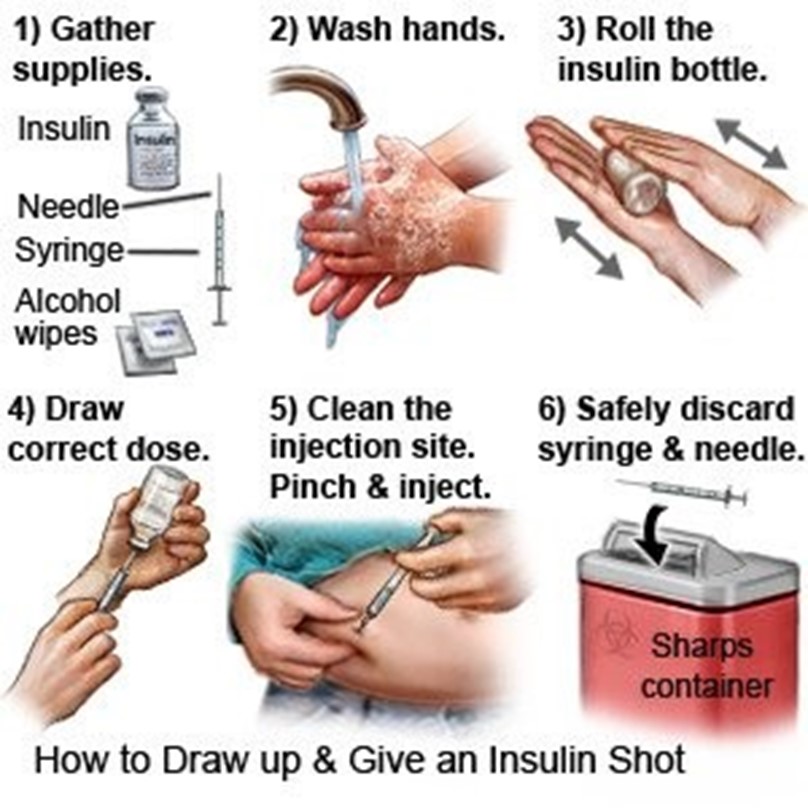
A nurse is providing teaching about self-administration of insulin to the parent of a school-age child who has a new diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates a need for further teaching?
"The insulin can be injected anywhere there is adipose tissue."
"I will be sure my child rotates sites after 5 injections in one area."
"I will be sure my child aspirates before injecting the insulin."
"The insulin should be injected at a 90-degree angle."
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A: This statement does not indicate a need for further teaching, as it is correct that insulin can be injected anywhere there is adipose tissue. Adipose tissue is the layer of fat under the skin that can absorb insulin and prevent damage to muscles or organs. The common sites for insulin injection are the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, or upper arms.
Choice B: This statement does not indicate a need for further teaching, as it is correct that the child should rotate sites after 5 injections in one area. Rotating sites can prevent lipodystrophy, which is a condition that causes abnormal changes in fat tissue due to repeated injections. Lipodystrophy can affect the appearance and absorption of insulin in the affected area.
Choice C: This statement indicates a need for further teaching, as it is incorrect that the child should aspirate before injecting the insulin. Aspiration is the process of pulling back on the plunger of the syringe to check for blood before injecting the medication. Aspiration is not recommended for insulin injection, as it can cause pain, bruising, or leakage of insulin from the injection site.
Choice D: This statement does not indicate a need for further teaching, as it is correct that insulin should be injected at a 90-degree angle. Injecting insulin at a 90-degree angle can ensure that the medication reaches the adipose tissue and prevents skin irritation or muscle damage. The only exception is if the child has very thin skin or uses very short needles, in which case they may inject at a 45-degree angle.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
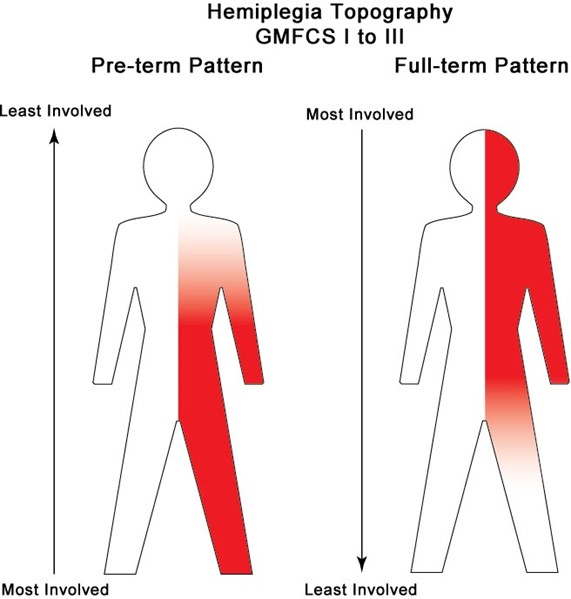
Choice A: Improving the client's school attendance skills is not the priority goal for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy, which is a condition that affects one side of the body and causes muscle weakness, spasticity, and impaired coordination. Improving the client's school attendance skills is a long-term goal that requires collaboration with the school staff, the child, and the parents. The priority goal for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy is to ensure their safety and mobility at home.
Choice B: Providing teaching on self-care activities is not the priority goal for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy, which is a condition that affects one side of the body and causes muscle weakness, spasticity, and impaired coordination. Providing teaching on self-care activities is an important goal that requires assessment of the child's abilities, needs, and preferences. The priority goal for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy is to ensure their safety and mobility at home.
Choice C: Modifying the environment for optimal safety and mobility is the priority goal for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy, which is a condition that affects one side of the body and causes muscle weakness, spasticity, and impaired coordination. Modifying the environment for optimal safety and mobility can prevent falls, injuries, or complications and promote independence and function. The nurse should include interventions such as removing clutter, securing rugs, installing grab bars, providing adaptive equipment, and arranging furniture.
Choice D: Providing counseling services for the parents is not the priority goal for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy, which is a condition that affects one side of the body and causes muscle weakness, spasticity, and impaired coordination. Providing counseling services for the parents is a supportive goal that requires referral to appropriate resources, such as social workers, psychologists, or support groups. The priority goal for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy is to ensure their safety and mobility at home.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is a therapeutic response that acknowledges the parent's feelings and provides reassurance that the behavior is normal and temporary. The other responses are either dismissive, judgmental, or self-disclosing, which are not helpful for the parent.
Choice B reason: This is a judgmental response that implies that the parent is overreacting or has unrealistic expectations for their child.
Choice C reason: This is a dismissive response that minimizes the parent's concern and does not offer any support
or information.
Choice D reason: This is a self-disclosing response that shifts the focus from the parent to the nurse and does not
address the issue at hand.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
