A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client who is receiving filgrastim. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse monitor to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment?
INR
BUN
WBC count
Potassium level
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A Reason:
INR (International Normalized Ratio) is incorrect. INR is a measurement used to monitor the effects of anticoagulants like warfarin. It assesses the blood's ability to clot. Filgrastim does not directly affect INR levels, so monitoring INR would not provide information about the effectiveness of filgrastim in stimulating white blood cell production.
Choice B Reason:
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) is incorrect. BUN levels primarily indicate kidney function and hydration status. They are not directly influenced by filgrastim treatment. Monitoring BUN is essential for assessing kidney function but does not reflect the effectiveness of filgrastim therapy in increasing white blood cell counts.
Choice C Reason:
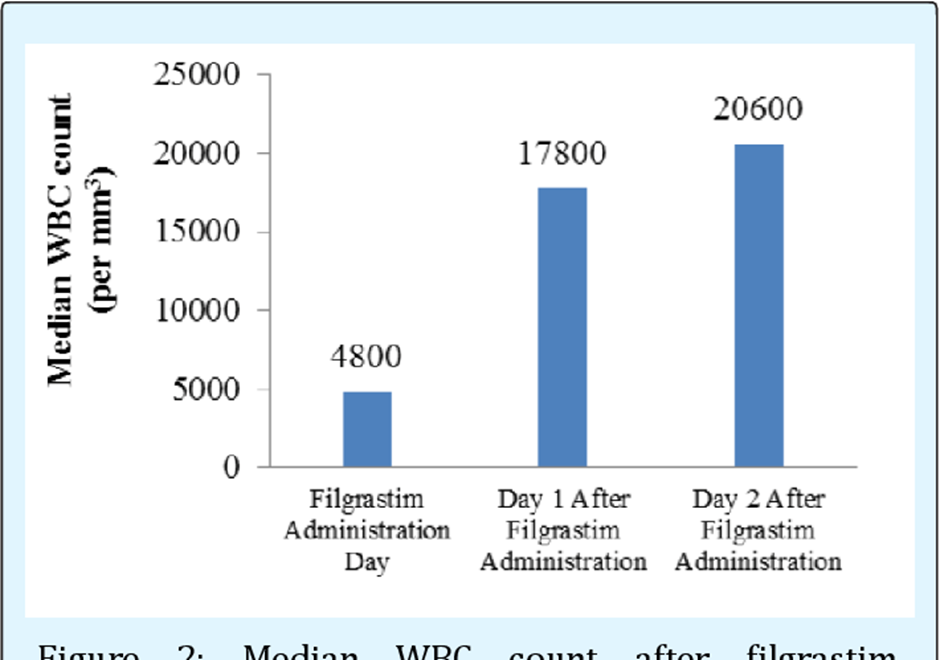
WBC count is correct. Filgrastim is a medication that stimulates the production of white blood cells (WBCs), particularly neutrophils. Therefore, the key laboratory value to monitor for assessing the effectiveness of filgrastim therapy is the WBC count. An increase in the WBC count, particularly in the neutrophil count, signifies the intended therapeutic effect of filgrastim in boosting the immune system's response by increasing the production of these infection-fighting cells.
Choice D Reason:
Potassium level is incorrect. Potassium levels are crucial for heart and muscle function. While certain medications might affect potassium levels, filgrastim's primary action is on stimulating white blood cell production and does not directly impact potassium levels. Monitoring potassium levels is essential for overall health but does not specifically indicate the effectiveness of filgrastim treatment.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Weight gain of 0.7 kg (1.5 lb) in 24 hours is not recommendable. While sudden weight gain can indicate fluid retention, it is not a direct contraindication for administering digoxin. However, it might indicate worsening heart failure, which needs attention, but it doesn't specifically necessitate withholding digoxin.
Choice B Reason:
Urinary output 30 mL/hr is not recommendable. A low urinary output might indicate decreased kidney perfusion or renal issues. While monitoring urinary output is important, it is not a direct reason to withhold digoxin unless it's coupled with severe renal impairment or an acute kidney injury.
