A nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing an external nonstress test at 40 weeks of gestation and notes variable decelerations on the fetal monitor tracing that are unresponsive to interventions such as repositioning and oxygen administration.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take next?
Prepare the client for an amnioinfusion
Apply an internal fetal scalp electrode
Administer IV fluid bolus to the client
Discontinue oxytocin infusion if present
The Correct Answer is A
Prepare the client for an amnioinfusion. An amnioinfusion is a procedure that adds fluid to the uterus during labor to relieve cord compression and improve fetal condition. Variable decelerations on the fetal monitor tracing are a sign of cord compression and fetal distress. If repositioning and oxygen administration do not resolve the decelerations, an amnioinfusion may be indicated.
Choice B is wrong because applying an internal fetal scalp electrode does not address the cause of variable decelerations, which is cord compression.
An internal fetal scalp electrode is used to monitor the fetal heart rate more accurately, but it does not improve fetal oxygenation or prevent cord compression.
Choice C is wrong because administering IV fluid bolus to the client may help increase maternal blood volume and placental perfusion, but it does not directly increase amniotic fluid volume or relieve cord compression.
Choice D is wrong because discontinuing oxytocin infusion if present may reduce uterine contractions and decrease cord compression, but it may also prolong labor and increase the risk of infection or fetal compromise. Oxytocin infusion should only be discontinued if there are signs of uterine hyperstimulation or fetal intolerance.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
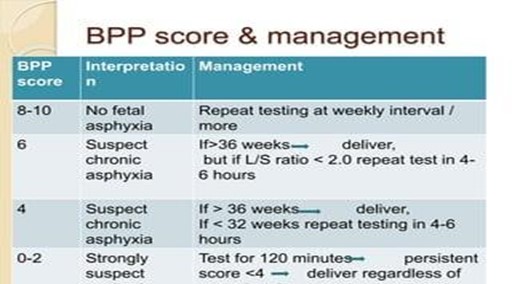
The client should count the baby’s kicks every day to monitor fetal well-being.A nonreactive nonstress test (NST) indicates that the fetal heart rate did not increase adequately with fetal movement, which may suggest fetal hypoxia or distress.A biophysical profile (BPP) is a combination of NST and ultrasound that assesses five parameters: fetal breathing, movement, tone, amniotic fluid volume, and NST.
Each parameter is scored 0 or 2, and the total score ranges from 0 to 10.A score of 8/10 or 10/10 is considered normal, while a score of 6/10 is equivocal and ≤ 4/10 is abnormal.A BPP score of 8/10 with a nonreactive NST means that the fetus has normal biophysical activities but may have chronic hypoxia.
Choice A is wrong because the client does not need to have another BPP in a week unless there are other indications of fetal compromise.The BPP may be repeated once or twice a week depending on the clinical situation.
Choice C is wrong because the client does not need to have an amniocentesis as soon as possible.
Amniocentesis is an invasive procedure that involves inserting a needle into the uterus to obtain amniotic fluid for analysis.It is usually done for prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders or fetal lung maturity, not for fetal well-being.
Choice D is wrong because the client does not need to deliver the baby by cesarean section.Cesarean section is a surgical delivery that may be indicated for various maternal or fetal conditions, such as placenta previa, breech presentation, fetal distress, or failure to progress in labor.A BPP score of 8/10 with a nonreactive NST does not warrant a cesarean section unless there are other risk factors or complications.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Prepare the client for an amnioinfusion.An amnioinfusion is a procedure that adds fluid to the uterus during labor to relieve cord compression and improve fetal condition.Variable decelerations on the fetal monitor tracing are a sign of cord compression and fetal distress.If repositioning and oxygen administration do not resolve the decelerations, an amnioinfusion may be indicated.
Choice B is wrong because applying an internal fetal scalp electrode does not address the cause of variable decelerations, which is cord compression.
An internal fetal scalp electrode is used to monitor the fetal heart rate more accurately, but it does not improve fetal oxygenation or prevent cord compression.
Choice C is wrong because administering IV fluid bolus to the client may help increase maternal blood volume and placental perfusion, but it does not directly increase amniotic fluid volume or relieve cord compression.
Choice D is wrong because discontinuing oxytocin infusion if present may reduce uterine contractions and decrease cord compression, but it may also prolong labor and increase the risk of infection or fetal compromise.Oxytocin infusion should only be discontinued if there are signs of uterine hyperstimulation or fetal intolerance.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
