiazide does not typically cause an increase in magnesium levels. It's more likely to cause magnesium loss through increased urination, potentially leading to hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels) rather than hypermagnesemia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A.PT (Prothrombin Time) 11 seconds: The prothrombin time measures the extrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. A PT of 11 seconds is within the normal range, and it indicates that the extrinsic clotting pathway is functioning appropriately. There is no need to report this value.
B. APTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time) 50 seconds: The APTT measures the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. A value of 50 seconds is prolonged and may suggest that the client is receiving an effective anticoagulant dose. However, the APTT target range can vary based on the specific therapeutic goal and the heparin protocol in use. It's essential to follow the healthcare provider's guidance on the target APTT range.
C. Hematocrit 456: The normal range for hematocrit is usually expressed as a percentage. A value of 456 is outside the normal range and likely represents an error or a misinterpretation. The nurse should verify this value, as an extremely high hematocrit could be indicative of an issue such as dehydration or an analytical error.
D. Platelets 300,000/mm²: A platelet count of 300,000/mm² is within the normal range. There is no need to report this value as it suggests a normal platelet count.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
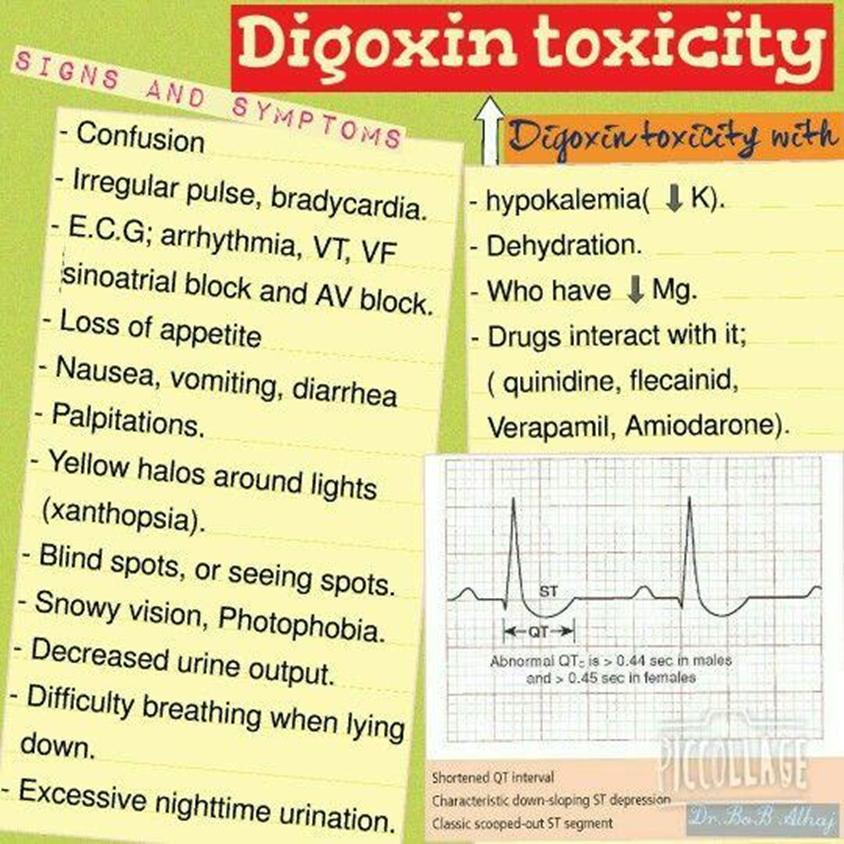
A. Visual disturbances:
Visual disturbances, such as blurred or yellow-tinted vision, are common signs of digoxin toxicity. Clients should report any changes in vision promptly.
B. Potassium 4.4 mEq/L:
While electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium levels, can increase the risk of digoxin toxicity, a potassium level of 4.4 mEq/L is within the normal range and, by itself, does not indicate digoxin toxicity.
C. Insomnia:
Insomnia is not a typical sign of digoxin toxicity. Symptoms of toxicity are more likely to involve the gastrointestinal and visual systems.
D. Sudden weight gain:
Sudden weight gain can be a symptom of heart failure exacerbation but is not a direct indication of digoxin toxicity. Other signs, such as visual disturbances, are more specific to digoxin toxicity.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