For a client receiving digoxin, certain findings would warrant withholding the medication due to potential complications. Among the options provided:
Choice C Reason:
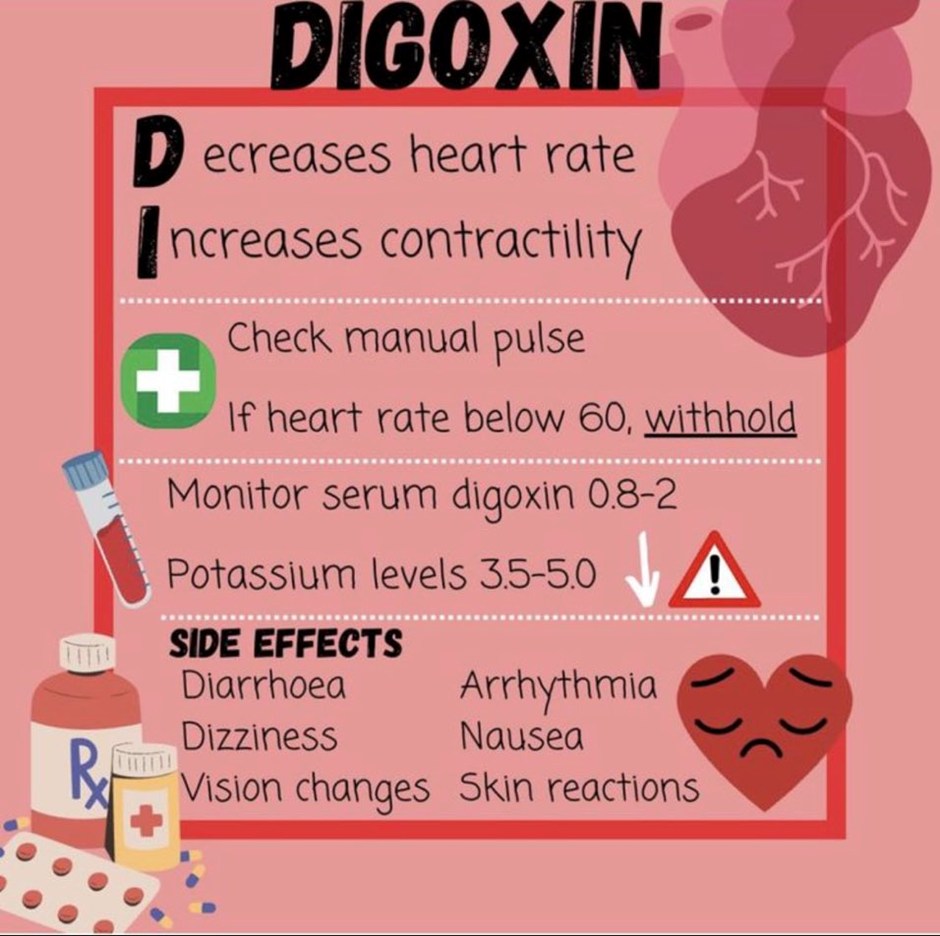
Pulse rate 56/min is the correct recommendation. A low pulse rate (bradycardia), especially below 60 beats per minute, is a reason to withhold digoxin. Digoxin can further decrease the heart rate, potentially leading to excessive bradycardia or heart block. The nurse should hold the medication and consult with the healthcare provider to determine the appropriate action.
Choice D Reason:
BP 160/90 mm Hg is not recommendable. Elevated blood pressure alone is not a direct contraindication for administering digoxin to a patient with heart failure. Digoxin is not primarily used for controlling blood pressure; its use is more focused on managing heart rate and contractility in heart failure patients.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Bilateral muscle weakness is not typically associated specifically with fluid volume excess. Muscle weakness can result from various causes, such as electrolyte imbalances or certain medical conditions, but it's not a primary manifestation of fluid volume excess.
