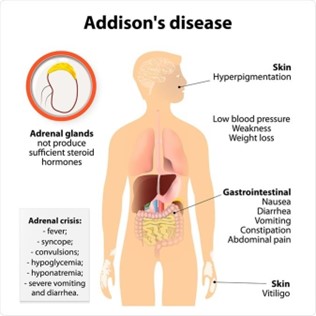
A patient is admitted to the hospital in Addisonian Crisis a month after a diagnosis of Addison’s disease. The nurse identifies the nursing diagnosis of ineffective therapeutic regimen management related to lack of knowledge of management of the condition when the patient says:
“I double my dose of hydrocortisone on the days that I go for a run.”
“I had the stomach flu earlier this week and couldn't take the hydrocortisone.”
“I frequently eat at restaurants, and so my food has a lot of added salt."
“I do yoga exercises almost every day to help me reduce stress and relax.”
The Correct Answer is B
The statement "I had the stomach flu earlier this week and couldn't take the hydrocortisone" indicates that the patient may not be adhering to their prescribed medication regimen, which can lead to an Addisonian crisis. Therefore, the nursing diagnosis of ineffective therapeutic regimen management related to lack of knowledge of management of the condition is appropriate.
Addison’s disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. Hydrocortisone is a glucocorticoid medication that is often used to replace the cortisol that the adrenal glands are not producing. In the Addisonian crisis, the body is unable to produce the necessary levels of cortisol and aldosterone, which can lead to potentially life-threatening complications such as hypotension, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances.
The other statements may indicate areas where patient education is needed, but they do not directly relate to the immediate risk of an Addisonian crisis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
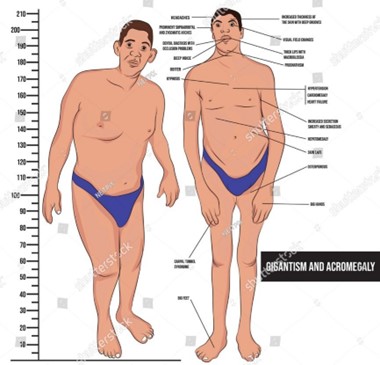
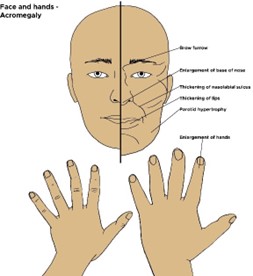
acromegaly typically causes an enlargement of the hands and feet. The nurse can inquire if the patient has noticed any changes in shoe size, as this may indicate abnormal growth.
"Are you experiencing tremors or anxiety" is not directly related to acromegaly, and although anxiety can be associated with some medical conditions, it is not a typical symptom of acromegaly.
"Is there any family history of acromegaly?" is also a relevant question, as acromegaly can be caused by a genetic disorder. If the patient has a family history of the condition, this may increase their risk of developing it.
"Have you had a recent head injury?" is not specifically related to acromegaly, although head trauma can cause a variety of medical conditions.
Overall, option a. is the most relevant question to ask a patient with suspected acromegaly.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
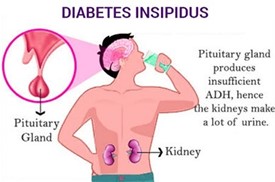
Diabetes insipidus is a condition where the body is not able to regulate water balance properly, leading to excessive urine output and dehydration. The patient's urine output of 800 ml/hr (option A) and low urine specific gravity of 1.003 (option C) is consistent with diabetes insipidus and requires monitoring, but they are not as immediately concerning as the patient's confusion and lethargy.
Confusion and lethargy may indicate severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, or even brain swelling (if the patient had a recent head injury, as mentioned in option D). These symptoms require immediate attention to prevent further complications and ensure the patient's safety.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
