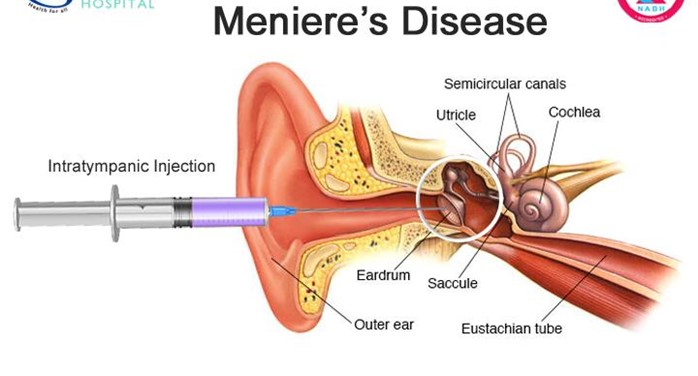
A nurse is providing education to a client recently diagnosed with Meniere's disease. Which of the following will the nurse include in the teaching? (Select all that apply.)
Avoid swimming underwater
Wear earphones when in crowded places
Keep eyes open during an acute attack
Sit or lie down if whirling occurs
We do not know the exact cause
Damage to the ear from excess noise is the cause
Correct Answer : A,D,E
Choice A reason: This is correct because avoiding swimming underwater can help prevent the worsening of Meniere's disease. Meniere's disease is a disorder of the inner ear that causes episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and fullness in the ear. Swimming underwater can increase pressure in the ear and trigger an attack. The nurse should advise the client to avoid activities that involve changes in altitude or pressure, such as flying, diving, or climbing.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because wearing earphones when in crowded places can worsen Meniere's disease. Earphones can increase noise exposure and damage hearing, which is already impaired by Meniere's disease. The nurse should advise the client to avoid loud noises and use hearing aids if needed.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because keeping eyes open during an acute attack can increase vertigo and nausea. Vertigo is a sensation of spinning or moving when still, which can be caused by Meniere's disease. Keeping eyes open can make vertigo worse by creating a visual mismatch with vestibular signals from the inner ear. The nurse should advise the client to close their eyes or focus on a stationary object during an attack.
Choice D reason: This is correct because sitting or lying down if whirling occurs can help prevent falls or injuries due to vertigo. Whirling is another term for vertigo, which can affect balance and coordination. Sitting or lying down can reduce movement and stabilize posture during an attack. The nurse should advise
the client to avoid driving or operating machinery when experiencing vertigo.
Choice E reason: This is correct because we do not know the exact cause of Meniere's disease. Meniere's disease is thought to be related to abnormal fluid balance or pressure in the inner ear, but what triggers this condition is unknown. The nurse should educate the client about possible risk factors, such as genetics, infections, allergies, autoimmune disorders, or head trauma, but also acknowledge the uncertainty and variability of the disease.
Choice F reason: This is incorrect because damage to the ear from excess noise is not the cause of Meniere's disease. Damage to the ear from excess noise can cause noise-induced hearing loss, which is a type of sensorineural hearing loss that affects the cochlea or the auditory nerve. Meniere's disease is a type of mixed hearing loss that affects both the cochlea and the middle ear. The nurse should not confuse or misinform the client about the cause of their condition.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This choice is incorrect. Inability to perform within normal limits is a vague and general term that does not describe the specific finding of left facial droop. The nurse should document the exact observation and compare it to the expected or normal range.
Choice B Reason: This choice is incorrect. Symmetrical findings mean that both sides of the body or face are equal or similar in appearance or function. Left facial droop indicates that one side of the face is lower or weaker than the other, which is not symmetrical.
Choice C Reason: This is the correct choice. Asymmetrical findings mean that both sides of the body or face are unequal or different in appearance or function. Left facial droop indicates that one side of the face is lower or weaker than the other, which is asymmetrical.
Choice D Reason: This choice is incorrect. Bilateral strength present means that both sides of the body or face have normal or adequate muscle power or force. Left facial droop indicates that one side of the face has reduced or impaired muscle power or force, which is not bilateral strength present.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Measuring the abdominal girth is not related to asterixis, which is a tremor of the hand when the wrist is extended. It may indicate ascites, which is a complication of cirrhosis, but not asterixis.
Choice B Reason: This is the correct choice. Asterixis is a flapping tremor of the hand when the wrist is extended, sometimes said to resemble a bird flapping its wings. It is caused by abnormal function of the diencephalic motor centers that regulate the muscles involved in maintaining posture. It is a sign of hepatic encephalopathy, which is a neuropsychiatric disorder that occurs in patients with liver disease.
Choice C Reason: Having the client flex and extend their foot is not related to asterixis, which affects the hand and wrist. It may test for ankle clonus, which is a rhythmic contraction of the calf muscles when the foot is dorsiflexed. It indicates an upper motor neuron lesion, but not hepatic encephalopathy.
Choice D Reason: Asking the client to walk heel to toe is not related to asterixis, which affects the hand and wrist. It may test for balance and coordination, which can be impaired in patients with hepatic encephalopathy, but it is not a specific sign of asterixis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