Choice B Reason:
Thready pulse is not correct. A thready pulse refers to a weak and barely palpable pulse. This is more commonly associated with conditions like shock or reduced cardiac output rather than fluid volume excess.
Choice C Reason:
Decreased bowel sounds is not correct. Reduced or absent bowel sounds may indicate gastrointestinal issues, but they are not a direct manifestation of fluid volume excess. Increased bowel sounds might be more associated with certain types of gastrointestinal disturbances or fluid imbalances, but decreased sounds are not a typical sign of fluid volume excess.
Choice D Reason:
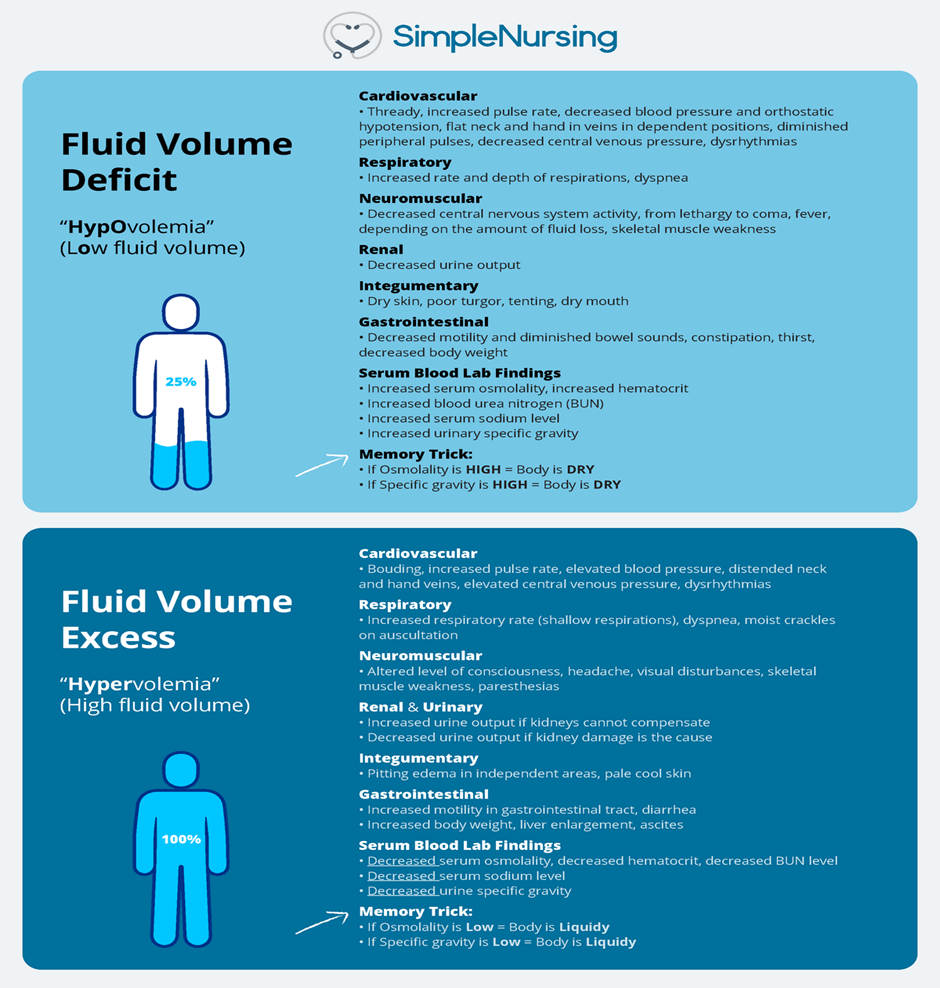
Distended neck veins is correct. In a client experiencing fluid volume excess, distended neck veins can often be observed due to increased venous pressure. This occurs as a result of the body retaining more fluid than it can handle, leading to an increase in blood volume and pressure within the vascular system. This can cause the jugular veins in the neck to appear distended or prominent.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
