A nurse is caring for a school-age child who has a systemic disorder and is
receiving antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and corticosteroids. Both of the child's parents have a smoking history.
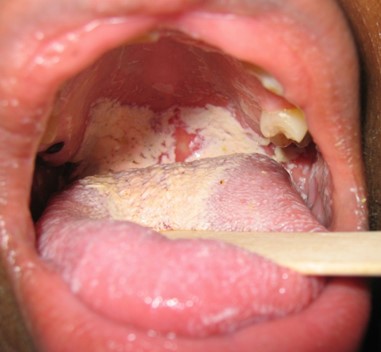
The child reports soreness in his mouth and refuses to eat.
Inspection of his mouth reveals a white, milky plaque that does not come off with
rubbing.
The nurse should suspect which of the following conditions?
Dermatitis
Candidiasis
Herpes simplex
Squamous cell carcinoma.
The Correct Answer is B
The nurse should suspect candidiasis, also known as oral thrush.
Candidiasis is a fungal infection that can occur in the mouth and is characterized by the presence of a white, milky plaque that does not come off with rubbing.
The child’s use of antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and corticosteroids can increase the risk of developing candidiasis.
Choice A is incorrect because dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin and
would not present as a white plaque in the mouth.
Choice C is incorrect because herpes simplex typically presents as painful blisters or sores in the mouth.
Choice D is incorrect because squamous cell carcinoma typically presents as a firm, painless growth, or ulcer in the mouth.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Infants with spina bifida are at an increased risk of developing a latex allergy
due to repeated exposure to latex products during medical procedures.
Providing a latex-free environment can help prevent the development of an allergy.
Choice A is not correct because limiting visitors to immediate family members is not necessary for the care of an infant undergoing surgical closure of the myelomeningocele sac.
Choice B is not correct because maintaining the infant in the supine position is not necessary for this procedure.
Choice D is not correct because initiating contact precautions is not necessary for this procedure.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
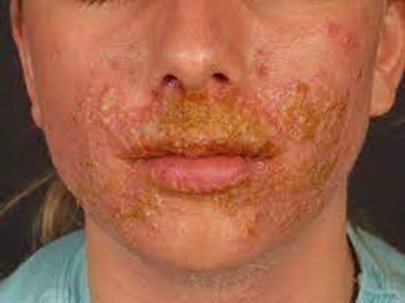
This is an important measure to prevent the spreading of impetigo to others and to other parts of the body, as the bacteria can survive on clothing and other objects12.
Choice A.
Keeping the child on droplet precautions at home is incorrect, as impetigo is not spread by respiratory droplets, but by direct contact with the sores or contaminated items.
Choice C.
Immunizing household contacts for the disease is incorrect, as there is no vaccine for impetigo, which is caused by different types of bacteria.
Choice D.
Giving the child a chlorine bath twice daily is incorrect, as chlorine can irritate the skin and worsen impetigo.
The recommended treatment is to wash the sores with soap and water and
apply antibiotic ointment or cream23.
Therefore, choice B is the best answer to this question.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
